This is a SUPER easy guide on Strontium element.
In fact, the table mentioned below is the perfect information box (Which gives you every single detail about the Strontium element in Periodic table.)
So if you want to know anything about Strontium element, then this guide is for you.
Let’s dive right into it!
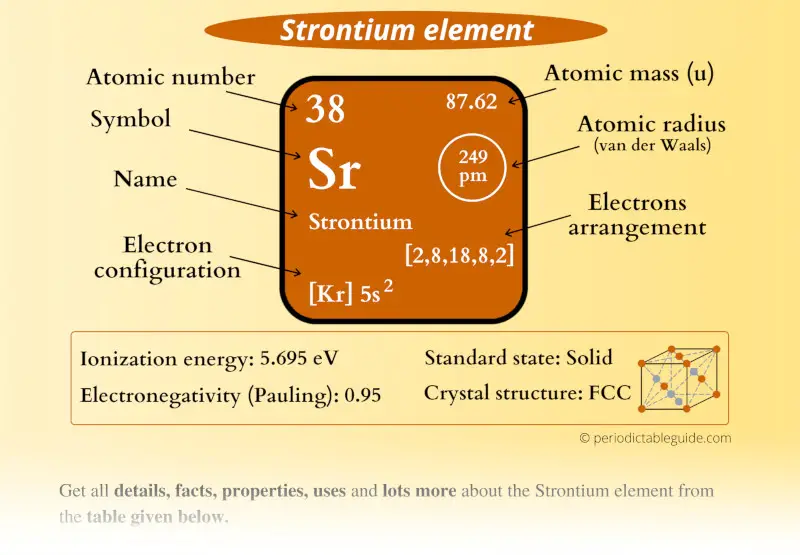
Strontium Element (Sr) Information
| Appearance |  Silvery metallic surface with yellow tint |
| State (at STP) | Solid |
| Position in Periodic table | 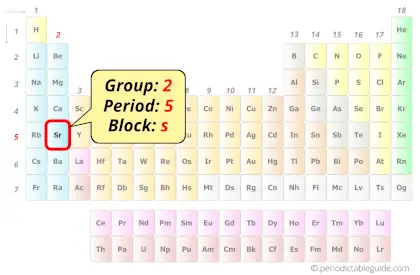 Group: 2, Period: 5, Block: s |
| Category | 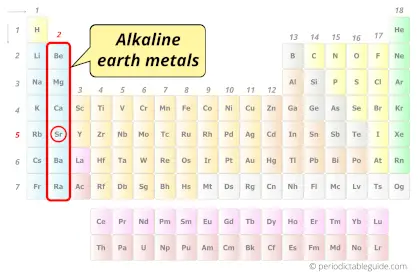 Alkaline earth metals |
| Atomic number or Protons | 38 |
| Neutrons | 50 |
| Electrons | 38 |
| Symbol | Sr |
| Atomic mass |  87.62 u |
| Electrons arrangement or Bohr model | 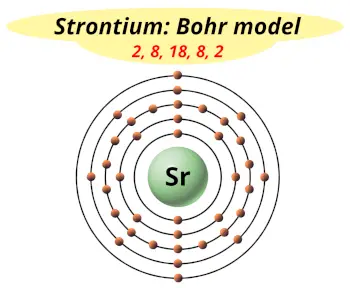 2, 8, 18, 8, 2 |
| Electronic configuration | [Kr] 5s2 |
| Atomic radius | 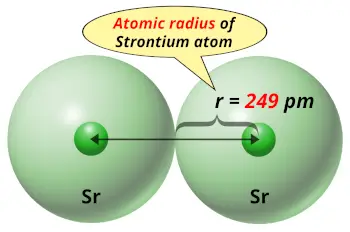 249 picometers (van der Waals radius) |
| Valence electrons | 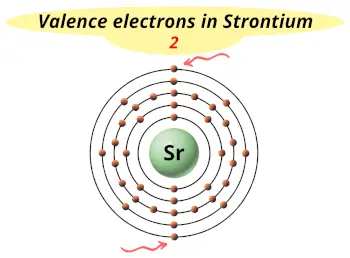 2 |
| 1st Ionization energy | 5.695 eV |
| Electronegativity | 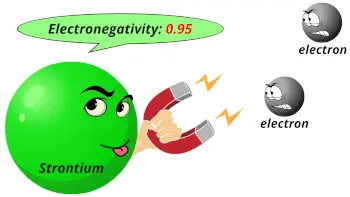 0.95 (Pauling scale) |
| Crystal structure | 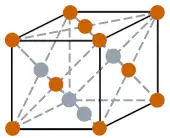 FCC (Face centered cubic) |
| Melting point | 1050 K or 777 °C or 1431 °F |
| Boiling point | 1650 K or 1377 °C or 2511 °F |
| Density | 2.63 g/cm3 |
| Main isotope | 88Sr |
| Who discovered Strontium and when? |  William Cruickshank in 1787 |
| CAS number | 7440-24-6 |
Strontium in Periodic table
Strontium element is in group 2 and period 5 of the Periodic table. Strontium is the s-block element and it belongs to alkaline earth metals group.
| H | He | ||||||||||||||||
| Li | Be | B | C | N | O | F | Ne | ||||||||||
| Na | Mg | Al | Si | P | S | Cl | Ar | ||||||||||
| K | Ca | Sc | Ti | V | Cr | Mn | Fe | Co | Ni | Cu | Zn | Ga | Ge | As | Se | Br | Kr |
| Rb | Sr | Y | Zr | Nb | Mo | Tc | Ru | Rh | Pd | Ag | Cd | In | Sn | Sb | Te | I | Xe |
| Cs | Ba | La* | Hf | Ta | W | Re | Os | Ir | Pt | Au | Hg | Tl | Pb | Bi | Po | At | Rn |
| Fr | Ra | Ac** | Rf | Db | Sg | Bh | Hs | Mt | Ds | Rg | Cn | Nh | Fl | Mc | Lv | Ts | Og |
| *Ce | Pr | Nd | Pm | Sm | Eu | Gd | Tb | Dy | Ho | Er | Tm | Yb | Lu | ||||
| **Th | Pa | U | Np | Pu | Am | Cm | Bk | Cf | Es | Fm | Md | No | Lr |
←Move to: Rubidium (Rb) element – Periodic Table
→Move to: Yttrium (Y) element – Periodic Table
Why is Strontium in Group 2?
