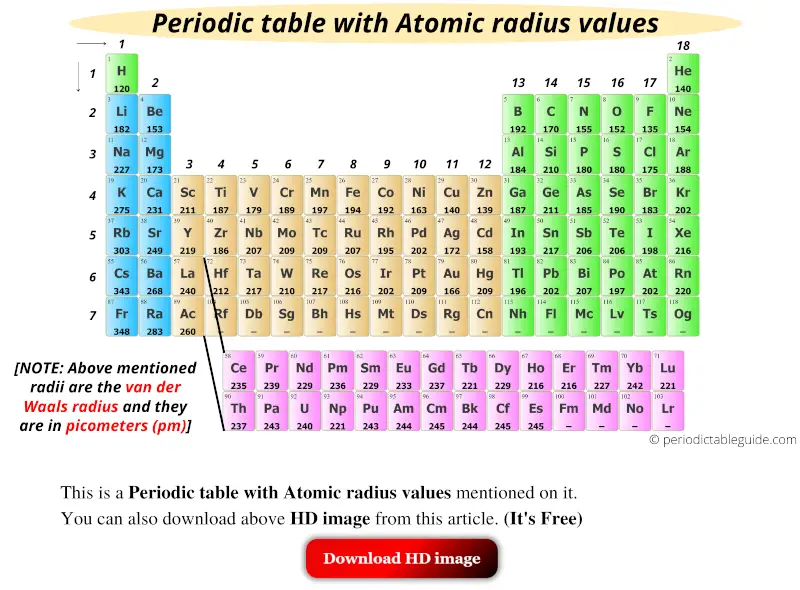
Here is an image of Periodic table with atomic radius values.
You can also download the HD image of the above Periodic table with atomic size, later from this article. (It’s Free)
Plus I have also mentioned the Atomic radius chart for elements in this article. (You can download this too)
But before that…
I have few questions for you.
- Do you really know what exactly is the atomic radius?
- What is that picometer (pm) written on the Periodic table?
- Which is the smallest atom in Periodic table?
- Which is the largest atom in Periodic table?
I’ll clear all these doubts,
Now let me finish few concepts very quickly.
What exactly is the Atomic radius in Periodic table?
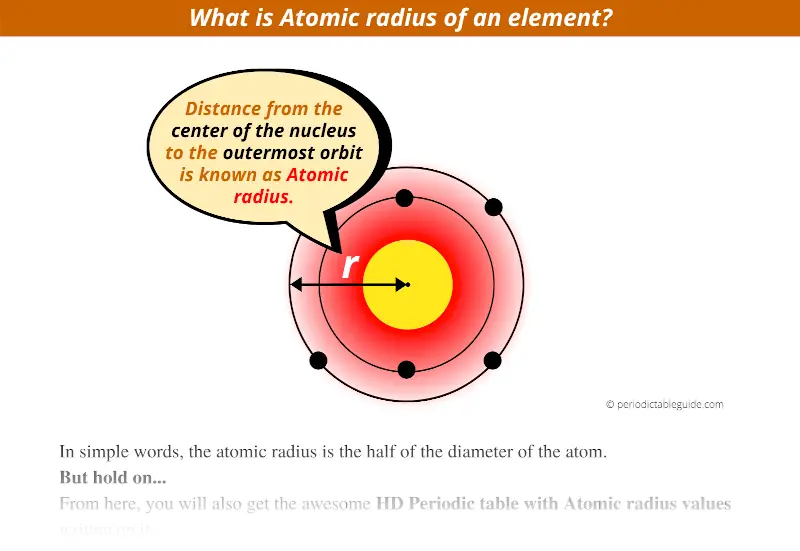
In simple words, the distance from the center of the nucleus to the outermost orbit is known as atomic radius.
Or
The atomic radius is the half of the diameter of the atom.
How is atomic radius measured?
