This is a SUPER easy guide on Neptunium element.
In fact, the table mentioned below is the perfect information box (Which gives you every single detail about the Neptunium element in Periodic table.)
So if you want to know anything about Neptunium element, then this guide is for you.
Let’s finish this very quickly.
Neptunium Element (Np) Information
| Appearance | Silvery metallic appearance |
| State (at STP) | Solid |
| Position in Periodic table |  Group: actinides, Period: 7, Block: f |
| Category | 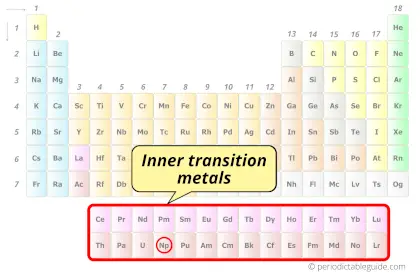 Inner transition metals |
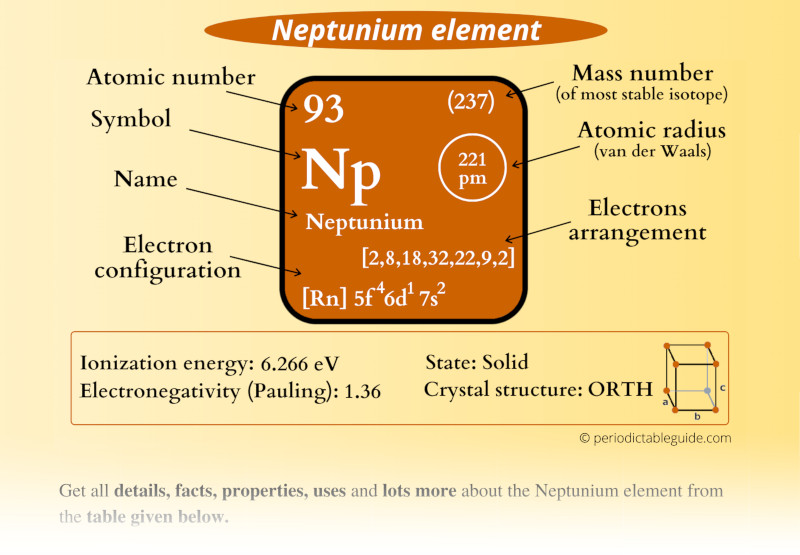
| Atomic number or Protons | 93 |
| Neutrons | 144 |
| Electrons | 93 |
| Symbol | Np |
| Atomic mass of Neptunium (most stable isotope) | 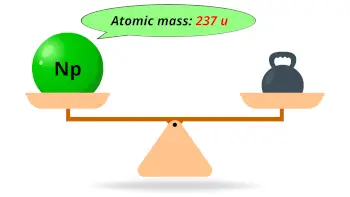 237 u |
| Electrons arrangement or Bohr model | 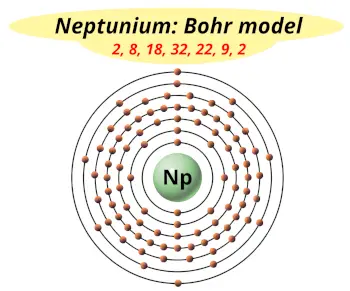 2, 8, 18, 32, 22, 9, 2 |
| Electronic configuration | [Rn] 5f4 6d1 7s2 |
| Atomic radius | 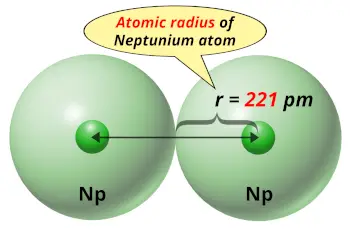 221 picometers (van der Waals radius) |
| 1st Ionization energy | 6.266 eV |
| Electronegativity | 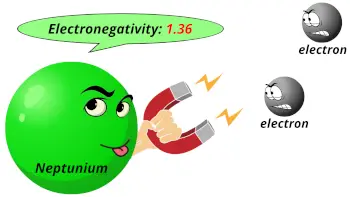 1.36 (Pauling scale) |
| Crystal structure | 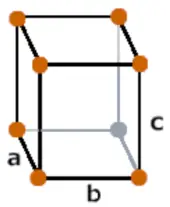 Orthorhombic |
| Density | 20.45 g/cm3 |
| Main isotope | 237Np |
| Who discovered Neptunium and when? | Edwin McMillan and Philip Abelson (in 1940) |
| CAS number | 7439-99-8 |
Neptunium in Periodic table
Neptunium element is in period 7 and in actinides group of the Periodic table. Neptunium is the f-block element and it belongs to inner transition metals group.
