This is a SUPER easy guide on Sulfur element.
In fact, the table mentioned below is the perfect information box (Which gives you every single detail about the Sulfur element in Periodic table.)
So if you want to know anything about Sulfur element, then this guide is for you.
Let’s finish this very quickly.
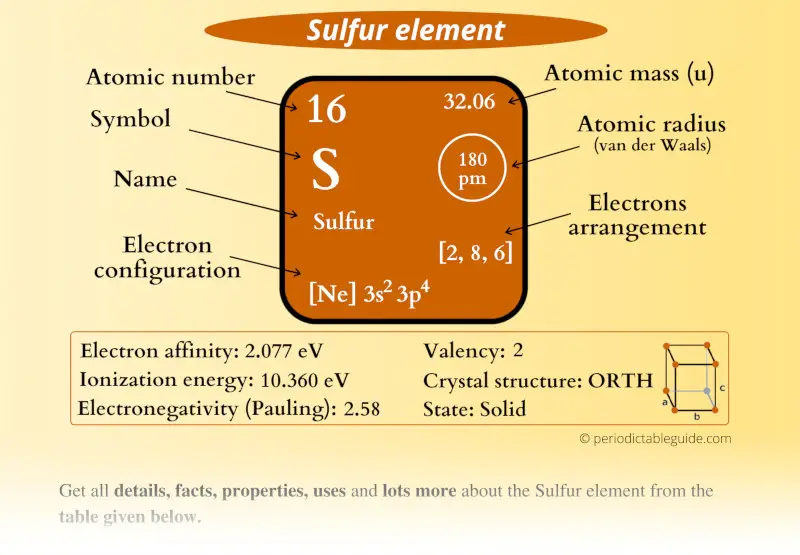
Sulfur Element (S) Information
| Appearance |  Lemon yellow colored |
| State (at STP) | Solid |
| Position in Periodic table | 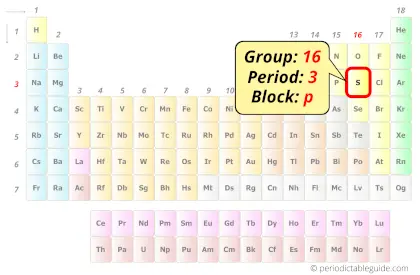 Group: 16, Period: 3, Block: p |
| Category | 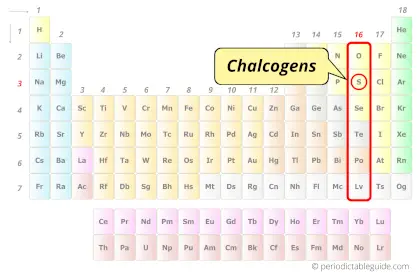 Chalcogens |
| Atomic number or Protons | 16 |
| Neutrons | 16 |
| Electrons | 16 |
| Symbol | S |
| Atomic mass | 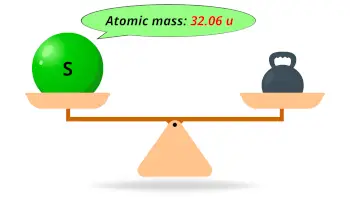 32.06 u |
| Electrons arrangement or Bohr model | 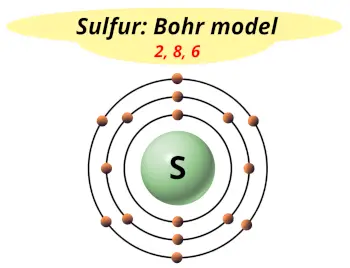 2, 8, 6 |
| Electronic configuration | [Ne] 3s2 3p4 |
| Atomic radius | 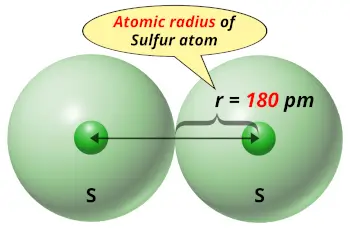 180 picometers (van der Waals radius) |
| Valence electrons | 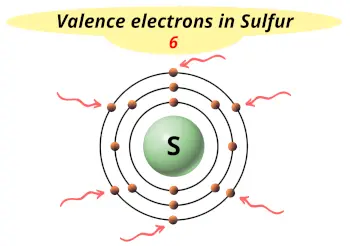 6 |
| 1st Ionization energy | 10.360 eV |
| Electronegativity | 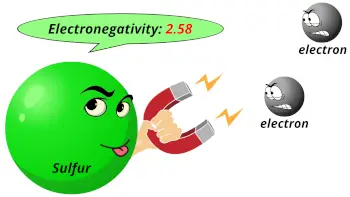 2.58 (Pauling scale) |
| Crystal structure | 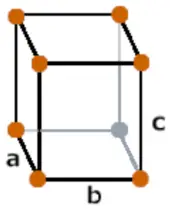 Orthorhombic |
| Melting point | 388.3 K or 115.2 °C or 239.3 °F |
| Boiling point | 717.8 K or 444.6 °C or 832.3 °F |
| Density | 1.96 g/cm3 |
| Main isotope | 32S |
| CAS number | 7704-34-9 |
Sulfur in Periodic table
Sulfur element is in group 16 and period 3 of the Periodic table. Sulfur is the p-block element and it belongs to chalcogens group.
| H | He | ||||||||||||||||
| Li | Be | B | C | N | O | F | Ne | ||||||||||
| Na | Mg | Al | Si | P | S | Cl | Ar | ||||||||||
