This is a SUPER easy guide on Tungsten element.
In fact, the table mentioned below is the perfect information box (Which gives you every single detail about the Tungsten element in Periodic table.)
So if you want to know anything about Tungsten element, then this guide is for you.
Let’s dive right into it!
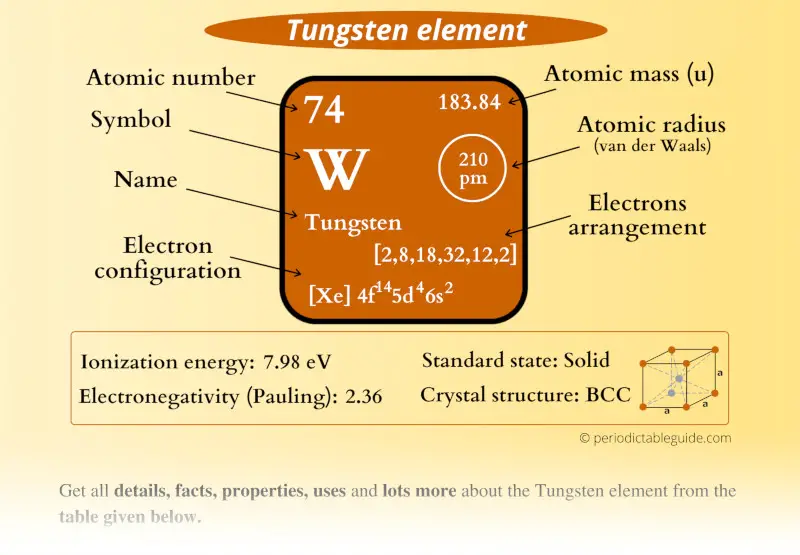
Tungsten Element (W) Information
| Appearance |  Gray-white lustrous appearance |
| State (at STP) | Solid |
| Position in Periodic table | 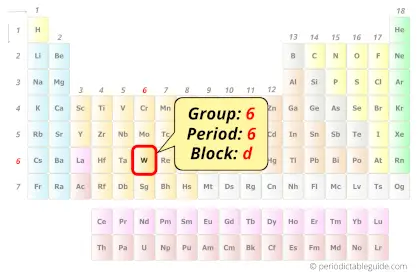 Group: 6, Period: 6, Block: d |
| Category | 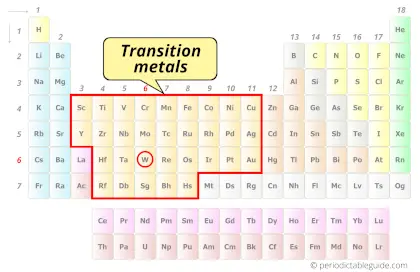 Transition metals |
| Atomic number or Protons | 74 |
| Neutrons | 110 |
| Electrons | 74 |
| Symbol | W |
| Atomic mass |  183.84 u |
| Electrons arrangement or Bohr model | 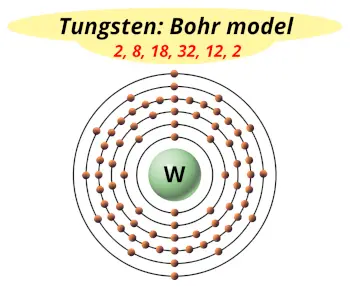 2, 8, 18, 32, 12, 2 |
| Electronic configuration | [Xe] 4f14 5d4 6s2 |
| Atomic radius | 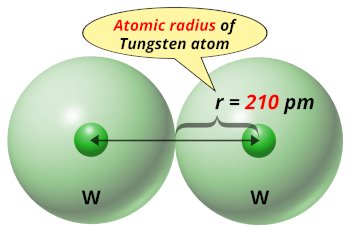 210 picometers (van der Waals radius) |
| 1st Ionization energy | 7.98 eV |
| Electronegativity | 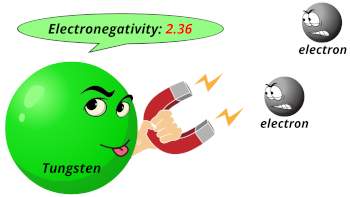 2.36 (Pauling scale) |
| Crystal structure | 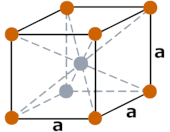 BCC (Body centered cubic) |
| Melting point | 3695 K or 3422 °C or 6192 °F |
| Boiling point | 6203 K or 5930 °C or 10706 °F |
| Density | 19.25 g/cm3 |
| Main isotopes | 182W (26.5%), 184W (30.6%), 186W (28.4%) |
| Who discovered Tungsten and when? | Fausto Elhuyar and Juan Jose Elhuyar (in 1783) |
| CAS number | 7440-33-7 |
Tungsten in Periodic table
Tungsten element is in group 6 and period 6 of the Periodic table. Tungsten is the d-block element and it belongs to transition metals group.
