This is a SUPER easy guide on Vanadium element.
In fact, the table mentioned below is the perfect information box (Which gives you every single detail about the Vanadium element in Periodic table.)
So if you want to know anything about Vanadium element, then this guide is for you.
Let’s finish this very quickly.
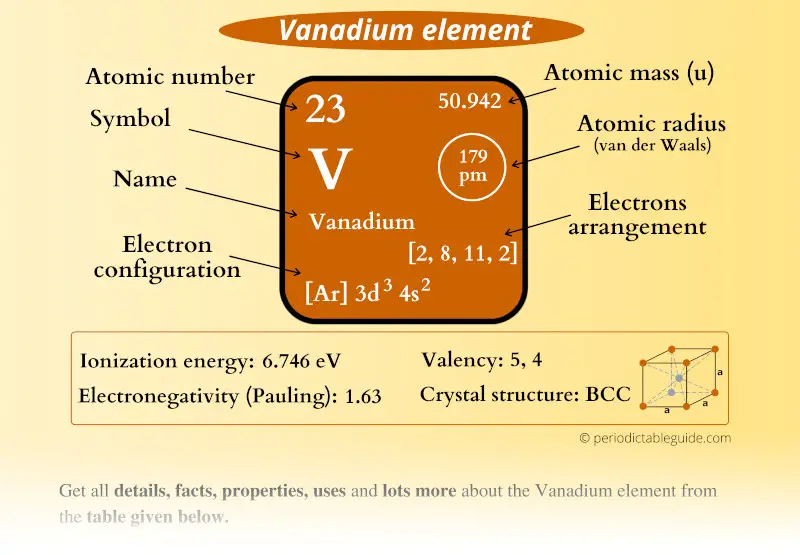
Vanadium Element (V) Information
| Appearance |  Shiny bluish-grey |
| State (at STP) | Solid |
| Position in Periodic table | 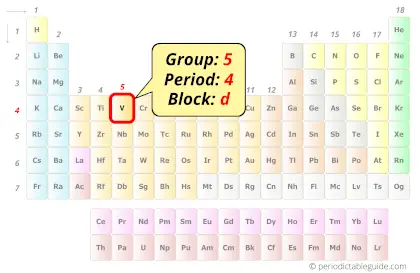 Group: 5, Period: 4, Block: d |
| Category | 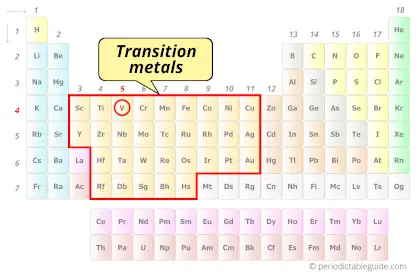 Transition metals |
| Atomic number or Protons | 23 |
| Neutrons | 28 |
| Electrons | 23 |
| Symbol | V |
| Atomic mass | 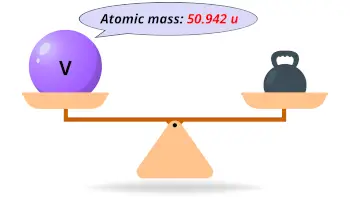 50.942 u |
| Electrons arrangement or Bohr model | 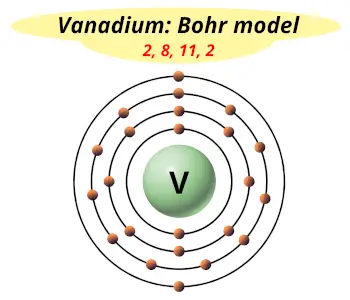 2, 8, 11, 2 |
| Electronic configuration | [Ar] 3d3 4s2 |
| Atomic radius | 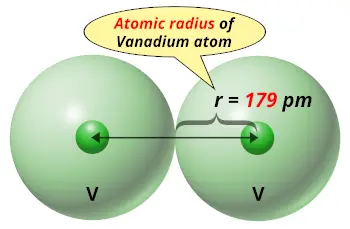 179 picometers (van der Waals radius) |
| 1st Ionization energy | 6.746 eV |
| Electronegativity | 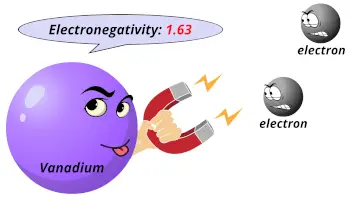 1.63 (Pauling scale) |
| Crystal structure | 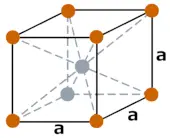 BCC (Body Centered Cubic) |
| Melting point | 2183 K or 1910 °C or 3470 °F |
| Boiling point | 3680 K or 3407 °C or 6165 °F |
| Density | 6.11 g/cm3 |
| Main isotope | 51V |
| Who discovered Vanadium and when? |  Andres Manuel del Rio in 1801 |
| CAS number | 7440-62-2 |
Vanadium in Periodic table
Vanadium element is in group 5 and period 4 of the Periodic table. Vanadium is the d-block element and it belongs to transition metals group.
