This is a SUPER easy guide on Darmstadtium element.
In fact, the table mentioned below is the perfect information box (Which gives you every single detail about the Darmstadtium element in Periodic table.)
So if you want to know anything about Darmstadtium element, then this guide is for you.
Let’s finish this very quickly.
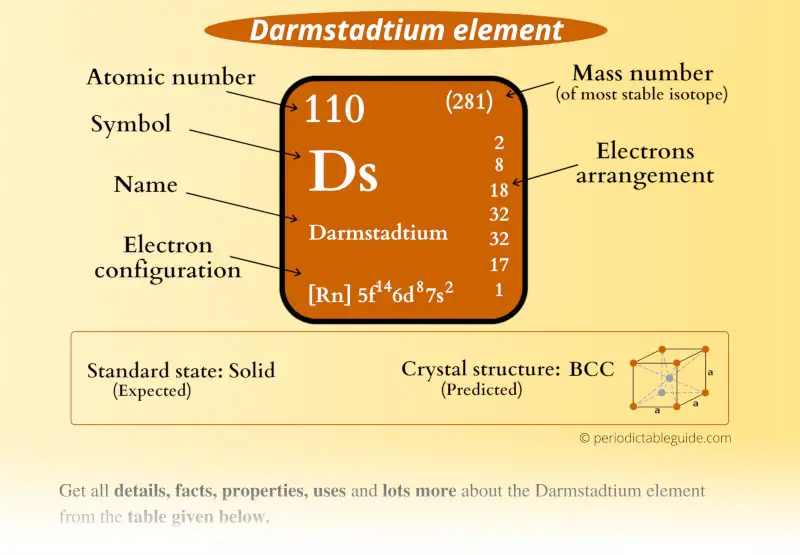
Darmstadtium Element (Ds) Information
| State (at STP) | Solid (predicted) |
| Position in Periodic table | 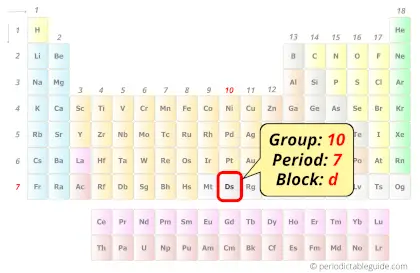 Group: 10, Period: 7, Block: d |
| Category | Synthetic element |
| Atomic number or Protons | 110 |
| Neutrons | 151 |
| Electrons | 110 |
| Symbol | Ds |
| Atomic mass of Darmstadtium (most stable isotope) | 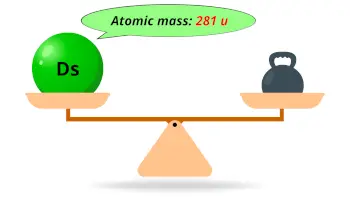 281 u |
| Electrons arrangement or Bohr model | 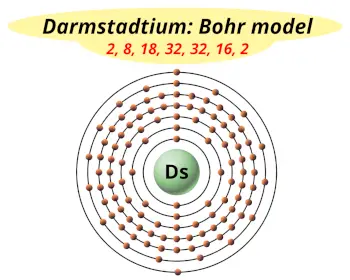 2, 8, 18, 32, 32, 16, 2 |
| Electronic configuration | [Rn] 5f14 6d8 7s2 |
| Crystal structure (predicted) | 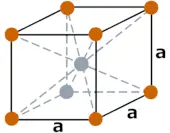 BCC (body centered cubic) |
| Density | 26-27 g/cm3 |
| Main isotope | 281Ds |
| CAS number | 54083-77-1 |
Darmstadtium in Periodic table
Darmstadtium element is in group 10 and in period 7 of the Periodic table. Darmstadtium is the d-block element and it is a radioactive synthetic element.
