This is a SUPER easy guide on Cadmium element.
In fact, the table mentioned below is the perfect information box (Which gives you every single detail about the Cadmium element in Periodic table.)
So if you want to know anything about Cadmium element, then this guide is for you.
Let’s finish this very quickly.
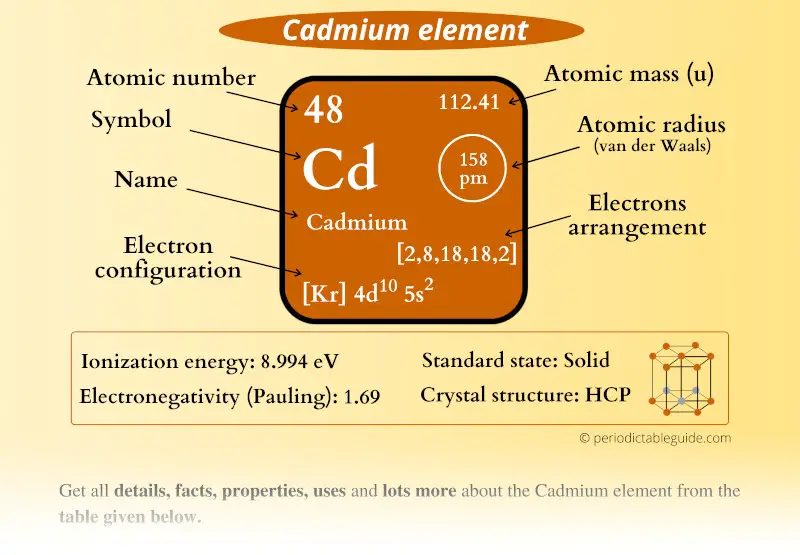
Cadmium Element (Cd) Information
| Appearance |  Shiny bluish-grey metallic |
| State (at STP) | Solid |
| Position in Periodic table | 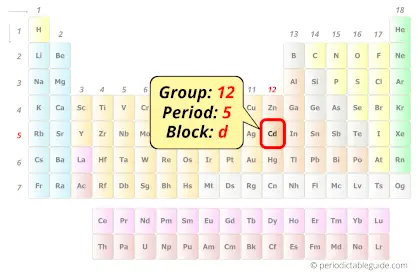 Group: 12, Period: 5, Block: d |
| Category | 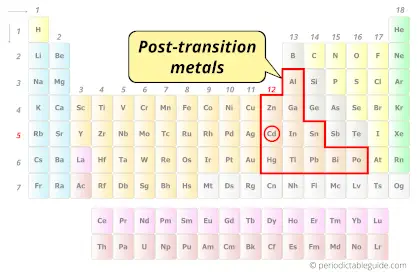 Post-transition metals |
| Atomic number or Protons | 48 |
| Neutrons | 64 |
| Electrons | 48 |
| Symbol | Cd |
| Atomic mass | 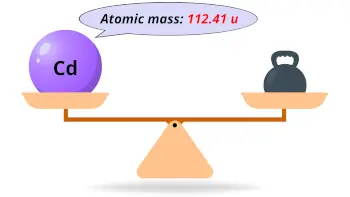 112.41 u |
| Electrons arrangement or Bohr model | 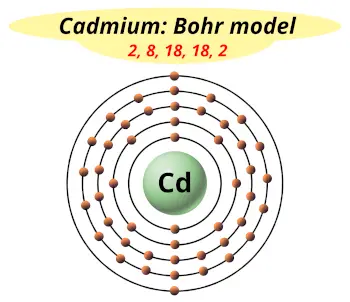 2, 8, 18, 18, 2 |
| Electronic configuration | [Kr] 4d10 5s2 |
| Atomic radius | 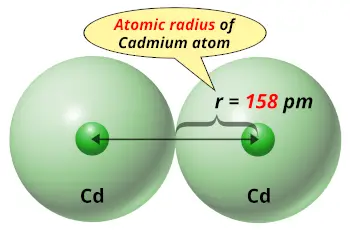 158 picometers (van der Waals radius) |
| Valence electrons | 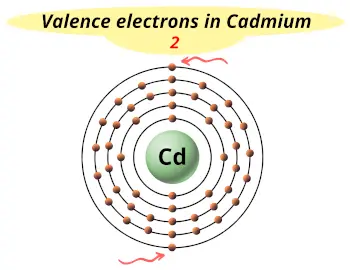 2 |
| 1st Ionization energy | 8.994 eV |
| Electronegativity | 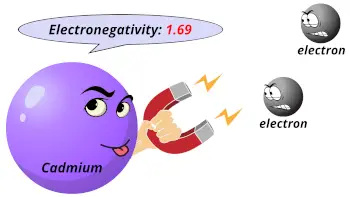 1.69 (Pauling scale) |
| Crystal structure | 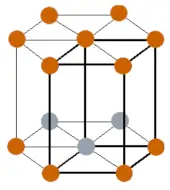 HCP (Hexagonal closed packing) |
| Melting point | 594.2 K or 321 °C or 610 °F |
| Boiling point | 1040 K or 767 °C or 1413 °F |
| Density | 8.65 g/cm3 |
| Main isotope | 114Cd, 112Cd |
| Who discovered Cadmium and when? |  Friedrich Stromeyer in 1817 |
| CAS number | 7440-43-9 |
Cadmium in Periodic table
Cadmium element is in group 12 and period 5 of the Periodic table. Cadmium is a metal and it belongs to the post-transition metals group (also known as other metals).