| H | He | ||||||||||||||||
| Li | Be | B | C | N | O | F | Ne | ||||||||||
| Na | Mg | Al | Si | P | S | Cl | Ar | ||||||||||
| K | Ca | Sc | Ti | V | Cr | Mn | Fe | Co | Ni | Cu | Zn | Ga | Ge | As | Se | Br | Kr |
| Rb | Sr | Y | Zr | Nb | Mo | Tc | Ru | Rh | Pd | Ag | Cd | In | Sn | Sb | Te | I | Xe |
| Cs | Ba | La* | Hf | Ta | W | Re | Os | Ir | Pt | Au | Hg | Tl | Pb | Bi | Po | At | Rn |
| Fr | Ra | Ac** | Rf | Db | Sg | Bh | Hs | Mt | Ds | Rg | Cn | Nh | Fl | Mc | Lv | Ts | Og |
| *Ce | Pr | Nd | Pm | Sm | Eu | Gd | Tb | Dy | Ho | Er | Tm | Yb | Lu | ||||
| **Th | Pa | U | Np | Pu | Am | Cm | Bk | Cf | Es | Fm | Md | No | Lr |
←Move to: Titanium (Ti) element – Periodic Table
→Move to: Chromium (Cr) element – Periodic Table
Why is Vanadium in d block?
Before knowing this reason, first of all a simple question to you.
How can you determine the blocks wise position of elements?
The simple answer: The elements will lie in the s, p, d or f block will completely depend upon the subshell in which the last electron will enter.
For example; the electron configuration of Vanadium is [Ar] 4s2 3d3.
So the last electron of Vanadium enters the d-subshell or d-orbital.
Hence, Vanadium is the d-block element.
Is Vanadium a Metal, Nonmetal or Metalloid?
Vanadium is a Metal. It’s a Shiny bluish-grey colored hard and malleable metal (that means it can achieve the desired shape when higher pressure is applied to it). Vanadium also shows good resistance towards alkalis and acids.

But do you know what exactly the metals are?
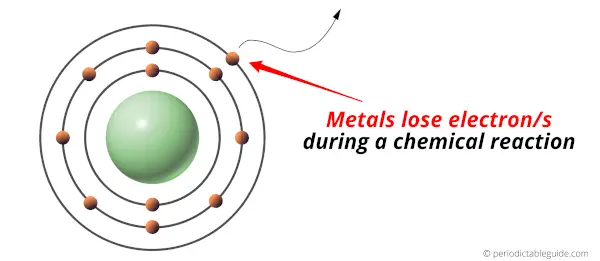
- Metals are the elements which lose electron/s during a chemical reaction.
In other words, metals are electron donors.
Metals are found on the left side of the Periodic table.
For more clarification, see the location of metals on the Periodic table (Image).