| H | He | ||||||||||||||||
| Li | Be | B | C | N | O | F | Ne | ||||||||||
| Na | Mg | Al | Si | P | S | Cl | Ar | ||||||||||
| K | Ca | Sc | Ti | V | Cr | Mn | Fe | Co | Ni | Cu | Zn | Ga | Ge | As | Se | Br | Kr |
| Rb | Sr | Y | Zr | Nb | Mo | Tc | Ru | Rh | Pd | Ag | Cd | In | Sn | Sb | Te | I | Xe |
| Cs | Ba | La* | Hf | Ta | W | Re | Os | Ir | Pt | Au | Hg | Tl | Pb | Bi | Po | At | Rn |
| Fr | Ra | Ac** | Rf | Db | Sg | Bh | Hs | Mt | Ds | Rg | Cn | Nh | Fl | Mc | Lv | Ts | Og |
| *Ce | Pr | Nd | Pm | Sm | Eu | Gd | Tb | Dy | Ho | Er | Tm | Yb | Lu | ||||
| **Th | Pa | U | Np | Pu | Am | Cm | Bk | Cf | Es | Fm | Md | No | Lr |
←Move to: Uranium (U) element – Periodic Table
→Move to: Plutonium (Pu) element – Periodic Table
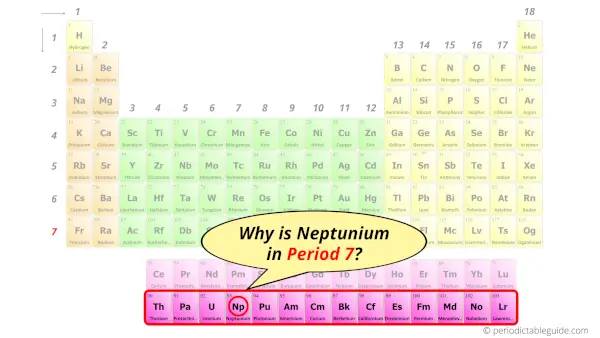
Why is Neptunium in Period 7?
Let me ask you a question.
How many shells does neptunium have?
It’s 7. Right?
You have already seen the bohr model of neptunium atom in the above table.
From the Bohr model, it can be found that the number of orbits or shells in neptunium is 7. Hence, as neptunium has 7 orbits, it lies in period 7 of the Periodic table.
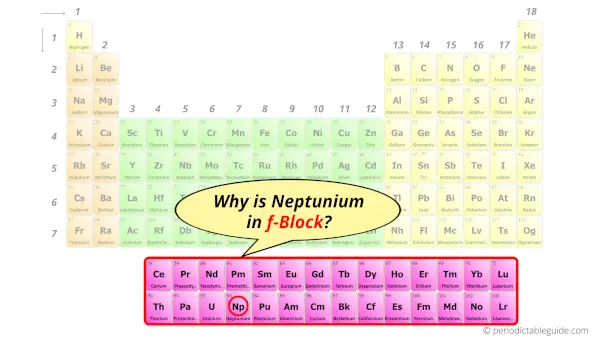
Why is Neptunium in f-block?
Before knowing this reason, first of all I want to ask you a simple question.
How can you determine the blocks-wise position of elements?
The simple answer: The elements will lie in the s, p, d or f block will completely depend upon the subshell in which the last electron will enter.