| H | He | ||||||||||||||||
| Li | Be | B | C | N | O | F | Ne | ||||||||||
| Na | Mg | Al | Si | P | S | Cl | Ar | ||||||||||
| K | Ca | Sc | Ti | V | Cr | Mn | Fe | Co | Ni | Cu | Zn | Ga | Ge | As | Se | Br | Kr |
| Rb | Sr | Y | Zr | Nb | Mo | Tc | Ru | Rh | Pd | Ag | Cd | In | Sn | Sb | Te | I | Xe |
| Cs | Ba | La* | Hf | Ta | W | Re | Os | Ir | Pt | Au | Hg | Tl | Pb | Bi | Po | At | Rn |
| Fr | Ra | Ac** | Rf | Db | Sg | Bh | Hs | Mt | Ds | Rg | Cn | Nh | Fl | Mc | Lv | Ts | Og |
| *Ce | Pr | Nd | Pm | Sm | Eu | Gd | Tb | Dy | Ho | Er | Tm | Yb | Lu | ||||
| **Th | Pa | U | Np | Pu | Am | Cm | Bk | Cf | Es | Fm | Md | No | Lr |
←Move to: Silver (Ag) element – Periodic Table
→Move to: Indium (In) element – Periodic Table
Is Cadmium a Metal, Nonmetal or Metalloid?
Cadmium is a Metal. It’s a Shiny bluish-grey metallic colored soft and malleable metal (that means it can achieve the desired shape when pressure is applied to it). It is a good conductor of electricity, and it is also resistant to corrosion and chemical attacks.

But do you know what exactly the metals are?
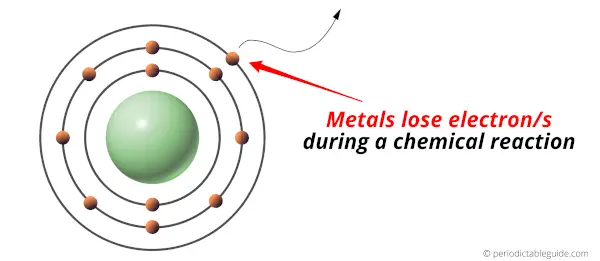
- Metals are the elements which lose electron/s during a chemical reaction.
In other words, metals are electron donors.
Metals are found on the left side of the Periodic table.
For more clarification, see the location of metals on the Periodic table (Image).
Why is Cadmium not a Transition Metal?
Cadmium lies in group 12 and it is a d-block element (see the above periodic table).
But the question is;
“Is Cadmium a transition metal?”
Answer: Cadmium element is not a transition metal because its d-orbitals are completely filled in its most common oxidation state (Cd+2).
Let me explain the exact meaning of this.
According to the definition of transition metals;
The element should compulsorily have incomplete d-orbitals, either in their ground state (M) or most common oxidation states (M1+, M2+, etc) then only they are called transition metals.
Now, the oxidation state of any element means it is a state in which it has either gained or lost electron/s.
And the most common oxidation state of Cadmium element is +2.
The normal ground state electronic configuration of Cadmium element is Cd: [Kr] 4d10 5s2.
