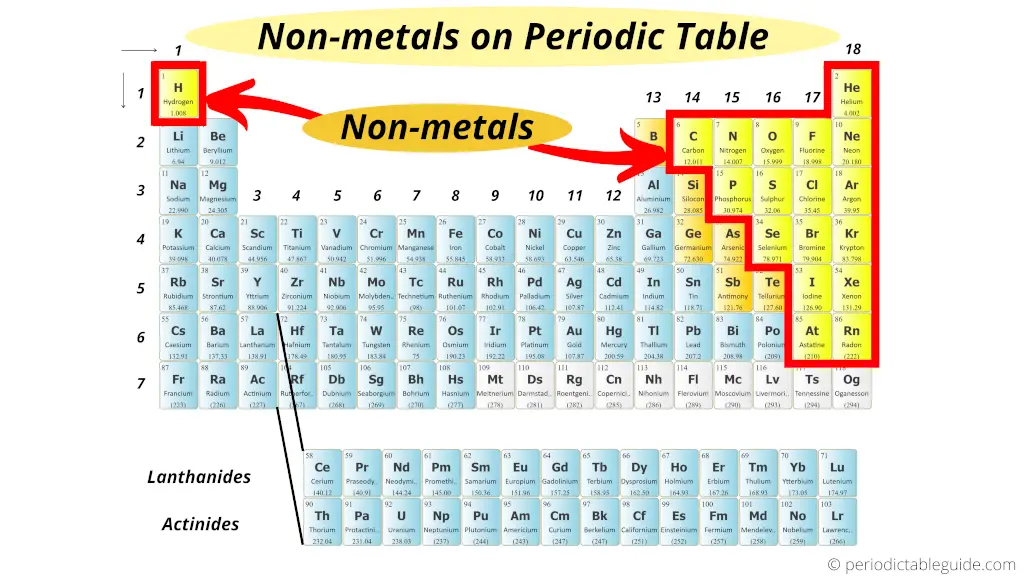
Nonmetals are located on the upper right side of the Periodic table (see above image).
Exception: Hydrogen is a nonmetal which is located on the left top corner of the Periodic table.
Well, you have got the answer of “Where are Nonmetals located on the Periodic Table?” But there are lot more things that you should know about the nonmetals like;
- What exactly are the nonmetals?
- How many nonmetals are there on the Periodic table?
- List of nonmetals on Periodic table
- Where are the most reactive nonmetals on the periodic table
- Properties of nonmetals on the periodic table
Let us discuss all these topics quickly.
Let’s get started.
What are nonmetals?
The simple answer: “Non metals” are “not” the “metals”
Or in other words nonmetals are those elements which do not possess the properties of metals.
Well, now let me tell you the proper definition of nonmetals used in chemistry.
Nonmetals are the chemical elements which gain electron/s during a chemical reaction and form a negative ion.
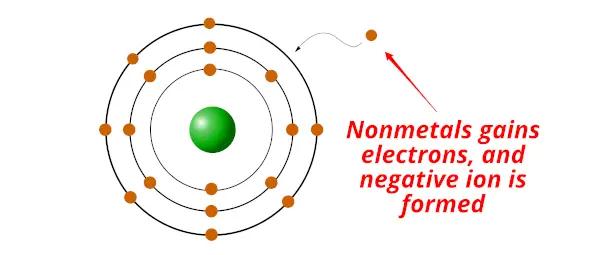
Non metals have exactly the opposite property than that of the metal.
In short remember that;
- Nonmetals are electrons gainers (nonmetals accept/gains electrons)
Elements which show these properties are known as Nonmetals.
I have discussed more physics and chemistry properties of nonmetals in this article only.
Stay tuned…
Now let us see the total number of nonmetals on the Periodic table.
How many nonmetals are there on the Periodic table?

There are 18 nonmetals on the Periodic table.
All these nonmetals are located on the upper right corner of the Periodic table (Hydrogen is located on the left top corner)
In the above image, the nonmetals are represented in yellow color.
[Note: Astatine (atomic number 85) shows characteristics of nonmetals (halogens) as well as metalloids. But many researchers have found that it shows more similar properties like that of nonmetals and hence Astatine (At) is considered as a nonmetal (halogen) by many researchers] Source: HRW texts
So on considering Astatine as a nonmetal, there are total 18 nonmetals on the Periodic table.
And if Astatine (At) is excluded from nonmetals, then there are total 17 nonmetals on the Periodic table.
But why is this number not exact?
Why is this number inexact?
The short answer: Because there is no widely agreed definition of metals, nonmetals and semimetals.
A chemist may define nonmetals on the basis of chemical properties of the element, while a physicist may define nonmetals on the basis of density or atomic number.