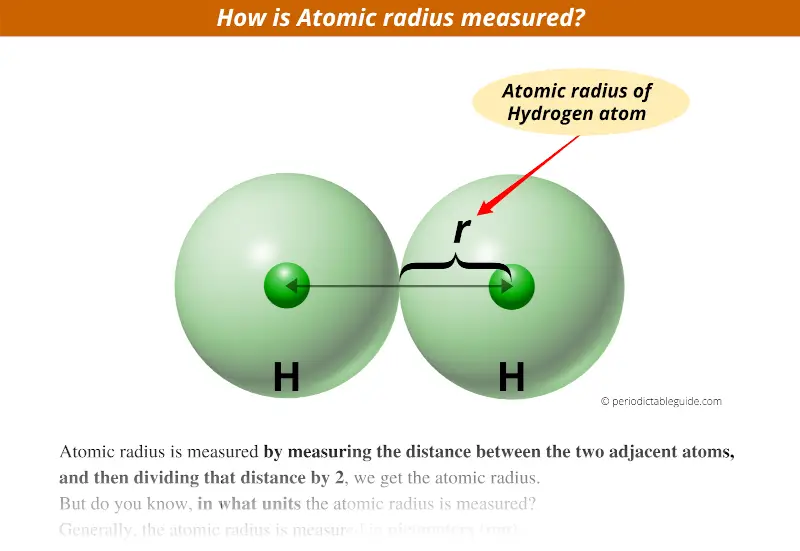
Atomic radius is measured by measuring the distance between the two adjacent atoms, and then dividing that distance by 2, we get the atomic radius.
Above image clearly shows you how the atomic radius is measured.
As you can see that the distance between two adjacent Hydrogen atoms is measured and then its half value will give you the atomic radius of that Atom.
Atomic radius is measured in…?
Picometers (pm).
Generally, the atomic radius is measured in picometers (pm).
1 pm = 10-12 m
1 picometer is equal to 10-12 meters.
Very small, isn’t it?
Yes, the atoms are very small in size. You can imagine the relative atomic size in Periodic table from the below image.
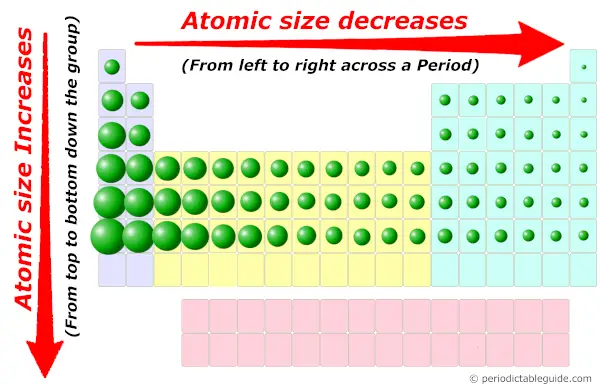
Must see: Atomic size trend in Periodic table (where you will come to know why and how the size of atoms changes across a period and along a group)
Now let’s see the atomic radius chart for elements of Periodic table.
Atomic radius chart for elements
The list of Atomic radius of elements in periodic table is mentioned below.
| Atomic no. | Element | Atomic radius / Atomic size (pm) |
| 1 | Hydrogen (H) | 120 |
| 2 | Helium (He) | 140 |
| 3 | Lithium (Li) | 182 |
| 4 | Beryllium (Be) | 153 |
| 5 | Boron (B) | 192 |
| 6 | Carbon (C) | 170 |
| 7 | Nitrogen (N) | 155 |
| 8 | Oxygen (O) | 152 |
| 9 | Fluorine (F) | 135 |
| 10 | Neon (Ne) | 154 |
| 11 | Sodium (Na) | 227 |
| 12 | Magnesium (Mg) | 173 |
| 13 | Aluminum (Al) | 184 |
| 14 | Silicon (Si) | 210 |
| 15 | Phosphorus (P) | 180 |
| 16 | Sulfur (S) | 180 |
| 17 | Chlorine (Cl) | 175 |
| 18 | Argon (Ar) | 188 |
| 19 | Potassium (K) | 275 |
| 20 | Calcium (Ca) | 231 |
| 21 | Scandium (Sc) | 211 |
| 22 | Titanium (Ti) | 187 |
| 23 | Vanadium (V) | 179 |
| 24 | Chromium (Cr) | 189 |
| 25 | Manganese (Mn) | 197 |
| 26 | Iron (Fe) | 194 |
| 27 | Cobalt (Co) | 192 |
| 28 | Nickel (Ni) | 163 |
| 29 | Copper (Cu) | 140 |
| 30 | Zinc (Zn) | 139 |
| 31 | Gallium (Ga) | 187 |
| 32 | Germanium (Ge) | 211 |
| 33 | Arsenic (As) | 185 |
| 34 | Selenium (Se) | 190 |
| 35 | Bromine (Br) | 183 |
| 36 | Krypton (Kr) | 202 |
| 37 | Rubidium (Rb) | 303 |
| 38 | Strontium (Sr) | 249 |
| 39 | Yttrium (Y) | 219 |
| 40 | Zirconium (Zr) | 186 |
| 41 | Niobium (Nb) | 207 |
| 42 | Molybdenum (Mo) | 209 |
| 43 | Technetium (Tc) | 209 |
| 44 | Ruthenium (Ru) | 207 |
| 45 | Rhodium (Rh) | 195 |
| 46 | Palladium (Pd) | 202 |
| 47 | Silver (Ag) | 172 |
| 48 | Cadmium (Cd) | 158 |
| 49 | Indium (In) | 193 |
| 50 | Tin (Sn) | 217 |
| 51 | Antimony (Sb) | 206 |
| 52 | Tellurium (Te) | 206 |
| 53 | Iodine (I) | 198 |
| 54 | Xenon (Xe) | 216 |
| 55 | Caesium (Cs) | 343 |
| 56 | Barium (Ba) | 268 |
| 57 | Lanthanum (La) | 240 |
| 58 | Cerium (Ce) | 235 |
| 59 | Praseodymium (Pr) | 239 |
