This is a SUPER easy guide on Arsenic element.
In fact, the table mentioned below is the perfect information box (Which gives you every single detail about the Arsenic element in Periodic table.)
So if you want to know anything about Arsenic element, then this guide is for you.
Let’s finish this very quickly.
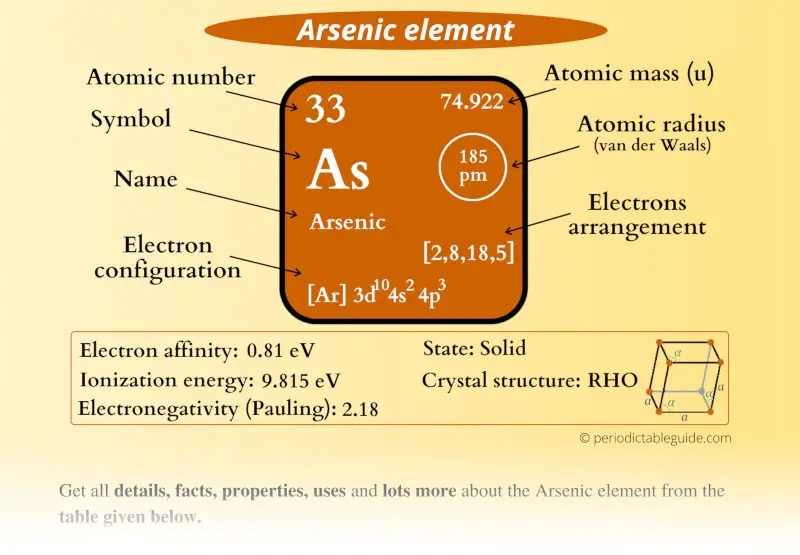
Arsenic Element (As) Information
| Appearance |  Grey metallic surface |
| State (at STP) | Solid |
| Position in Periodic table | 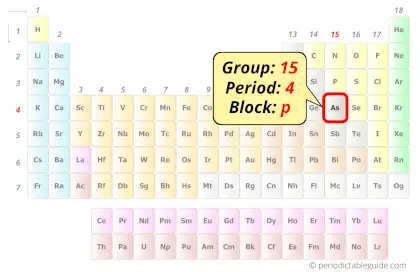 Group: 15, Period: 4, Block: p |
| Category | 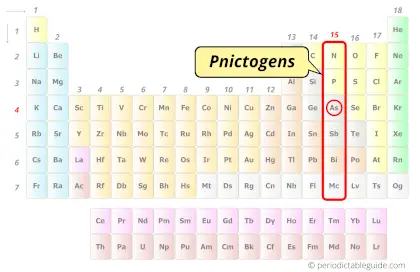 Pnictogens |
| Atomic number or Protons | 33 |
| Neutrons | 42 |
| Electrons | 33 |
| Symbol | As |
| Atomic mass | 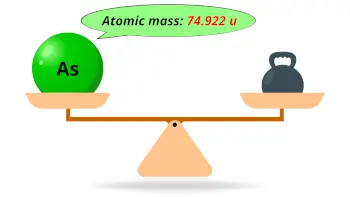 74.922 u |
| Electrons arrangement or Bohr model | 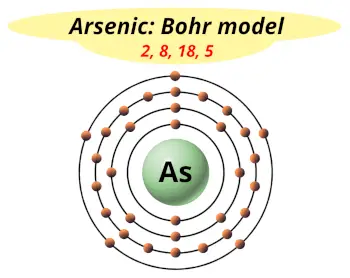 2, 8, 18, 5 |
| Electronic configuration | [Ar] 3d10 4s2 4p3 |
| Atomic radius | 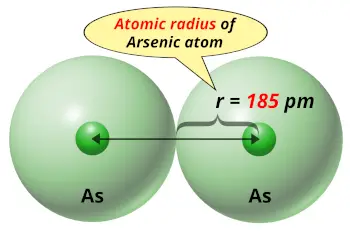 185 picometers (van der Waals radius) |
| Valence electrons | 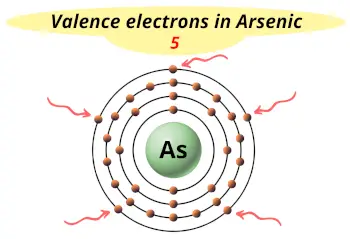 5 |
| 1st Ionization energy | 9.815 eV |
| Electronegativity | 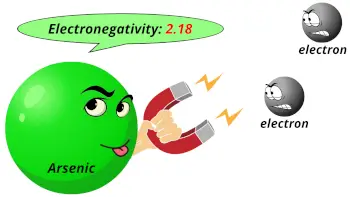 2.18 (Pauling scale) |
| Crystal structure | 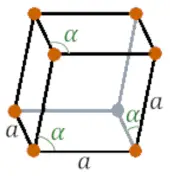 RHO (Rhombohedral) |
| Sublimation point | 887 K or 615 °C or 1137 °F |
| Density | 5.73 g/cm3 |
| Main isotope | 75As |
| CAS number | 7440-38-2 |
Arsenic in Periodic table
Arsenic element is in group 15 and period 4 of the Periodic table. Arsenic is the p-block element and it belongs to Pnictogens group.