So we can say that the total number of nonmetals on the Periodic table is 17 or 18.
State of nonmetals at room temperature
Nonmetals are found in solid state, liquid state as well as gaseous state.
- 11 non metals are in gaseous state at room temperature.
- Bromine (Br) is a nonmetal which is in liquid state at room temperature.
- Rest of the nonmetals are solids at room temperature.
List of nonmetals on Periodic table
Here is a complete list of all the 18 nonmetals on the Periodic table.
| Atomic number | Symbol | Name of element |
| 1 | H | Hydrogen |
| 2 | He | Helium |
| 6 | C | Carbon |
| 7 | N | Nitrogen |
| 8 | O | Oxygen |
| 9 | F | Fluorine |
| 10 | Ne | Neon |
| 15 | P | Phosphorus |
| 16 | S | Sulfur |
| 17 | Cl | Chlorine |
| 18 | Ar | Argon |
| 34 | Se | Selenium |
| 35 | Br | Bromine |
| 36 | Kr | Krypton |
| 53 | I | Iodine |
| 54 | Xe | Xenon |
| 85 | At | Astatine |
| 86 | Rn | Radon |
Keep reading… more important topics are on the way.
Most reactive nonmetal on the Periodic table
The short answer: Fluorine is a highly reactive nonmetal on the entire Periodic table.
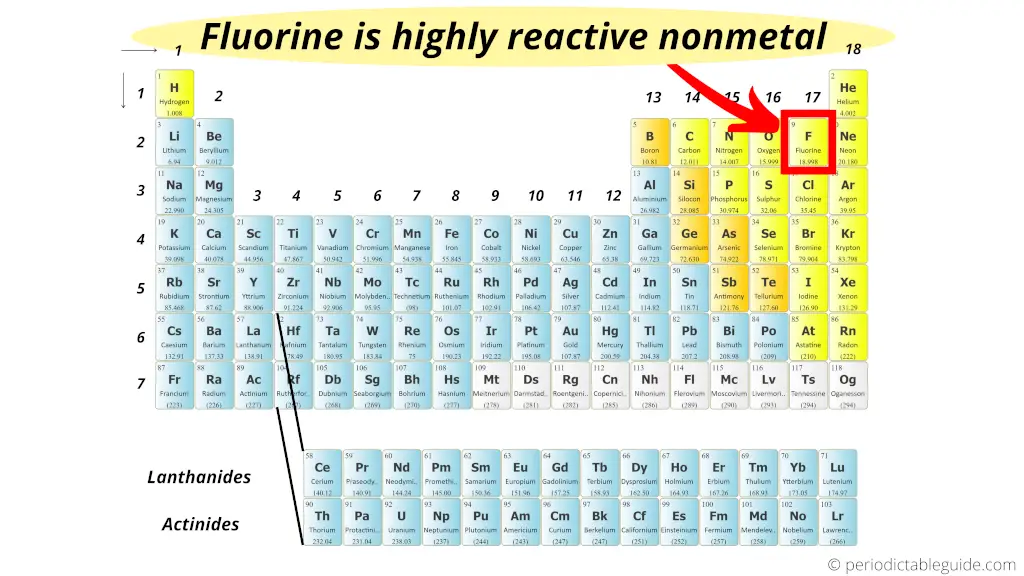
But why?
Don’t worry, I’ll tell you the reason behind this.
See, Atomic number of fluorine is 9. So it has 2 orbits and 7 electrons in its outermost orbit.
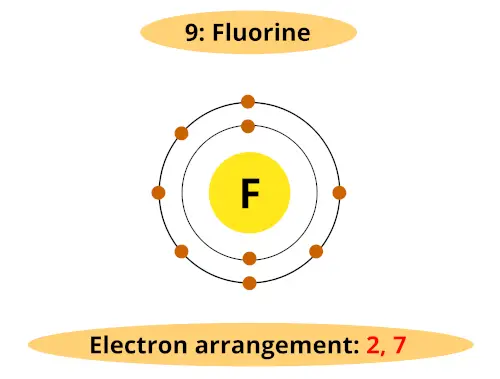
Fluorine requires only 1 electron to complete the octet. And it is very easy to gain one electron during a chemical reaction.
Also the atomic size of fluorine is very small. (Check this Periodic table guide, for atomic size trend)
And because of its smaller size and need of only one electron, it has the highest electronegativity.
Electronegativity is nothing but a tendency to attract the electron pair towards it.