| 60 | Neodymium (Nd) | 229 |
| 61 | Promethium (Pm) | 236 |
| 62 | Samarium (Sm) | 229 |
| 63 | Europium (Eu) | 233 |
| 64 | Gadolinium (Gd) | 237 |
| 65 | Terbium (Tb) | 221 |
| 66 | Dysprosium (Dy) | 229 |
| 67 | Holmium (Ho) | 216 |
| 68 | Erbium (Er) | 216 |
| 69 | Thulium (Tm) | 227 |
| 70 | Ytterbium (Yb) | 242 |
| 71 | Lutetium (Lu) | 221 |
| 72 | Hafnium (Hf) | 212 |
| 73 | Tantalum (Ta) | 217 |
| 74 | Tungsten (W) | 210 |
| 75 | Rhenium (Re) | 217 |
| 76 | Osmium (Os) | 216 |
| 77 | Iridium (Ir) | 202 |
| 78 | Platinum (Pt) | 209 |
| 79 | Gold (Au) | 166 |
| 80 | Mercury (Hg) | 209 |
| 81 | Thallium (Tl) | 196 |
| 82 | Lead (Pb) | 202 |
| 83 | Bismuth (Bi) | 207 |
| 84 | Polonium (Po) | 197 |
| 85 | Astatine (At) | 202 |
| 86 | Radon (Rn) | 220 |
| 87 | Francium (Fr) | 348 |
| 88 | Radium (Ra) | 283 |
| 89 | Actinium (Ac) | 260 |
| 90 | Thorium (Th) | 237 |
| 91 | Protactinium (Pa) | 243 |
| 92 | Uranium (U) | 240 |
| 93 | Neptunium (Np) | 221 |
| 94 | Plutonium (Pu) | 243 |
| 95 | Americium (Am) | 244 |
| 96 | Curium (Cm) | 245 |
| 97 | Berkelium (Bk) | 244 |
| 98 | Californium (Cf) | 245 |
| 99 | Einsteinium (Es) | 245 |
| 100 | Fermium (Fm) | – |
| 101 | Mendelevium (Md) | – |
| 102 | Nobelium (No) | – |
| 103 | Lawrencium (Lr) | – |
| 104 | Rutherfordium (Rf) | – |
| 105 | Dubnium (Db) | – |
| 106 | Seaborgium (Sg) | – |
| 107 | Bohrium (Bh) | – |
| 108 | Hassium (Hs) | – |
| 109 | Meitnerium (Mt) | – |
| 110 | Darmstadtium (Ds) | – |
| 111 | Roentgenium (Rg) | – |
| 112 | Copernicium (Cn) | – |
| 113 | Nihonium (Nh) | – |
| 114 | Flerovium (Fl) | – |
| 115 | Moscovium (Mc) | – |
| 116 | Livermorium (Lv) | – |
| 117 | Tennessine (Ts) | – |
| 118 | Oganesson (Og) | – |
(Note: Above mentioned radii are the van der Waals radius.)
I hope this article has helped you in solving your problem.
If you have any questions, then ask me in the comments below.
Also let me know, have you downloaded the HD image or not?
Explore our New Interactive Periodic Table (with Rotating Bohr Models and More)

Details about this Periodic table:
- Access detailed info on all elements: atomic mass, electron configurations, charges, and more.
- View rotating Bohr models for all 118 elements.
- Get a free HD image of the Periodic Table.
Note: For future use, bookmark this Periodic table or visit “PeriodicTableGuide.com”
Suggested Important articles for you:
- Periodic table of elements (Detailed guide + HD image)
- Periodic table with metals
- Periodic table with nonmetals
- Periodic table with metalloids
- Periodic table with halogens
- Periodic table with noble gases
- Periodic table showing alkali metals
- Periodic table showing alkaline earth metals
- Periodic table with transition metals
- Periodic table with inner transition metals
- All Periodic trends in periodic table