| H | He | ||||||||||||||||
| Li | Be | B | C | N | O | F | Ne | ||||||||||
| Na | Mg | Al | Si | P | S | Cl | Ar | ||||||||||
| K | Ca | Sc | Ti | V | Cr | Mn | Fe | Co | Ni | Cu | Zn | Ga | Ge | As | Se | Br | Kr |
| Rb | Sr | Y | Zr | Nb | Mo | Tc | Ru | Rh | Pd | Ag | Cd | In | Sn | Sb | Te | I | Xe |
| Cs | Ba | La* | Hf | Ta | W | Re | Os | Ir | Pt | Au | Hg | Tl | Pb | Bi | Po | At | Rn |
| Fr | Ra | Ac** | Rf | Db | Sg | Bh | Hs | Mt | Ds | Rg | Cn | Nh | Fl | Mc | Lv | Ts | Og |
| *Ce | Pr | Nd | Pm | Sm | Eu | Gd | Tb | Dy | Ho | Er | Tm | Yb | Lu | ||||
| **Th | Pa | U | Np | Pu | Am | Cm | Bk | Cf | Es | Fm | Md | No | Lr |
←Move to: Germanium (Ge) element – Periodic Table
→Move to: Selenium (Se) element – Periodic Table
Why is Arsenic in Group 15?
Do you know, how many electrons can be accommodated in the first shell, second shell, third shell, fourth shell, etc…?
Here is the table showing the capacity of orbits to hold electrons.
Number of electrons in shells.
| Orbit / Shell (n) | Maximum no. of electrons this orbit can hold |
| K shell, n = 1 | 2 × 1² = 2 |
| L shell, n = 2 | 2 × 2² = 8 |
| M shell, n = 3 | 2 × 3² = 18 |
| N shell, n = 4 | 2 × 4² = 32 |
Thus,
- 1st shell can hold 2 electrons.
- 2nd shell can hold 8 electrons.
- 3rd shell can hold 18 electrons.
- 4th shell can hold 32 electrons.
Now the atomic number of arsenic (As) is 33.
Hence the arsenic element has electrons arrangement 2, 8, 18, 5.
This electron arrangement indicates that the outermost orbit of Arsenic element (As) has 5 electrons.
Hence, it lies in group 15.
Why is Arsenic in Period 4?
Let me ask you a question.
How many shells does arsenic have?
It’s 4. Right?
You have already seen the bohr model of arsenic atom in the above table.
From the Bohr model, it can be found that the number of orbits or shells in arsenic is 4. Hence, as arsenic has 4 orbits, it lies in period 4 of the Periodic table.
Why is Arsenic in p-block?
Before knowing this reason, first of all I want to ask you a simple question.
How can you determine the blocks-wise position of elements?
The simple answer: The elements will lie in the s, p, d or f block will completely depend upon the subshell in which the last electron will enter.
