This is a SUPER easy guide on Fermium element.
In fact, the table mentioned below is the perfect information box (Which gives you every single detail about the Fermium element in Periodic table.)
So if you want to know anything about Fermium element, then this guide is for you.
Let’s finish this very quickly.
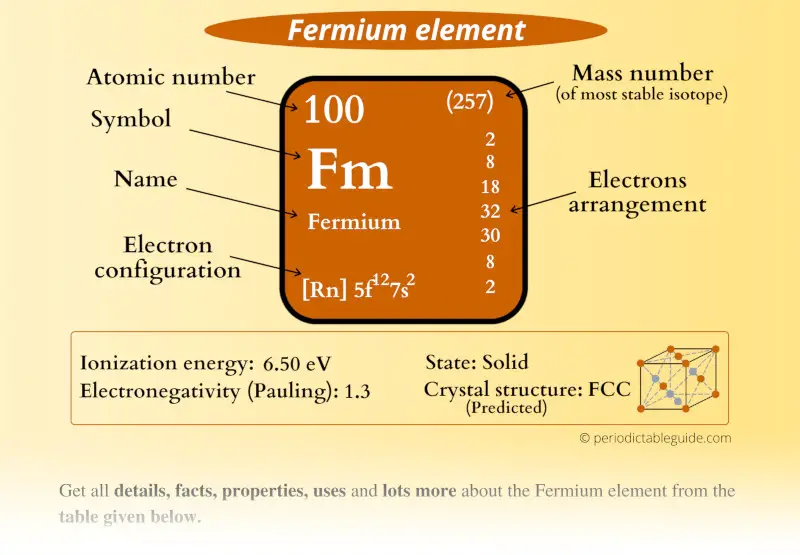
Fermium Element (Fm) Information
| State (at STP) | Solid (predicted) |
| Position in Periodic table | 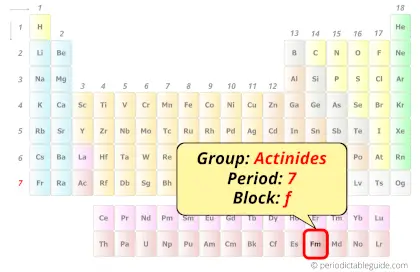 Group: actinides, Period: 7, Block: f |
| Category | 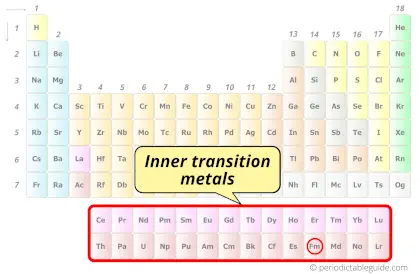 Inner transition metals |
| Atomic number or Protons | 100 |
| Neutrons | 157 |
| Electrons | 100 |
| Symbol | Fm |
| Atomic mass of Fermium (most stable isotope) | 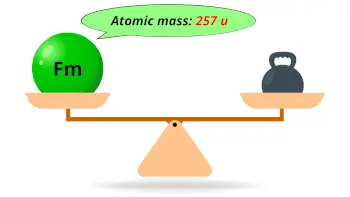 257 u |
| Electrons arrangement or Bohr model | 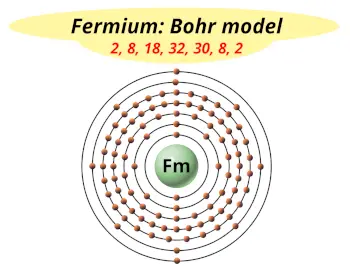 2, 8, 18, 32, 30, 8, 2 |
| Electronic configuration | [Rn] 5f12 7s2 |
| 1st Ionization energy | 6.50 eV |
| Electronegativity | 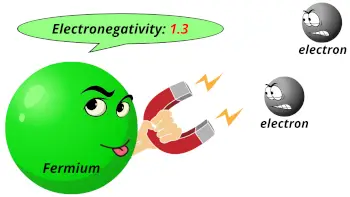 1.3 (Pauling scale) |
| Crystal structure (predicted) | 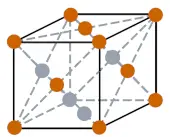 FCC (face centered cubic) |
| Melting point (predicted) | 1800 K or 1527 °C or 2781 °F |
| Density (predicted) | 9.7 g/cm3 |
| Main isotope | 257Fm |
| Who discovered Fermium and when? | Albert Ghiorso and his team (in 1952) |
| CAS number | 7440-72-4 |
Fermium in Periodic table
Fermium element is in period 7 and in actinides group of the Periodic table. Fermium is the f-block element and it belongs to inner transition metals group.
