This is a SUPER easy guide on the Holmium element.
In fact, the table mentioned below is the perfect information box (Which gives you every single detail about the Holmium element in Periodic table.)
So if you want to know anything about Holmium element, then this guide is for you.
Let’s dive right into it!
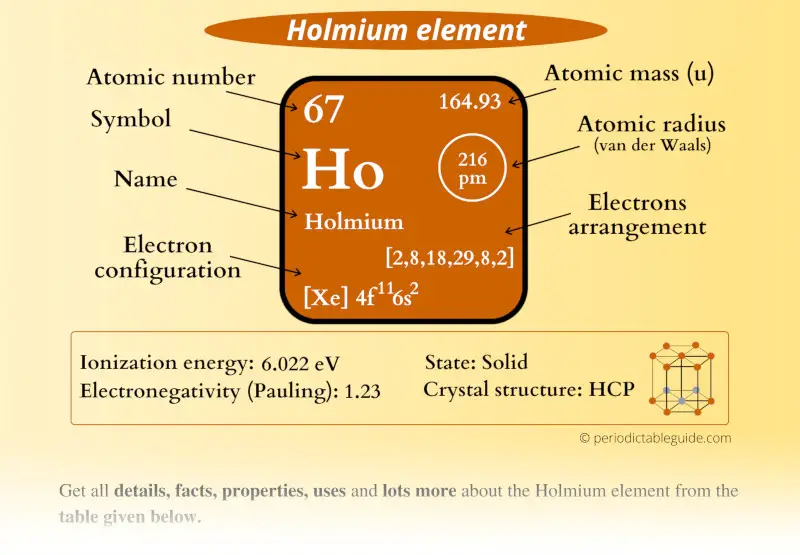
Holmium Element (Ho) Information
| Appearance |  Silvery white metallic |
| State (at STP) | Solid |
| Position in Periodic table | 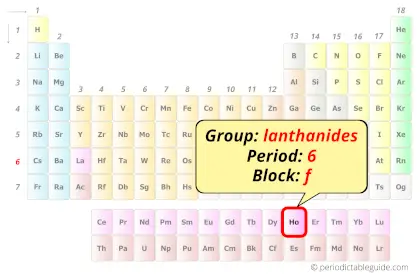 Group: lanthanides, Period: 6, Block: f |
| Category | 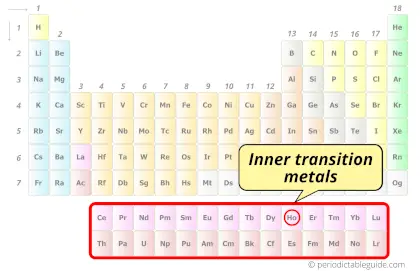 Inner transition metals |
| Atomic number or Protons | 67 |
| Neutrons | 98 |
| Electrons | 67 |
| Symbol | Ho |
| Atomic mass |  164.93 u |
| Electrons arrangement or Bohr model | 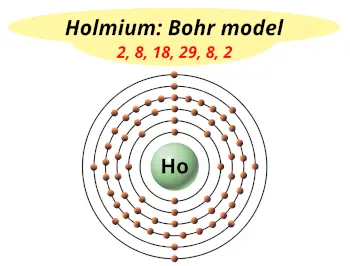 2, 8, 18, 29, 8, 2 |
| Electronic configuration | [Xe] 4f11 6s2 |
| Atomic radius | 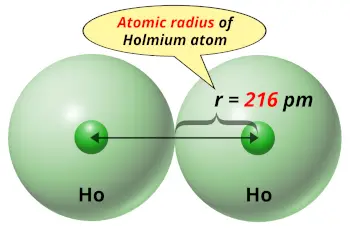 216 picometers (van der Waals radius) |
| 1st Ionization energy | 6.022 eV |
| Electronegativity |  1.23 (Pauling scale) |
| Crystal structure | 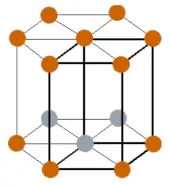 HCP (Hexagonal close packed) |
| Melting point | 1734 K or 1461 °C or 2662 °F |
| Boiling point | 2873 K or 2600 °C or 4712 °F |
| Density | 8.8 g/cm3 |
| Main isotope | 165Ho |
| Who discovered Holmium and when? | 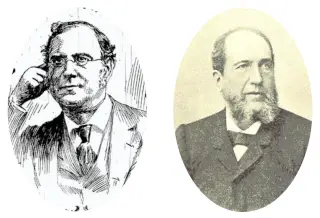 Marc Delafontaine and Jacques Louis Soret (in 1878) |
| CAS number | 7440-60-0 |
Holmium in Periodic table
Holmium element is in period 6 and in lanthanide group of the Periodic table. Holmium is the f-block element and it belongs to inner transition metals group.