| H | He | ||||||||||||||||
| Li | Be | B | C | N | O | F | Ne | ||||||||||
| Na | Mg | Al | Si | P | S | Cl | Ar | ||||||||||
| K | Ca | Sc | Ti | V | Cr | Mn | Fe | Co | Ni | Cu | Zn | Ga | Ge | As | Se | Br | Kr |
| Rb | Sr | Y | Zr | Nb | Mo | Tc | Ru | Rh | Pd | Ag | Cd | In | Sn | Sb | Te | I | Xe |
| Cs | Ba | La* | Hf | Ta | W | Re | Os | Ir | Pt | Au | Hg | Tl | Pb | Bi | Po | At | Rn |
| Fr | Ra | Ac** | Rf | Db | Sg | Bh | Hs | Mt | Ds | Rg | Cn | Nh | Fl | Mc | Lv | Ts | Og |
| *Ce | Pr | Nd | Pm | Sm | Eu | Gd | Tb | Dy | Ho | Er | Tm | Yb | Lu | ||||
| **Th | Pa | U | Np | Pu | Am | Cm | Bk | Cf | Es | Fm | Md | No | Lr |
←Move to: Tantalum (Ta) element – Periodic Table
→Move to: Rhenium (Re) element – Periodic Table
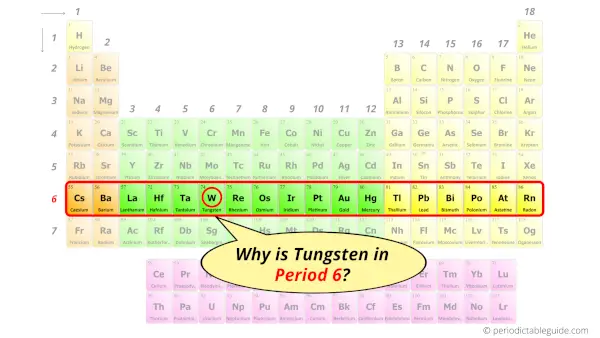
Why is Tungsten in Period 6?
Let me ask you a question.
How many shells does a tungsten atom have?
It’s 6. Right?
You have already seen the bohr model of tungsten atom in the above table.
From the Bohr model, it can be found that the number of orbits or shells in tungsten is 6. Hence, as tungsten has 6 orbits, it lies in period 6 of the Periodic table.
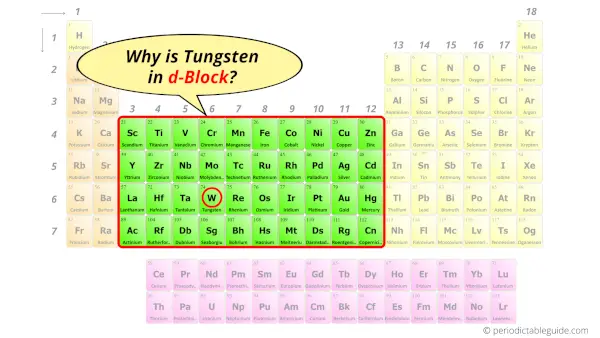
Why is Tungsten in d-block?
Before knowing this reason, first of all I want to ask you a simple question.
How can you determine the blocks-wise position of elements?
The simple answer: The elements will lie in the s, p, d or f block will completely depend upon the subshell in which the last electron will enter.
For example; the electron configuration of tungsten is [Xe] 4f14 5d4 6s2.
So the last electron of tungsten enters the d-subshell or d-orbital.
Hence, tungsten is the d-block element.
Is Tungsten a Transition Metal? Why?
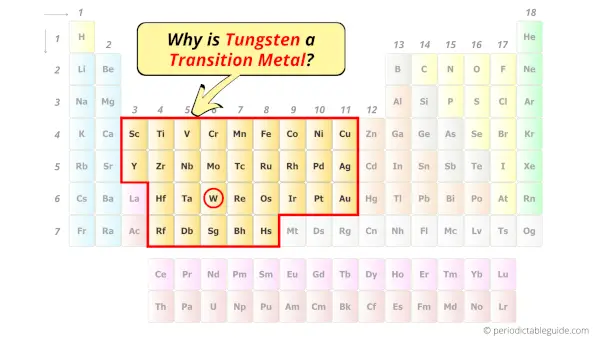
Yes, Tungsten is a transition metal because it has incompletely filled d-orbital in its ground state.