| K | Ca | Sc | Ti | V | Cr | Mn | Fe | Co | Ni | Cu | Zn | Ga | Ge | As | Se | Br | Kr |
| Rb | Sr | Y | Zr | Nb | Mo | Tc | Ru | Rh | Pd | Ag | Cd | In | Sn | Sb | Te | I | Xe |
| Cs | Ba | La* | Hf | Ta | W | Re | Os | Ir | Pt | Au | Hg | Tl | Pb | Bi | Po | At | Rn |
| Fr | Ra | Ac** | Rf | Db | Sg | Bh | Hs | Mt | Ds | Rg | Cn | Nh | Fl | Mc | Lv | Ts | Og |
| *Ce | Pr | Nd | Pm | Sm | Eu | Gd | Tb | Dy | Ho | Er | Tm | Yb | Lu | ||||
| **Th | Pa | U | Np | Pu | Am | Cm | Bk | Cf | Es | Fm | Md | No | Lr |
←Move to: Phosphorus (P) element – Periodic Table
→Move to: Chlorine (Cl) element – Periodic Table
Why is Sulfur in Group 16?
Do you know, how many electrons can be accommodated in the first shell, second shell, third shell, fourth shell, etc…?
Here is the table showing the capacity of orbits to hold electrons.
Number of electrons in shells.
| Orbit / Shell (n) | Maximum no. of electrons this orbit can hold |
| K shell, n = 1 | 2 × 1² = 2 |
| L shell, n = 2 | 2 × 2² = 8 |
| M shell, n = 3 | 2 × 3² = 18 |
| N shell, n = 4 | 2 × 4² = 32 |
Thus,
- 1st shell can hold 2 electrons.
- 2nd shell can hold 8 electrons.
- 3rd shell can hold 18 electrons.
- 4th shell can hold 32 electrons.
Now the atomic number of sulfur (S) is 16.
Hence the sulfur element has electrons arrangement 2, 8, 6.
This electron arrangement indicates that the outermost orbit of sulfur element (S) has 6 electrons.
Hence, it lies in group 16.
Why is Sulfur in Period 3?
Let me ask you a question.
How many shells does sulfur have?
It’s 3. Right?
You have already seen the bohr model of sulfur element in the above table.
From the Bohr model, it can be found that the number of orbits or shells in sulfur is 3. Hence, as sulfur has 3 orbits, it lies in period 3 of the Periodic table.