| H | He | ||||||||||||||||
| Li | Be | B | C | N | O | F | Ne | ||||||||||
| Na | Mg | Al | Si | P | S | Cl | Ar | ||||||||||
| K | Ca | Sc | Ti | V | Cr | Mn | Fe | Co | Ni | Cu | Zn | Ga | Ge | As | Se | Br | Kr |
| Rb | Sr | Y | Zr | Nb | Mo | Tc | Ru | Rh | Pd | Ag | Cd | In | Sn | Sb | Te | I | Xe |
| Cs | Ba | La* | Hf | Ta | W | Re | Os | Ir | Pt | Au | Hg | Tl | Pb | Bi | Po | At | Rn |
| Fr | Ra | Ac** | Rf | Db | Sg | Bh | Hs | Mt | Ds | Rg | Cn | Nh | Fl | Mc | Lv | Ts | Og |
| *Ce | Pr | Nd | Pm | Sm | Eu | Gd | Tb | Dy | Ho | Er | Tm | Yb | Lu | ||||
| **Th | Pa | U | Np | Pu | Am | Cm | Bk | Cf | Es | Fm | Md | No | Lr |
←Move to: Dysprosium (Dy) element – Periodic Table
→Move to: Erbium (Er) element – Periodic Table
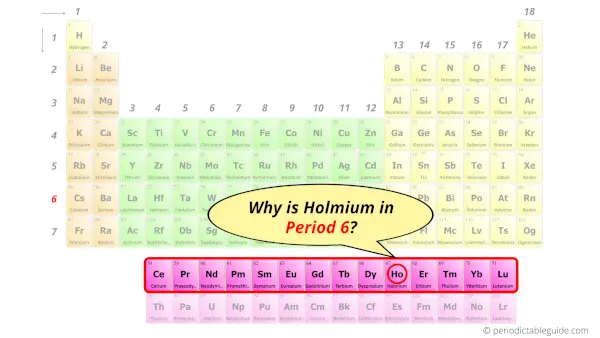
Why is Holmium in Period 6?
Let me ask you a question.
How many shells does holmium have?
It’s 6. Right?
You have already seen the bohr model of holmium atom in the above table.
From the Bohr model, it can be found that the number of orbits or shells in holmium is 6. Hence, as holmium has 6 orbits, it lies in period 6 of the Periodic table.
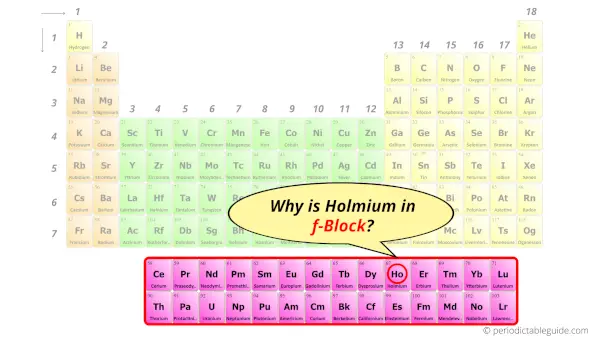
Why is Holmium in f-block?
Before knowing this reason, first of all I want to ask you a simple question.
How can you determine the blocks-wise position of elements?
The simple answer: The elements will lie in the s, p, d or f block will completely depend upon the subshell in which the last electron will enter.
For example; the electron configuration of holmium is [Xe] 6s2 4f11.
So the last electron of holmium enters the f-subshell or f-orbital.
Hence, holmium is the f-block element.
5 Interesting facts about Holmium
Interesting facts about holmium element are mentioned below.
- The name Holmium was derived from the Greek word “Holmia” which means stockholm.
- Holmium was discovered by two chemists Marc Delafontaine and Jacques Louis Soret (in 1878).
- The abundance of holmium in the earth’s crust is approximately 1.2 ppm by weight.
- Holmium is the 56th most abundant element in the earth’s crust.
- Holmium is mostly obtained from regions like China, USA, India, Sri Lanka, Brazil and Australia. These regions have estimated reserves of 400,000 tons of holmium in total.
Properties of Holmium
The physical and chemical properties of holmium element are mentioned below.
Physical properties of Holmium
Physical properties of holmium are mentioned below.
- Holmium is a soft and malleable metal having a Silvery white metallic appearance.
- The melting point of holmium is 1461 °C and its boiling point is 2600 °C.
- The atomic mass of holmium is 164.93 u and its density is 8.8 g/cm3.
- There are many isotopes of holmium, but out of those isotopes, the most abundant isotope is 165Ho (which has an abundance of almost 100%). Rest of the isotopes are synthetically made by humans in the laboratory.
- The crystal structure of holmium is HCP (Hexagonal close packed).
Chemical properties of Holmium
Chemical properties of holmium are mentioned below.
- Holmium is a reactive metal and hence it is not found in a free state in nature. But it is always found as a compound in the earth’s crust.
- When holmium is kept open in dry air, it does not tarnish. But if the air is moist, then it tarnishes and forms holmium oxide.
- The most common oxidation state of holmium is +3. And it exists as in Ho3+ state in its compounds.
Uses of Holmium
Uses of holmium are mentioned below.
- Holmium has magnetic properties and hence it is used as an alloying element in manufacturing of magnets.
- Holmium oxides are yellow in color and hence it is used in manufacturing of yellow colored glass.
- Holmium is also used in making solid state lasers as well as it is also used in medical applications to treat cancer as well as kidney stones.
Explore our New Interactive Periodic Table (with Rotating Bohr Models and More)

Details about this Periodic table:
- Access detailed info on all elements: atomic mass, electron configurations, charges, and more.
- View rotating Bohr models for all 118 elements.
- Get a free HD image of the Periodic Table.
Note: For future use, bookmark this Periodic table or visit “PeriodicTableGuide.com”
External resources:
- Holmium – Element information, properties and uses | Periodic Table. (n.d.). Holmium – Element Information, Properties and Uses | Periodic Table. https://www.rsc.org/periodic-table/element/67/holmium
- P. (n.d.). Holmium | Ho (Element) – PubChem. Holmium | Ho (Element) – PubChem. https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/element/Holmium
- Holmium – Wikipedia. (2019, December 30). Holmium – Wikipedia. https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Holmium
- It’s Elemental – The Element Holmium. (n.d.). It’s Elemental – the Element Holmium. https://education.jlab.org/itselemental/ele067.html
- Atomic Data for Holmium (Ho). (n.d.). Atomic Data for Holmium (Ho). https://physics.nist.gov/PhysRefData/Handbook/Tables/holmiumtable1.htm