| H | He | ||||||||||||||||
| Li | Be | B | C | N | O | F | Ne | ||||||||||
| Na | Mg | Al | Si | P | S | Cl | Ar | ||||||||||
| K | Ca | Sc | Ti | V | Cr | Mn | Fe | Co | Ni | Cu | Zn | Ga | Ge | As | Se | Br | Kr |
| Rb | Sr | Y | Zr | Nb | Mo | Tc | Ru | Rh | Pd | Ag | Cd | In | Sn | Sb | Te | I | Xe |
| Cs | Ba | La* | Hf | Ta | W | Re | Os | Ir | Pt | Au | Hg | Tl | Pb | Bi | Po | At | Rn |
| Fr | Ra | Ac** | Rf | Db | Sg | Bh | Hs | Mt | Ds | Rg | Cn | Nh | Fl | Mc | Lv | Ts | Og |
| *Ce | Pr | Nd | Pm | Sm | Eu | Gd | Tb | Dy | Ho | Er | Tm | Yb | Lu | ||||
| **Th | Pa | U | Np | Pu | Am | Cm | Bk | Cf | Es | Fm | Md | No | Lr |
←Move to: Einsteinium (Es) element – Periodic Table
→Move to: Mendelevium (Md) element – Periodic Table
Why is Fermium in Period 7?
Let me ask you a question.
How many shells does fermium have?
It’s 7. Right?
You have already seen the bohr model of fermium atom in the above table.
From the Bohr model, it can be found that the number of orbits or shells in fermium is 7. Hence, as fermium has 7 orbits, it lies in period 7 of the Periodic table.
Why is Fermium in f-block?
Before knowing this reason, first of all I want to ask you a simple question.
How can you determine the blocks-wise position of elements?
The simple answer: The elements will lie in the s, p, d or f block will completely depend upon the subshell in which the last electron will enter.
For example; the electron configuration of fermium is [Rn] 5f12 7s2.
So the last electron of fermium enters the f-subshell or f-orbital.
Hence, fermium is the f-block element.
5 Interesting facts about Fermium
Interesting facts about fermium element are mentioned below.
- The name of the element “Fermium” came from the Italian physicist Enrico Fermi.
- Fermium element was identified by Albert Ghiorso and his team (in 1952) at Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory, California.
- Fermium does not occur naturally, but it is artificially prepared in a nuclear reactor.
- Fermium has 20 isotopes and all those isotopes are radioactive.
- Out of all the isotopes of fermium, the isotope 257Fm is the longest lived isotope, which has a half-life of 100 days.
Properties of Fermium
The physical and chemical properties of fermium element are mentioned below.
Physical properties of Fermium
Physical properties of fermium are mentioned below.
- The predicted crystal structure of fermium metal is FCC (i.e face centered cubic).
- The atomic mass of most stable isotope of fermium (257Fm) is 257 u, and its predicted density is 9.7 g/cm3.
- The calculated melting point of fermium metal is 1527 °C.
Chemical properties of Fermium
Chemical properties of fermium are mentioned below.
- Fermium is a chemically toxic and radioactive metal.
- The fermium exists as a Fm3+ ion in most of the solution. Hence its most common oxidation state in solutions is +3.
- Just similar to other actinides, fermium also shows +2 oxidation state.
- The electronic configuration of fermium is [Rn] 5f12 7s2, which indicates that it is a f-block element (this is because the last electron enters the f-orbital).
Uses of Fermium
Fermium is generally used in research work in chemistry. It has no commercial uses due to its radioactivity.
Explore our New Interactive Periodic Table (with Rotating Bohr Models and More)

Details about this Periodic table:
- Access detailed info on all elements: atomic mass, electron configurations, charges, and more.
- View rotating Bohr models for all 118 elements.
- Get a free HD image of the Periodic Table.
Note: For future use, bookmark this Periodic table or visit “PeriodicTableGuide.com”
External resources:
- Fermium – Element information, properties and uses | Periodic Table. (n.d.). Fermium – Element Information, Properties and Uses | Periodic Table. https://www.rsc.org/periodic-table/element/100/fermium
- Fermium – Wikipedia. (2007, December 7). Fermium – Wikipedia. https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Fermium
- It’s Elemental – The Element Fermium. (n.d.). It’s Elemental – the Element Fermium. https://education.jlab.org/itselemental/ele100.html
- P. (n.d.). Fermium | Fm (Element) – PubChem. Fermium | Fm (Element) – PubChem. https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/element/Fermium
- Periodic Table of Elements: Los Alamos National Laboratory. (n.d.). Periodic Table of Elements: Los Alamos National Laboratory. https://periodic.lanl.gov/100.shtml
- Periodic Table of Nottingham – University of Nottingham. (n.d.). Periodic Table of Nottingham – University of Nottingham. https://www.nottingham.ac.uk/periodicnottingham/fermium
- Thornton, B. F., & Burdette, S. C. (2017, June 23). Frantically forging fermium. Nature Chemistry, 9(7), 724–724. https://doi.org/10.1038/nchem.2806