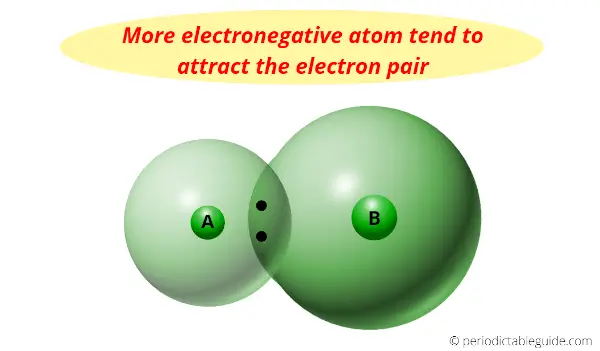
Actually the halogens are the most reactive nonmetals, but we know that as we move down the group, the electronegativity decreases.
In other words, Fluorine is at the top of the halogen group and it has less atomic size plus it needs only one electron to complete the octet.
So it has highest electronegativity (it has maximum tendency to attract the electrons pair)
And because of this, fluorine has a highest tendency to react with any other element to form a compound.
Even fluorine reacts with noble gas like xenon, and forms compounds like XeF4 (Xenon tetrafluoride) and XeF6 (Xenon hexafluoride)
Thus fluorine is highly reactive nonmetal.
(Note: Noble gases have even smaller atomic size compared to halogens, but they have complete octet. So they do not participate in any chemical reaction. Hence noble gases are chemically inert)
Also visit:
1). Where are halogens on the periodic table? (with images)
2). Where are nonmetals on the periodic table? (with images)
Properties of nonmetals on the periodic table
Well, now I’ll discuss the physical and chemical properties of nonmetals.
Nonmetals have exactly the opposite characteristics that of the metals.
Let’s get started with physical properties.
Physical properties of nonmetals
#1 State: solid, liquid as well as gas
At room temperature, nonmetals are found in solid state, liquid state as well as gaseous state.
- 11 non metals are in gaseous state at room temperature.
- Bromine (Br) is a nonmetal which is in liquid state at room temperature.
- Rest of the nonmetals are solids at room temperature.
#2 Little or no lusture
Nonmetals are generally non lustrous but few solid nonmetals have shiny lustrous surface (For example: Iodine have a lustrous surface)
#3 Poor conductor of heat and electricity
Nonmetals do not allow heat and electricity to pass through them.
Hence they are poor conductors of heat and electricity.
#4 Brittle
Solid nonmetals are brittle in nature. That means they break easily when force is applied on them.
#5 Lower melting point and boiling point
Nonmetals have lower melting point as well as boiling point and thus most of the nonmetals are gaseous at room temperature.
#6 Low density
Nonmetals have lower density, hence they are light in weight.
#7 Not sonorous
Nonmetals do not conduct sound. Hence they are not sonorous.
Chemical properties of nonmetals
#1 Valency
Nonmetals have 4 to 8 electrons in their outermost orbit. (Halogens have 7 electrons and noble gases have 8 electrons in outermost orbit)
#2 High electronegativity
Nonmetallic elements have the higher tendency to attract the electron pair towards it during a chemical reaction.
Hence nonmetals are highly electronegative in nature.
#3 Gain of electrons
Nonmetals have 4 to 8 electrons in their outermost orbit. Hence nonmetals show tendency to gain electrons during a chemical reaction to complete the octet.
#4 Forms acidic oxides
Nonmetals react with water and form acidic oxides.
#5 Good oxidizing agents
Nonmetals are oxidizing agents because they gain electron/s during a chemical reaction and get reduced.
Explore our New Interactive Periodic Table (with Rotating Bohr Models and More)

Details about this Periodic table:
- Access detailed info on all elements: atomic mass, electron configurations, charges, and more.
- View rotating Bohr models for all 118 elements.
- Get a free HD image of the Periodic Table.
Note: For future use, bookmark this Periodic table or visit “PeriodicTableGuide.com”
Summary
So in the entire article, we have discussed the definition or exact meaning of nonmetals and then we saw the position of nonmetals on the Periodic table.
Now you know that nonmetals are present on the upper right corner of the Periodic table.
Then we also discussed that there are total 18 nonmetals on the Periodic table (I also mentioned a list of these 18 elements)
Then we discussed about the most reactive nonmetal on the Periodic table (i.e Fluorine).
And finally we discussed the physical and chemical properties of nonmetals.
I hope this article “Where are Nonmetals located on the Periodic Table” has helped you in solving your doubts.
Let me know in the comments below, has this article helped you or not?
Suggested Important articles for you:
- Periodic table (with everything you need to know)
- Metals on the periodic table
- Metalloids on periodic table
- Halogens on periodic table
- Alkali metals on periodic table
- Alkaline earth metals on periodic table
- Noble gases on periodic table
- Transition metals on Periodic table
- Inner transition metals on periodic table
- What do elements in the same group have in common
