This is a SUPER easy guide on Flerovium element.
In fact, the table mentioned below is the perfect information box (Which gives you every single detail about the Flerovium element in Periodic table.)
So if you want to know anything about Flerovium element, then this guide is for you.
Let’s dive right into it!
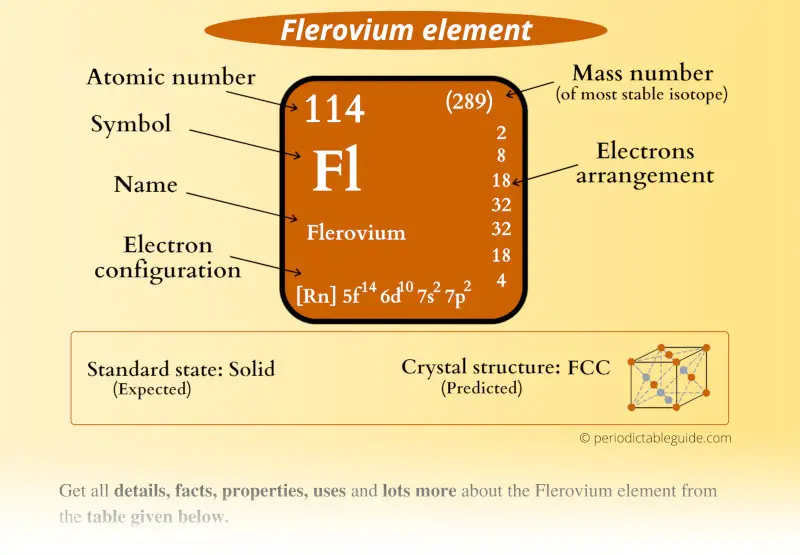
Flerovium Element (Fl) Information
| State (at STP) | Liquid (predicted) |
| Position in Periodic table | 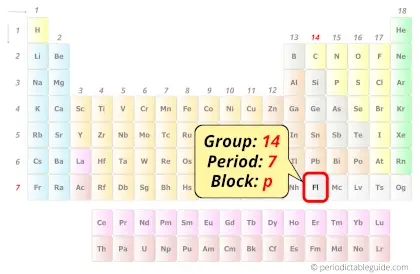 Group: 14, Period: 7, Block: p |
| Category | Synthetic element |
| Atomic number or Protons | 114 |
| Electrons | 114 |
| Symbol | Fl |
| Atomic mass of Flerovium (most stable isotope) | 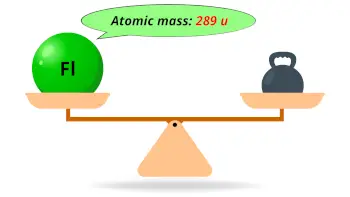 289 u |
| Electrons arrangement or Bohr model | 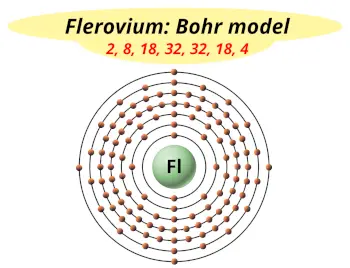 2, 8, 18, 32, 32, 18, 4 |
| Electronic configuration | [Rn] 5f14 6d10 7s2 7p2 |
| Crystal structure (predicted) | 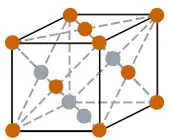 FCC (face centered cubic) |
| Melting point (predicted) | -73 °C |
| Boiling point (predicted) | 107 °C |
| Density | 9.93 g/cm3 |
| Main isotope | 289Fl |
| CAS number | 54085-16-4 |
Flerovium in Periodic table
Flerovium element is in group 14 and period 7 of the Periodic table. Flerovium is the p-block element and it is a radioactive synthetic element.
| H | He | ||||||||||||||||
| Li | Be | B | C | N | O | F | Ne | ||||||||||
| Na | Mg | Al | Si | P | S | Cl | Ar | ||||||||||
| K | Ca | Sc | Ti | V | Cr | Mn | Fe | Co | Ni | Cu | Zn | Ga | Ge | As | Se | Br | Kr |
| Rb | Sr | Y | Zr | Nb | Mo | Tc | Ru | Rh | Pd | Ag | Cd | In | Sn | Sb | Te | I | Xe |
| Cs | Ba | La* | Hf | Ta | W | Re | Os | Ir | Pt | Au | Hg | Tl | Pb | Bi | Po | At | Rn |
| Fr | Ra | Ac** | Rf | Db | Sg | Bh | Hs | Mt | Ds | Rg | Cn | Nh | Fl | Mc | Lv | Ts | Og |
| *Ce | Pr | Nd | Pm | Sm | Eu | Gd | Tb | Dy | Ho | Er | Tm | Yb | Lu | ||||
| **Th | Pa | U | Np | Pu | Am | Cm | Bk | Cf | Es | Fm | Md | No | Lr |
←Move to: Nihonium (Nh) element – Periodic Table
→Move to: Moscovium (Mc) element – Periodic Table
Why is Flerovium in Group 14?