Let me explain the exact meaning of this.
According to the definition of transition metals;
The element should compulsorily have incomplete d-orbitals, either in their ground state (M) or most common oxidation states (M1+, M2+, etc) then only they are called transition metals.
Now, the ground state of Tungsten means its normal state in which it has neither gained nor lost any electron/s.
So the ground state of Tungsten is W.
And the ground state electronic configuration of Tungsten is [Xe] 4f14 5d4 6s2.
In this state, if we see the electron configuration of Tungsten, then it possesses incomplete d-orbitals.
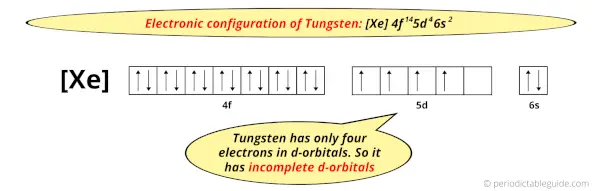
Because, there are only four electrons in the d-orbitals (here 5d orbitals).
In order to have the complete d-orbitals, there must be 10 electrons in it.
But in the ground state electronic configuration of tungsten, you can see that it has only 4 electrons in d-orbitals.
Thus, tungsten has incomplete d-orbitals.
And hence, as Tungsten has incomplete d-orbitals, it is considered as a transition metal.
5 facts about Tungsten
Interesting facts about tungsten element are mentioned below.
- In earlier times, this element was named as “wolfram” in European countries, but later on it was named “Tungsten” by IUPAC.
- The name tungsten was derived from the swedish words “tung sten”, which means “heavy stone”.
- Out of all the metals on the periodic table, tungsten has the highest melting point (i.e 3695 K or 3422 °C).
- Tungsten is the 4th hardest element found on the periodic table of elements, followed by carbon (diamond), boron and chromium.
- The abundance of tungsten in the earth’s crust is approximately 1.25 ppm by weight.
Properties of Tungsten
The physical and chemical properties of tungsten element are mentioned below.
Physical properties of Tungsten
Physical properties of tungsten are mentioned below.
- Tungsten is a tough metal having grey-white lustrous appearance.
- The powdered form of tungsten is grey in color.
- The atomic mass of tungsten is 183.84 u and its density is 19.25 g/cm3.
- The melting point and boiling point of tungsten are 3422 °C and 5930 °C respectively.
- There are many isotopes of tungsten, but out of those isotopes, the main isotopes are 182W (26.5%), 184W (30.6%) and 186W (28.4%).
- The crystal structure of tungsten is BCC (Body centered cubic).
Chemical properties of Tungsten
Chemical properties of tungsten are mentioned below.
- At room temperature, tungsten does not react with water, acids as well as bases.
- Tungsten is not reactive to oxygen at room temperature. But at higher temperature, it reacts with oxygen to form its oxide.
- When tungsten is present in its compounds, it mostly exists in +6 oxidation state.
- Tungsten has incomplete d-orbitals and hence it is classified as a transition metal on the periodic table.
Uses of Tungsten
Uses of tungsten are mentioned below.
- As tungsten has a very high melting point, it is used as a filament material in electric bulbs.
- Around 18% tungsten is used in high speed steels which is used to cut metal at higher speed.
- Tungsten is also used as an alloying element as well as it is also used in high temperature applications like welding.
- Tungsten carbide is a material that is used in making drill bits as well as it is also used in the manufacturing of other cutting tools.
Explore our New Interactive Periodic Table (with Rotating Bohr Models and More)

Details about this Periodic table:
- Access detailed info on all elements: atomic mass, electron configurations, charges, and more.
- View rotating Bohr models for all 118 elements.
- Get a free HD image of the Periodic Table.
Note: For future use, bookmark this Periodic table or visit “PeriodicTableGuide.com”
External resources:
- Tungsten – Wikipedia. (2020, May 2). Tungsten – Wikipedia. https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Tungsten
- Tungsten – Element information, properties and uses | Periodic Table. (n.d.). Tungsten – Element Information, Properties and Uses | Periodic Table. https://www.rsc.org/periodic-table/element/74/tungsten
- P. (n.d.). Tungsten | W (Element) – PubChem. Tungsten | W (Element) – PubChem. https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/element/Tungsten
- It’s Elemental – The Element Tungsten. (n.d.). It’s Elemental – the Element Tungsten. https://education.jlab.org/itselemental/ele074.html