Do you know, how many electrons can be accommodated in the first shell, second shell, third shell, fourth shell, etc…?
Here is the table showing the capacity of orbits to hold electrons.
Number of electrons in shells.
| Orbit / Shell (n) | Maximum no. of electrons this orbit can hold (2 × n2) |
| K shell, n = 1 | 2 × 1² = 2 |
| L shell, n = 2 | 2 × 2² = 8 |
| M shell, n = 3 | 2 × 3² = 18 |
| N shell, n = 4 | 2 × 4² = 32 |
| . . . | . . . |
Thus,
- 1st shell can hold 2 electrons.
- 2nd shell can hold 8 electrons.
- 3rd shell can hold 18 electrons.
- 4th shell can hold 32 electrons, and so on.
Now the atomic number of strontium (Sr) is 38.
Hence the electron arrangement in strontium is 2, 8, 18, 8, 2. And the electron configuration of strontium is 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6 3d10 4s2 4p6 5s2.
This electron arrangement and electron configuration indicates that the outermost orbit (i.e orbit number 5) of strontium atom has 2 electrons.
Hence, it lies in group 2.
Why is Strontium in Period 5?
Let me ask you a question.
How many shells does strontium have?
It’s 5. Right?
You have already seen the bohr model of strontium atom in the above table.
From the Bohr model, it can be found that the number of orbits or shells in strontium is 5. Hence, as strontium has 5 orbits, it lies in period 5 of the Periodic table.
Why is Strontium in s-block?
Before knowing this reason, first of all I want to ask you a simple question.
How can you determine the blocks-wise position of elements?
The simple answer: The elements will lie in the s, p, d or f block will completely depend upon the subshell in which the last electron will enter.
For example; the electron configuration of strontium is [Kr] 5s2.
So the last electron of strontium enters the s-subshell or s-orbital.
Hence, strontium is the s-block element.
8 Interesting facts about Strontium
Interesting facts about strontium element are mentioned below.
- Strontium is mostly obtained from the earth’s crust and it is the 15th most abundant element found from the earth’s crust.
- Amount of strontium present in earth’s crust is around 360 ppm (parts per million).
- China and Spain are the leading producers of strontium in the world.
- In the entire world, approximately 3 lakh tons of strontium is produced annually.
- Most of the strontium metal is extracted from its ore strontianite and celestite.
- Strontium is reactive even in the open atmosphere. Hence it is kept under kerosene or mineral oil.
- Strontium is classified as an “Alkaline earth metal” on the periodic table as it forms an alkaline solution on reacting with water, plus strontium is obtained from the earth.
- The nonradioactive isotopes of strontium are non-toxic.
Properties of Strontium
The physical and chemical properties of strontium element are mentioned below.
Physical properties of Strontium
Physical properties of strontium are mentioned below.
- Strontium is a soft metal having a silvery metallic surface with yellow tint.
- The atomic mass of strontium is 87.62 u and its density is 2.63 g/cm3.
- The melting point of strontium is 777 °C and its boiling point is 1377 °C.
- Strontium has many isotopes including stable isotopes as well as radioactive isotopes. Out of them, 88Sr is the most abundant (around 82.5 %).
Chemical properties of Strontium
Chemical properties of strontium are mentioned below.
- Strontium is a reactive chemical element, and hence it is not found in a free state in nature. But it is always found as a compound with other elements.
- When strontium reacts with water, it forms strontium hydroxide and liberates hydrogen gas.
- If strontium is exposed to air, it burns with a bright red flame.
Uses of Strontium
Uses of strontium are mentioned below.
- As strontium burns with a bright red light, it is used in fireworks as well as flares.
- Strontium chloride hexahydrate is a compound containing strontium that is used in toothpaste for sensitive teeth.
- Strontium titanate has a very high refractive index and hence it is used in gemstones also.
- Strontium aluminate glows in dark, hence it is also used in toys that glow in dark.
- Strontium has various radioactive isotopes. Out of them, 89Sr is used to treat bone cancer.
Explore our New Interactive Periodic Table (with Rotating Bohr Models and More)

Details about this Periodic table:
- Access detailed info on all elements: atomic mass, electron configurations, charges, and more.
- View rotating Bohr models for all 118 elements.
- Get a free HD image of the Periodic Table.
Note: For future use, bookmark this Periodic table or visit “PeriodicTableGuide.com”
External resources:
- Strontium – Wikipedia. (2022, December 7). Strontium – Wikipedia. https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Strontium
- Strontium – Element information, properties and uses | Periodic Table. (n.d.). Strontium – Element Information, Properties and Uses | Periodic Table. https://www.rsc.org/periodic-table/element/38/strontium
- It’s Elemental – The Element Strontium. (n.d.). It’s Elemental – the Element Strontium. https://education.jlab.org/itselemental/ele038.html
- P. (n.d.). Strontium | Sr (Element) – PubChem. Strontium | Sr (Element) – PubChem. https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/element/Strontium