Do you know, how many electrons can be accommodated in the first shell, second shell, third shell, fourth shell, etc…?
Here is the table showing the capacity of orbits to hold electrons.
Number of electrons in shells.
| Orbit / Shell (n) | Maximum no. of electrons this orbit can hold (2 × n2) |
| K shell, n = 1 | 2 × 1² = 2 |
| L shell, n = 2 | 2 × 2² = 8 |
| M shell, n = 3 | 2 × 3² = 18 |
| N shell, n = 4 | 2 × 4² = 32 |
| . . . | . . . |
Thus,
- 1st shell can hold 2 electrons.
- 2nd shell can hold 8 electrons.
- 3rd shell can hold 18 electrons.
- 4th shell can hold 32 electrons, and so on…
Now the atomic number of Flerovium (Fl) is 114.
Hence the flerovium element has electrons arrangement 2, 8, 18, 32, 32, 18, 4.
This electron arrangement indicates that the outermost orbit of flerovium element (Fl) has 4 electrons.
Hence, it lies in group 14.
Why is Flerovium in Period 7?
Let me ask you a question.
How many shells does flerovium have?
It’s 7. Right?
You have already seen the bohr model of flerovium atom in the above table.
From the Bohr model, it can be found that the number of orbits or shells in flerovium is 7. Hence, as flerovium has 7 orbits, it lies in period 7 of the Periodic table.
5 facts about Flerovium
Interesting facts about flerovium element are mentioned below.
- The element was given the name “Flerovium” to honor the physicist Georgy Flerov.
- Flerovium is an artificially prepared element and it has a very short half-life.
- Flerovium was discovered by team of scientists of Joint Institute of Nuclear Research (Russia), as well as team of scientists from Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory (California).
- Flerovium has several isotopes and all the isotopes are highly radioactive.
- The most stable isotope of flerovium is 289Fl, and it has a half life of 1.9 seconds.
Properties of Flerovium
The physical and chemical properties of flerovium element are mentioned below.
- Flerovium is highly radioactive and has a very short half life (in seconds).
- The flerovium is predicted to have a liquid state at STP.
- The predicted crystal structure of flerovium is FCC (face centered cubic).
- The stable oxidation state of flerovium is predicted to be +2.
- The atomic mass of most stable isotope of flerovium is 289 u and its density is predicted to be 9.93 g/cm3.
Uses of Flerovium
Flerovium is generally used for scientific research work. Flerovium has no commercial use due to its high radioactivity and scarcity.
Explore our New Interactive Periodic Table (with Rotating Bohr Models and More)

Details about this Periodic table:
- Access detailed info on all elements: atomic mass, electron configurations, charges, and more.
- View rotating Bohr models for all 118 elements.
- Get a free HD image of the Periodic Table.
Note: For future use, bookmark this Periodic table or visit “PeriodicTableGuide.com”
External resources:
- Flerovium – Element information, properties and uses | Periodic Table. (n.d.). Flerovium – Element Information, Properties and Uses | Periodic Table. https://www.rsc.org/periodic-table/element/114/flerovium
- Flerovium – Wikipedia. (2012, June 4). Flerovium – Wikipedia. https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Flerovium
- P. (n.d.). Flerovium | Fl (Element) – PubChem. Flerovium | Fl (Element) – PubChem. https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/element/Flerovium
- It’s Elemental – The Element Flerovium. (n.d.). It’s Elemental – the Element Flerovium. https://education.jlab.org/itselemental/ele114.html
- It’s a metal, not a gas: flerovium chemical properties unveiled. (2022, September 29). It’s a Metal, Not a Gas: Flerovium Chemical Properties Unveiled | Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory. https://www.llnl.gov/news/its-metal-not-gas-flerovium-chemical-properties-unveiled
- Periodic Table of Elements: Los Alamos National Laboratory. (n.d.). Periodic Table of Elements: Los Alamos National Laboratory. https://periodic.lanl.gov/114.shtml
- Yakushev, A., Gates, J. M., Türler, Et al. (2014, January 23). Superheavy Element Flerovium (Element 114) Is a Volatile Metal. Inorganic Chemistry, 53(3), 1624–1629. https://doi.org/10.1021/ic4026766
