This is a SUPER easy guide on Radon element.
In fact, the table mentioned below is the perfect information box (Which gives you every single detail about the Radon element in Periodic table.)
So if you want to know anything about Radon element, then this guide is for you.
Let’s dive right into it!
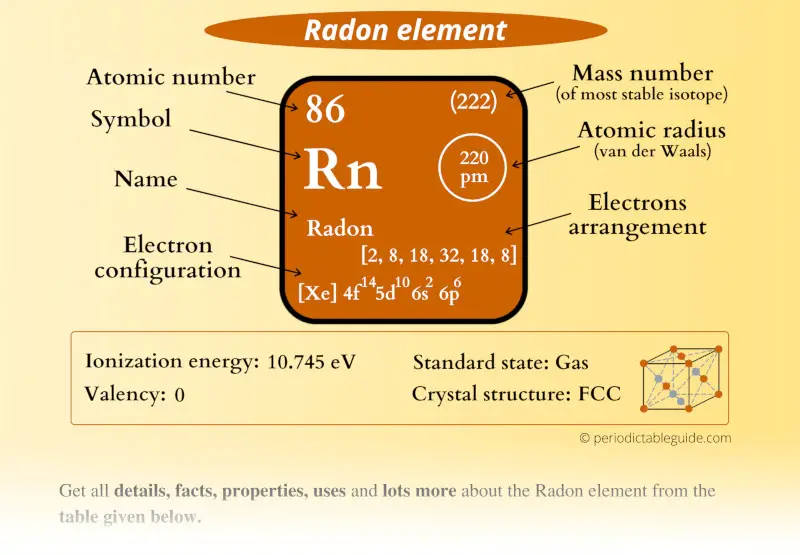
Radon Element (Rn) Information
| Appearance | Colorless gas |
| State (at STP) | Gas |
| Position in Periodic table | 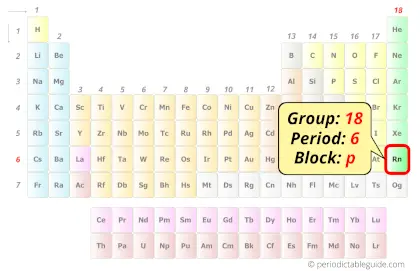 Group: 18, Period: 6, Block: p |
| Category | 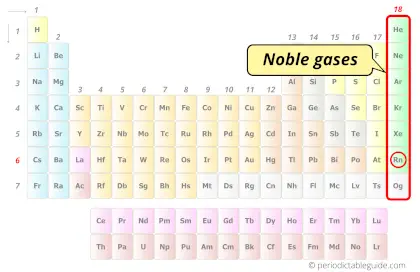 Noble gases |
| Atomic number or Protons | 86 |
| Neutrons | 136 |
| Electrons | 86 |
| Symbol | Rn |
| Atomic mass (predicted) | 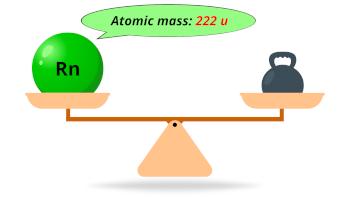 222 u |
| Electrons arrangement or Bohr model | 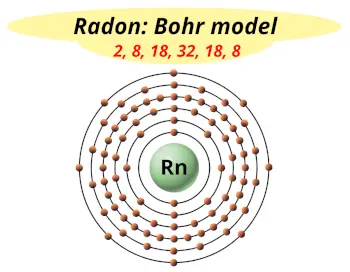 2, 8, 18, 32, 18, 8 |
| Electronic configuration | [Xe] 4f14 5d10 6s2 6p6 |
| Atomic radius | 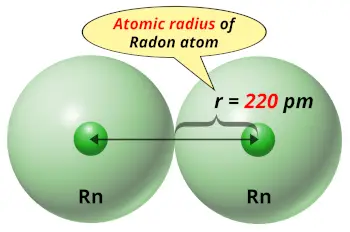 220 picometers (van der Waals radius) |
| Valence electrons | 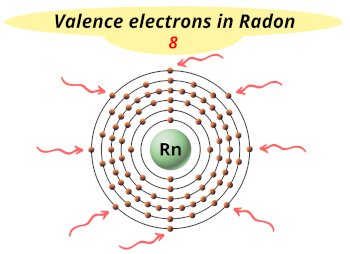 8 |
| 1st Ionization energy | 10.745 eV |
| Crystal structure | 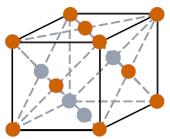 FCC (face centered cubic) |
| Melting point | 202 K or -71 °C or -96 °F |
| Boiling point | 211.5 K or -61.7 °C or -79.1 °F |
| Density | 9.73 g/L |
| Main isotope | 222Rn |
| Who discovered Radon and when? | Ernest Rutherford and Robert Owens (in 1899) |
| CAS number | 10043-92-2 |
Radon in Periodic table
Radon element is in group 18 and period 6 of the Periodic table. Radon is the p-block element and it belongs to noble gases group.