For example; the electron configuration of neptunium is [Rn] 5f4 6d1 7s2.
So the last electron of neptunium enters the f-subshell or f-orbital.
Hence, neptunium is the f-block element.
6 Interesting facts about Neptunium
Interesting facts about neptunium element are mentioned below.
- The name “Neptunium” came from the name of the planet “Neptune”.
- Neptunium was discovered by Edwin McMillan and Philip Abelson in 1940.
- Neptunium is the 5th most dense element on the periodic table.
- All the isotopes of neptunium are radioactive in nature. Out of all these radioactive isotopes, the isotope 237Np has the longest half-life (around 2.14 million years).
- Neptunium is a radioactive as well as dangerous element.
- Once it was believed that neptunium could only be made artificially in the lab. But few traces of naturally occurring neptunium also exist in uranium ores.
Properties of Neptunium
The physical and chemical properties of neptunium element are mentioned below.
Physical properties of Neptunium
Physical properties of neptunium are mentioned below.
- Neptunium is a solid metal having a silvery metallic appearance.
- The atomic mass of the most stable isotope of neptunium is 237 u and its density is 20.45 g/cm3.
- The crystal structure of neptunium is Orthorhombic.
- Neptunium is the element of actinide series of periodic table, which means it has a higher atomic size. Its van der Waals atomic radius is 221 picometers.
Chemical properties of Neptunium
Chemical properties of neptunium are mentioned below.
- When neptunium is exposed to air, it reacts with the oxygen of the air and forms a thin layer of oxide on it.
- The most common oxidation state of neptunium is +5. But it also shows other oxidation states ranging from +3 to +7.
- The electron configuration of neptunium is [Rn] 5f4 6d1 7s2, in which the last electron enters the f-orbital. Hence it is classified as f-block element.
Uses of Neptunium
The uses of neptunium are mentioned below.
- Neptunium is generally used for research work in chemistry. Neptunium has no commercial uses due to its radioactive nature and scarcity.
- Neptunium can be used to produce plutonium which can be used in spacecraft generators.
- Neptunium can also be used as a device that can detect high energy neutrons.
- Neptunium is also used in making alloys that are generally used to study magnetism and electrical conductivity.
Free Gift for you: Interactive Periodic Table
Let me tell you how this Interactive Periodic Table will help you in your studies.
1). You can effortlessly find every single detail about the elements from this single Interactive Periodic table.
2). You will get the detailed information about the periodic table which will convert a newbie into pro.
3). You will also get the HD images of the Periodic table (for FREE).
Checkout Interactive Periodic table and download it’s high resolution image now (It’s FREE)
External resources:
- Neptunium – Element information, properties and uses | Periodic Table. (n.d.). Neptunium – Element Information, Properties and Uses | Periodic Table. https://www.rsc.org/periodic-table/element/93/neptunium
- Neptunium – Wikipedia. (2014, August 6). Neptunium – Wikipedia. https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Neptunium
- It’s Elemental – The Element Neptunium. (n.d.). It’s Elemental – the Element Neptunium. https://education.jlab.org/itselemental/ele093.html
- P. (n.d.). Neptunium | Np (Element) – PubChem. Neptunium | Np (Element) – PubChem. https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/element/Neptunium
- Atomic Data for Neptunium (Np). (n.d.). Atomic Data for Neptunium (Np). https://physics.nist.gov/PhysRefData/Handbook/Tables/neptuniumtable1.htm
- C&EN: IT’S ELEMENTAL: THE PERIODIC TABLE – NEPTUNIUM. (n.d.). C&EN: IT’S ELEMENTAL: THE PERIODIC TABLE – NEPTUNIUM. https://pubsapp.acs.org/cen/80th/neptunium.html?
- D. (2005, November 29). Getting the Neptunium out of Nuclear Waste – Berkeley Lab. Berkeley Lab News Center. https://newscenter.lbl.gov/2005/11/29/getting-the-neptunium-out-of-nuclear-waste/