| H | He | ||||||||||||||||
| Li | Be | B | C | N | O | F | Ne | ||||||||||
| Na | Mg | Al | Si | P | S | Cl | Ar | ||||||||||
| K | Ca | Sc | Ti | V | Cr | Mn | Fe | Co | Ni | Cu | Zn | Ga | Ge | As | Se | Br | Kr |
| Rb | Sr | Y | Zr | Nb | Mo | Tc | Ru | Rh | Pd | Ag | Cd | In | Sn | Sb | Te | I | Xe |
| Cs | Ba | La* | Hf | Ta | W | Re | Os | Ir | Pt | Au | Hg | Tl | Pb | Bi | Po | At | Rn |
| Fr | Ra | Ac** | Rf | Db | Sg | Bh | Hs | Mt | Ds | Rg | Cn | Nh | Fl | Mc | Lv | Ts | Og |
| *Ce | Pr | Nd | Pm | Sm | Eu | Gd | Tb | Dy | Ho | Er | Tm | Yb | Lu | ||||
| **Th | Pa | U | Np | Pu | Am | Cm | Bk | Cf | Es | Fm | Md | No | Lr |
←Move to: Meitnerium (Mt) element – Periodic Table
→Move to: Roentgenium (Rg) element – Periodic Table
Why is Darmstadtium in Period 7?
Let me ask you a question.
How many shells does a darmstadtium atom have?
It’s 7. Right?
You have already seen the bohr model of darmstadtium atom in the above table.
From the Bohr model, it can be found that the number of orbits or shells in darmstadtium is 7. Hence, as darmstadtium has 7 orbits, it lies in period 7 of the Periodic table.
Why is Darmstadtium in d-block?
Before knowing this reason, first of all I want to ask you a simple question.
How can you determine the blocks-wise position of elements?
The simple answer: The elements will lie in the s, p, d or f block will completely depend upon the subshell in which the last electron will enter.
For example; the electron configuration of darmstadtium is [Rn] 5f14 6d8 7s2.
So the last electron of darmstadtium enters the d-subshell or d-orbital.
Hence, darmstadtium is the d-block element.
5 facts about Darmstadtium
Interesting facts about darmstadtium element are mentioned below.
- The name of element “Darmstadtium” came from “Darmstadt”, which is a city in Germany, where this element was discovered.
- Darmstadtium is not found naturally, but it is prepared artificially in a laboratory.
- Darmstadtium was discovered by Peter Armbruster and Gottfried Münzenberg under the guidance of Sigurd Hofmann, in Germany.
- There are 9 known isotopes of darmstadtium, and all these isotopes are extremely radioactive.
- Out of all the known isotopes of darmstadtium, the isotope 281Ds is most stable and has a half life of only 12.5 seconds.
Properties of Darmstadtium
The physical and chemical properties of darmstadtium element are mentioned below.
- The darmstadtium element is a radioactive synthetic element and it has a very short half-life (of few seconds).
- The predicted phase of darmstadtium is solid at room temperature.
- The calculated atomic mass of the most stable isotope of darmstadtium is 281 u and its density is 26-27 g/cm3.
- The predicted crystal structure of Darmstadtium element is BCC (body centered cubic).
- The most stable oxidation states of darmstadtium are predicted to be +6, +4 and +2.
Uses of Darmstadtium
Darmstadtium is generally used for scientific research work in chemistry. There is no commercial use of Darmstadtium due to its radioactive nature and very little half-life.
Explore our New Interactive Periodic Table (with Rotating Bohr Models and More)

Details about this Periodic table:
- Access detailed info on all elements: atomic mass, electron configurations, charges, and more.
- View rotating Bohr models for all 118 elements.
- Get a free HD image of the Periodic Table.
Note: For future use, bookmark this Periodic table or visit “PeriodicTableGuide.com”
External resources:
- Darmstadtium – Element information, properties and uses | Periodic Table. (n.d.). Darmstadtium – Element Information, Properties and Uses | Periodic Table. https://www.rsc.org/periodic-table/element/110/darmstadtium
- Darmstadtium – Wikipedia. (2012, October 19). Darmstadtium – Wikipedia. https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Darmstadtium
- Darmstadtium | chemical element. (n.d.). Encyclopedia Britannica. https://www.britannica.com/science/darmstadtium
- It’s Elemental – The Element Darmstadtium. (n.d.). It’s Elemental – the Element Darmstadtium. https://education.jlab.org/itselemental/ele110.html
- P. (n.d.). Darmstadtium | Ds (Element) – PubChem. Darmstadtium | Ds (Element) – PubChem. https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/element/Darmstadtium
- C&EN: IT’S ELEMENTAL: THE PERIODIC TABLE – DARMSTADTIUM AND BEYOND. (n.d.). C&EN: IT’S ELEMENTAL: THE PERIODIC TABLE – DARMSTADTIUM AND BEYOND. https://pubsapp.acs.org/cen/80th/darmstadtium.html?