| H | He | ||||||||||||||||
| Li | Be | B | C | N | O | F | Ne | ||||||||||
| Na | Mg | Al | Si | P | S | Cl | Ar | ||||||||||
| K | Ca | Sc | Ti | V | Cr | Mn | Fe | Co | Ni | Cu | Zn | Ga | Ge | As | Se | Br | Kr |
| Rb | Sr | Y | Zr | Nb | Mo | Tc | Ru | Rh | Pd | Ag | Cd | In | Sn | Sb | Te | I | Xe |
| Cs | Ba | La* | Hf | Ta | W | Re | Os | Ir | Pt | Au | Hg | Tl | Pb | Bi | Po | At | Rn |
| Fr | Ra | Ac** | Rf | Db | Sg | Bh | Hs | Mt | Ds | Rg | Cn | Nh | Fl | Mc | Lv | Ts | Og |
| *Ce | Pr | Nd | Pm | Sm | Eu | Gd | Tb | Dy | Ho | Er | Tm | Yb | Lu | ||||
| **Th | Pa | U | Np | Pu | Am | Cm | Bk | Cf | Es | Fm | Md | No | Lr |
←Move to: Astatine (As) element – Periodic Table
→Move to: Francium (Fr) element – Periodic Table
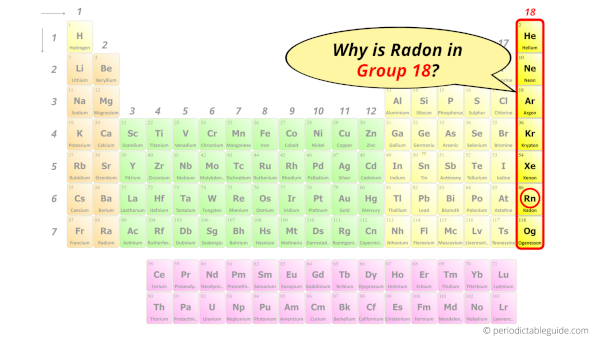
Why is Radon in Group 18?
Do you know, how many electrons can be accommodated in the first shell, second shell, third shell, fourth shell, etc…?
Here is the table showing the capacity of orbits to hold electrons.
Number of electrons in shells.
| Orbit / Shell (n) | Maximum no. of electrons this orbit can hold (2 × n2) |
| K shell, n = 1 | 2 × 1² = 2 |
| L shell, n = 2 | 2 × 2² = 8 |
| M shell, n = 3 | 2 × 3² = 18 |
| N shell, n = 4 | 2 × 4² = 32 |
| . . . | . . . |
Thus,
- 1st shell can hold 2 electrons.
- 2nd shell can hold 8 electrons.
- 3rd shell can hold 18 electrons.
- 4th shell can hold 32 electrons, and so on…
Now the atomic number of Radon (Rn) is 86.
Hence the Radon element has electrons arrangement 2, 8, 18, 32, 18, 8.
This electron arrangement indicates that the outermost orbit of a radon element (Rn) has 8 electrons.
Hence, it lies in group 18.
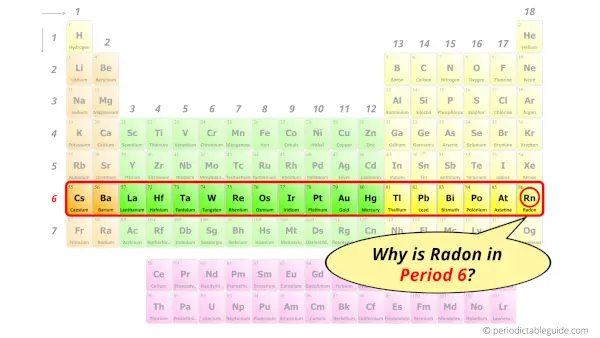
Why is Radon in Period 6?