Why is Sulfur in p-block?
Before explaining the reason, first of all I want to ask you a simple question.
How can you determine the blocks-wise position of elements?
The simple answer: The elements will lie in the s, p, d or f block will completely depend upon the subshell in which the last electron will enter.
For example; the electron configuration of sulfur is [Ne] 3s2 3p4.
So the last electron of sulfur enters the p-subshell or p-orbital.
Hence, sulfur is the p-block element.
10 Interesting facts about Sulfur
Interesting facts about sulfur element are mentioned below.
- Sulfur is the 10th most abundant element in the entire universe.
- 3% of the earth’s mass is occupied by sulfur.
- Sulfur is one of the few elements that can be found in a pure form.
- Sulfur element is mainly found in volcanoes and it is also present on meteorites.
- Acid rain occurs due to the increase in sulfur dioxide proportion in the atmosphere.
- Sulfur is present in foods as well as the human body.
- Sulfur is present in onions which makes you cry while cutting them.
- Smell of garlic is also due to the presence of sulfur in it.
- Discovery of sulfur is very ancient, so the person behind its discovery is still not known to us.
Properties of Sulfur
The physical and chemical properties of sulfur element are mentioned below.
Physical properties of Sulfur
Physical properties of sulfur are mentioned below.
- Sulfur is a nonmetallic solid element having a lemon yellow color.
- Sulfur turns reddish in color when it is burnt and after that it melts into liquid.
- Pure sulfur has no smell, but the sulfur compounds have strong smells.
- Hydrogen sulphide, which smells like rotten eggs is flammable and poisonous gas.
- The melting point of sulfur is 115.2 °C and its boiling point is 444.6 °C.
- Sulfur has an atomic mass of 32.06 amu and has a density of 1.96 g/cm3.
Chemical properties of Sulfur
Chemical properties of sulfur are mentioned below.
- When sulfur is burnt in the air, it produces blue flame and liberates SO2 gas (which is a pollutant for earth’s atmosphere.)
- Sulfur has variable oxidation states that allows it to form compounds with most other elements except noble gases.
- Sulfur does not dissolve in water but it dissolves in carbon disulphide.
- Sulfur dioxide gas reacts with the moisture of the atmosphere and forms a sulfuric acid, which comes down to the earth as an acid rain.
Uses of Sulfur
Uses of sulfur are mentioned below.
- Sulfur is mainly used in production of sulfuric acid.
- Sulfuric acid is utilized in the manufacturing of fertilizers for plants.
- It is also used in manufacturing of synthetic detergents, dyes and pigments.
- Sulfur is also helpful in making rubber and cement.
- Sulfuric acid is also used in manufacturing of electrical devices (i.e vehicle batteries).
Explore our New Interactive Periodic Table (with Rotating Bohr Models and More)

Details about this Periodic table:
- Access detailed info on all elements: atomic mass, electron configurations, charges, and more.
- View rotating Bohr models for all 118 elements.
- Get a free HD image of the Periodic Table.
Note: For future use, bookmark this Periodic table or visit “PeriodicTableGuide.com”
External resources:
- C&EN: IT’S ELEMENTAL: THE PERIODIC TABLE – SULFUR. (n.d.). C&EN: IT’S ELEMENTAL: THE PERIODIC TABLE – SULFUR. https://pubsapp.acs.org/cen/80th/sulfur.html?
- Sulfur General Fact Sheet. (2017, May 1). Sulfur General Fact Sheet. http://npic.orst.edu/factsheets/sulfurgen.html
- Sulfur – Energy Education. (n.d.). Sulfur – Energy Education. https://energyeducation.ca/encyclopedia/Sulfur
- P. (n.d.). Sulfur | S (Element) – PubChem. Sulfur | S (Element) – PubChem. https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/element/Sulfur
- It’s Elemental – The Element Sulfur. (n.d.). It’s Elemental – the Element Sulfur. https://education.jlab.org/itselemental/ele016.html