But when it loses 2 electrons, its electronic configuration becomes Cd+2: [Kr] 4d10.In this state, if we see the electron configuration of Cadmium, then the d-orbitals are completely filled (it has complete 10 electrons).
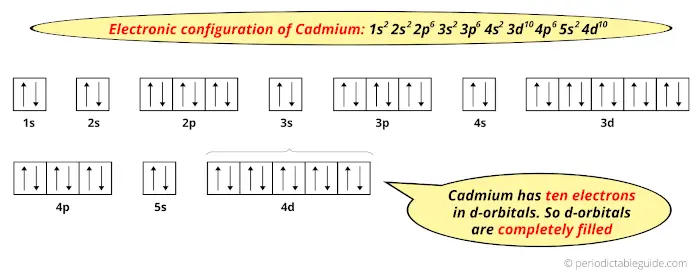
Thus, in the most common oxidation state (Cd+2) Cadmium has fully filled d-orbitals.
And hence, as the most common oxidation state has fully filled d-orbitals, Cadmium is not considered as a transition metal.
Why is Cadmium used as control rods?
In any nuclear reactors, the power is produced with the help of radioactive fuels like uranium or plutonium.
These radioactive materials undergo a fission process in which they emit neutrons and a high amount of energy is released.
Now in order to control the fission rate, there must be some element which can absorb the emitted neutrons.
So for that purpose, the cadmium element plays an important role. Cadmium has a capacity to absorb the emitted neutrons.
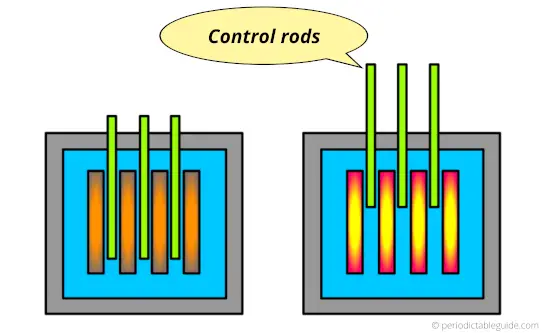
So in nuclear reactors, the Cadmium rods are used for controlling the fission rate of radioactive elements.
If cadmium rods are pulled out of the nuclear reactor, the fission rate increases.
And if the Cadmium rods are pushed inside the nuclear reactor, then cadmium rods will absorb the neutrons and ultimately the fission rate decreases.
Hence, Cadmium is used as control rods in a nuclear reactor to control the nuclear reaction.
Interesting Facts about Cadmium
5 interesting facts about cadmium element are mentioned below.
- In 1817, German chemist Friedrich Stromeyer was a person who discovered cadmium after isolating it from zinc carbonate.
- Cadmium is a shiny bluish-grey metallic colored soft and malleable metal which can also be cut using a kitchen knife.
- Our earth’s crust contains 0.150 ppm (parts per million) of cadmium.
- There are no ores of Cadmium, but it is obtained during the refining of zinc.
- Only 6.5 pounds of cadmium can be obtained from approximately 1 ton sample of zinc.
Free Gift for you: Interactive Periodic Table
Let me tell you how this Interactive Periodic Table will help you in your studies.
1). You can effortlessly find every single detail about the elements from this single Interactive Periodic table.
2). You will get the detailed information about the periodic table which will convert a newbie into pro.
3). You will also get the HD images of the Periodic table (for FREE).
Checkout Interactive Periodic table and download it’s high resolution image now (It’s FREE)
External resources:
- Chemistry of Cadmium. (2013, October 2). Chemistry LibreTexts. https://chem.libretexts.org/Bookshelves/Inorganic_Chemistry/Supplemental_Modules_and_Websites_(Inorganic_Chemistry)/Descriptive_Chemistry/Elements_Organized_by_Block/3_d-Block_Elements/Group_12%3A_Transition_Metals/Chemistry_of_Cadmium
- Cadmium – Element information, properties and uses | Periodic Table. (n.d.). Cadmium – Element Information, Properties and Uses | Periodic Table. https://www.rsc.org/periodic-table/element/48/cadmium
- Cadmium – Wikipedia. (2021, November 25). Cadmium – Wikipedia. https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Cadmium
- P. (n.d.). Cadmium | Cd (Element) – PubChem. Cadmium | Cd (Element) – PubChem. https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/element/Cadmium