Why is Vanadium a Transition Metal?
Vanadium element is a transition metal because it has incompletely filled d-orbital in its ground state.
Let me explain the exact meaning of this.
According to the definition of transition metals;
The element should compulsorily have incomplete d-orbitals, either in their ground state (M) or most common oxidation states (M1+, M2+, etc) then only they are called transition metals.
Now, the ground state of Vanadium means its normal state in which it has neither gained nor lost any electron/s.
So the ground state of Vanadium is V.
And the ground state electronic configuration of Vanadium is [Ar] 4s2 3d3.
In this state, if we see the electron configuration of Vanadium, then it possesses incomplete d-orbitals.
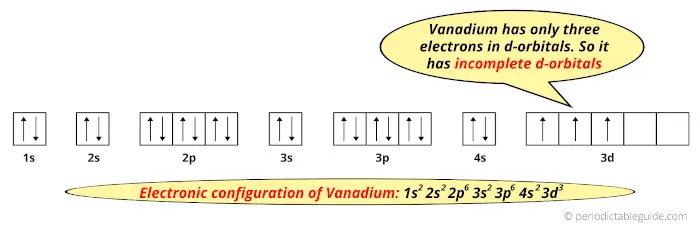
Because, there are only three electrons in the d-orbitals.
In order to have the complete d-orbitals, there must be 10 electrons in it.
But in the ground state electronic configuration of Vanadium, you can see that it has only 3 electrons in d-orbital.
Thus, Vanadium has incomplete d-orbitals.
And hence, as Vanadium has incomplete d-orbitals, it is considered as a transition metal.
Also see: Location of transition metals on periodic table (Image)
Where is Vanadium found in nature?
In nature, Vanadium is not found as a pure metal. But it is always found as a compound form with other minerals.
Vanadium comprises 0.018% of the Earth’s crust and it is found in the Earth’s crust from the minerals including vanadinite, patronite, carnotite, magnetite, etc.
Concentrations of vanadium are also present in the carbon containing deposits like coal, crude oil and oil shales.
South Africa, China and Russia have the largest deposits of Vanadium ores.
Interesting Facts about Vanadium
Facts about Vanadium are mentioned below.
- Vanadium was first discovered by Spanish scientist Andres Manuel del Rio in 1801.
- Vanadium gets its name from the Scandinavian goddess of beauty “Vanadis”.
- Around 80% of Vanadium is used in the production of steel.
- Vanadinite is a mineral of Vanadium which is red in color.
- Vanadium comprises 0.018% of the Earth’s crust which is around 150 ppm (parts per million)
- Vanadium also shows good resistance towards alkalis and acids.
- South Africa, China and Russia have the largest deposits (around 98%) of Vanadium ores.
Free Gift for you: Interactive Periodic Table
Let me tell you how this Interactive Periodic Table will help you in your studies.
1). You can effortlessly find every single detail about the elements from this single Interactive Periodic table.
2). You will get the detailed information about the periodic table which will convert a newbie into pro.
3). You will also get the HD images of the Periodic table (for FREE).
Checkout Interactive Periodic table and download it’s high resolution image now (It’s FREE)
External resources:
- P. (n.d.). Vanadium | V (Element) – PubChem. Vanadium | V (Element) – PubChem. https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/element/Vanadium
- It’s Elemental – The Element Vanadium. (n.d.). It’s Elemental – the Element Vanadium. https://education.jlab.org/itselemental/ele023.html
- Vanadium – Wikipedia. (2022, December 5). Vanadium – Wikipedia. https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Vanadium
- Vanadium – Element information, properties and uses | Periodic Table. (n.d.). Vanadium – Element Information, Properties and Uses | Periodic Table. https://www.rsc.org/periodic-table/element/23/vanadium
- Periodic Table of Elements: Los Alamos National Laboratory. (n.d.). Periodic Table of Elements: Los Alamos National Laboratory. https://periodic.lanl.gov/23.shtml