For example; the electron configuration of arsenic is [Ar] 3d10 4s2 4p3.
So the last electron of arsenic enters the p-subshell or p-orbital.
Hence, arsenic is the p-block element.
7 Interesting facts about Arsenic
Interesting facts about arsenic element are mentioned below.
- The word “Arsenic” was derived from the Persian word “Zarnikh” which means “yellow orpiment”.
- Arsenic is the 53rd most abundant element found from the earth’s crust.
- In the earth’s crust, the proportion of arsenic by weight is about 1.8 ppm (parts per million).
- On the earth, arsenic is mostly found in the igneous rocks.
- In some countries like India, Taiwan, South America and Pakistan the groundwater flowing over arsenic rich rocks may contain high concentrations of arsenic in it.
- Pure arsenic and its compounds are toxic. Arsenic was used as a poison.
- Arsenic has adverse effects on health that causes damage to organs like the immune system, skin, nervous system, excretory system, etc.
Properties of Arsenic
The physical and chemical properties of arsenic element are mentioned below.
Physical properties of Arsenic
Physical properties of arsenic are mentioned below.
- At standard atmospheric pressure, arsenic directly transforms from solid to gaseous state. This is known as the sublimation process. Arsenic does not come into liquid state at standard atmospheric pressure, but it does exist in a liquid state under high pressures.
- The sublimation point of arsenic at standard atmospheric temperature is 615 °C.
- Arsenic has natural as well as many other radioactive isotopes, but out of them only one isotope is stable (i.e 75As).
- The atomic mass of arsenic is 74.922 u and its density is 5.73 g/cm3.
Chemical properties of Arsenic
Chemical properties of arsenic are mentioned below.
- Arsenic is an element that shows the properties of metals as well as nonmetals. Hence it is classified as a metalloid on the periodic table.
- When arsenic is heated in the presence of air, it gets oxidized and it releases odour similar to that of garlic.
- If arsenic containing minerals are struck hard with a hammer, they release characteristic odour.
- The electron configuration of arsenic is [Ar] 3d10 4s2 4p3, which indicates that the last electron enters the p-orbital. Hence, arsenic is a p-block element.
Uses of Arsenic
Uses of arsenic are mentioned below.
- Grey arsenic is a very good conductor of electricity. Hence it is used in industries.
- Arsenic is used as an alloying metal with lead to form a harder and durable metal.
- Gallium arsenide is a compound of arsenic that is used in lasers which produces light when electric current is passed through it.
- Arsenic is also used as a doping agent in devices like transistors.
- Although arsenic is a poisonous element, it is used in manufacturing insecticides.
- Arsenic is also used to prevent wood degradation by termites and fungus.
- In earlier days, arsenic compounds were used in bronze to increase its hardness.
Explore our New Interactive Periodic Table (with Rotating Bohr Models and More)

Details about this Periodic table:
- Access detailed info on all elements: atomic mass, electron configurations, charges, and more.
- View rotating Bohr models for all 118 elements.
- Get a free HD image of the Periodic Table.
Note: For future use, bookmark this Periodic table or visit “PeriodicTableGuide.com”
External resources:
- Arsenic – Element information, properties and uses | Periodic Table. (n.d.). Arsenic – Element Information, Properties and Uses | Periodic Table. https://www.rsc.org/periodic-table/element/33/arsenic
- P. (n.d.). Arsenic | As (Element) – PubChem. Arsenic | as (Element) – PubChem. https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/element/Arsenic
- Arsenic – Wikipedia. (2018, February 25). Arsenic – Wikipedia. https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Arsenic
- The Facts on Arsenic | Dartmouth Toxic Metals. (n.d.). The Facts on Arsenic | Dartmouth Toxic Metals. https://sites.dartmouth.edu/toxmetal/arsenic/the-facts-on-arsenic/
- What is Arsenic? – Arsenic – University of Maine. (n.d.). What Is Arsenic? – Arsenic – University of Maine. https://umaine.edu/arsenic/what-is-arsenic/