Let me ask you a question.
How many shells does radon have?
It’s 6. Right?
You have already seen the bohr model of radon atom in the above table.
From the Bohr model, it can be found that the number of orbits or shells in radon is 6. Hence, as radon has 6 orbits, it lies in period 6 of the Periodic table.
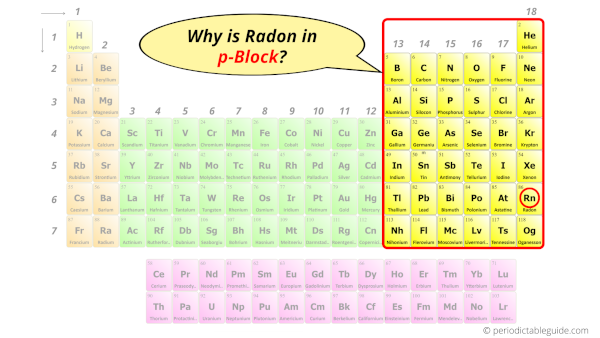
Why is Radon in p-block?
Before knowing this reason, first of all I want to ask you a simple question.
How can you determine the blocks-wise position of elements?
The simple answer: The elements will lie in the s, p, d or f block will completely depend upon the subshell in which the last electron will enter.
For example; the electron configuration of radon is [Xe] 4f14 5d10 6s2 6p6.
So the last electron of radon enters the p-subshell or p-orbital.
Hence, radon is the p-block element.
5 Interesting facts about Radon
Interesting facts about radon element are mentioned below.
- The name “Radon”came from the element “radium”, because radon is obtained by the decay of radium.
- Radon was discovered by Ernest Rutherford and Robert Owens in 1899.
- Radon is naturally available from the decay of radium, uranium and thorium.
- Radon is the heaviest known gas on the periodic table of elements.
- Radon is the 2nd leading cause of lung cancer after smoking. Hence radon is also called a “cancer causing radioactive gas”.
Properties of Radon
The physical and chemical properties of radon element are mentioned below.
Physical properties of Radon
Physical properties of radon are mentioned below.
- Radon is a colorless, odorless and tasteless gas.
- Radon has many isotopes and all those isotopes are radioactive in nature.
- Radon is a colorless gas at room temperature. But when it is cooled below its freezing point, it emits a light that changes from yellow to orange-red.
- The density of radon is 9.73 g/L, which is around 9 times denser than air.
Chemical properties of Radon
Chemical properties of radon are mentioned below.
- Radon is a chemically inert gas, that means it does not easily react with any other elements. However radon shows some chemical reactions under extreme conditions.
- Radon is slightly soluble in organic solvents as well as water.
- According to the National Cancer Institute, everyone breathes in radon everyday. Small amount of radon is harmless, but if a large amount of radon gas is inhaled, then it causes lung cancer because of its radioactive nature.
Free Gift for you: Interactive Periodic Table
Let me tell you how this Interactive Periodic Table will help you in your studies.
1). You can effortlessly find every single detail about the elements from this single Interactive Periodic table.
2). You will get the detailed information about the periodic table which will convert a newbie into pro.
3). You will also get the HD images of the Periodic table (for FREE).
Checkout Interactive Periodic table and download it’s high resolution image now (It’s FREE)
External resources:
- Radon – Element information, properties and uses | Periodic Table. (n.d.). Radon – Element Information, Properties and Uses | Periodic Table. https://www.rsc.org/periodic-table/element/86/radon
- Radon – Wikipedia. (2021, September 1). Radon – Wikipedia. https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Radon
- P. (n.d.). Radon | Rn (Element) – PubChem. Radon | Rn (Element) – PubChem. https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/element/Radon
- It’s Elemental – The Element Radon. (n.d.). It’s Elemental – the Element Radon. https://education.jlab.org/itselemental/ele086.html
- What is Radon? (n.d.). What Is Radon? https://www.michigan.gov/egle/about/organization/materials-management/indoor-radon/what-is-radon
- Radon. (2023, January 25). Radon. https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/radon-and-health