This is a SUPER easy guide on the Dysprosium element.
In fact, the table mentioned below is the perfect information box (Which gives you every single detail about the Dysprosium element in Periodic table.)
So if you want to know anything about the Dysprosium element, then this guide is for you.
Let’s finish this very quickly.
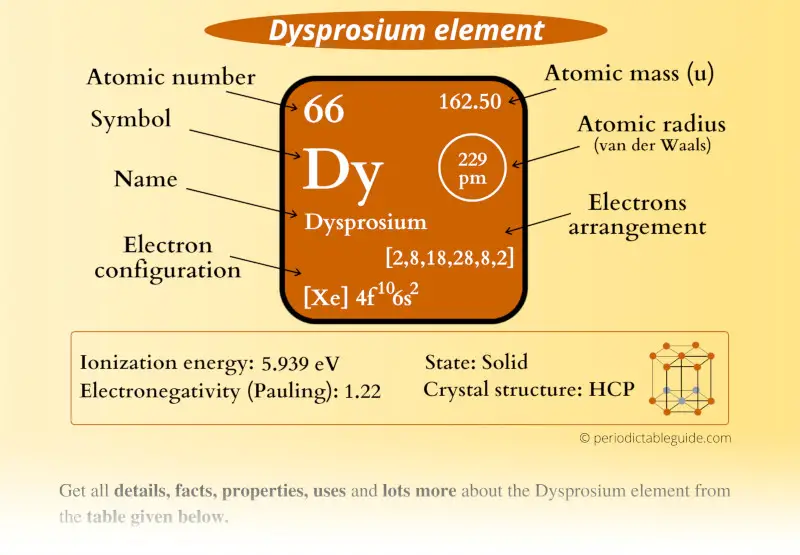
Dysprosium Element (Dy) Information
| Appearance |  Silvery white metallic surface |
| State (at STP) | Solid |
| Position in Periodic table | 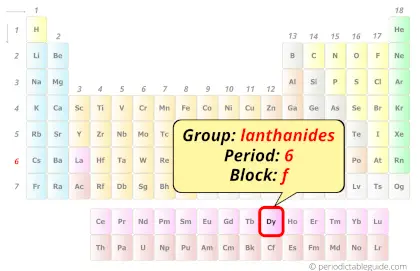 Group: lanthanides, Period: 6, Block: f |
| Category | 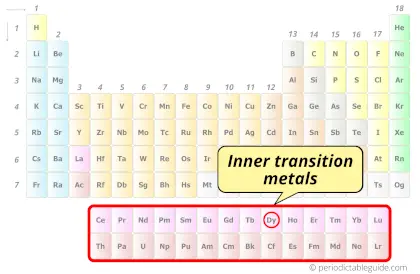 Inner transition metals |
| Atomic number or Protons | 66 |
| Neutrons | 97 |
| Electrons | 66 |
| Symbol | Dy |
| Atomic mass | 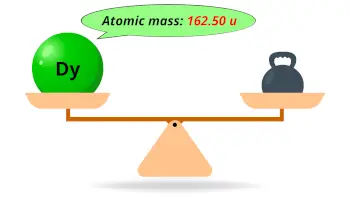 162.50 u |
| Electrons arrangement or Bohr model | 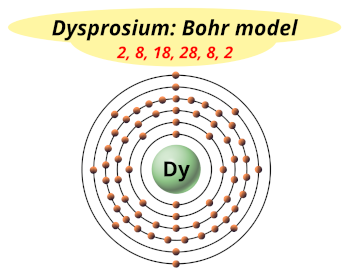 2, 8, 18, 28, 8, 2 |
| Electronic configuration | [Xe] 4f10 6s2 |
| Atomic radius | 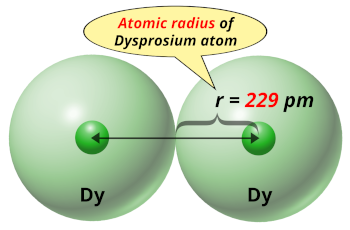 229 picometers (van der Waals radius) |
| 1st Ionization energy | 5.939 eV |
| Crystal structure | 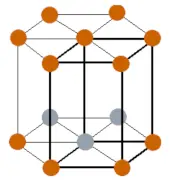 HCP (hexagonal close packed) |
| Melting point | 1680 K or 1407 °C or 2565 °F |
| Boiling point | 2840 K or 2562 °C or 4653 °F |
| Density | 8.55 g/cm3 |
| Main isotope | 164Dy |
| Who discovered Dysprosium and when? |  Lecoq de Boisbaudran in 1886 |
| CAS number | 7429-91-6 |
Dysprosium in Periodic table
Dysprosium element is in period 6 and in lanthanide group of the Periodic table. Dysprosium is the f-block element and it belongs to inner transition metals group.
| H | He | ||||||||||||||||
| Li | Be | B | C | N | O | F | Ne | ||||||||||
| Na | Mg | Al | Si | P | S | Cl | Ar | ||||||||||
| K | Ca | Sc | Ti | V | Cr | Mn | Fe | Co | Ni | Cu | Zn | Ga | Ge | As | Se | Br | Kr |
| Rb | Sr | Y | Zr | Nb | Mo | Tc | Ru | Rh | Pd | Ag | Cd | In | Sn | Sb | Te | I | Xe |
| Cs | Ba | La* | Hf | Ta | W | Re | Os | Ir | Pt | Au | Hg | Tl | Pb | Bi | Po | At | Rn |
| Fr | Ra | Ac** | Rf | Db | Sg | Bh | Hs | Mt | Ds | Rg | Cn | Nh | Fl | Mc | Lv | Ts | Og |
| *Ce | Pr | Nd | Pm | Sm | Eu | Gd | Tb | Dy | Ho | Er | Tm | Yb | Lu | ||||
| **Th | Pa | U | Np | Pu | Am | Cm | Bk | Cf | Es | Fm | Md | No | Lr |
←Move to: Terbium (Tb) element – Periodic Table
→Move to: Holmium (Ho) element – Periodic Table
Why is Dysprosium in Period 6?
Let me ask you a question.
How many shells does dysprosium have?
It’s 6. Right?
You have already seen the bohr model of dysprosium atom in the above table.
From the Bohr model, it can be found that the number of orbits or shells in dysprosium is 6. Hence, as dysprosium has 6 orbits, it lies in period 6 of the Periodic table.
Why is Dysprosium in f-block?
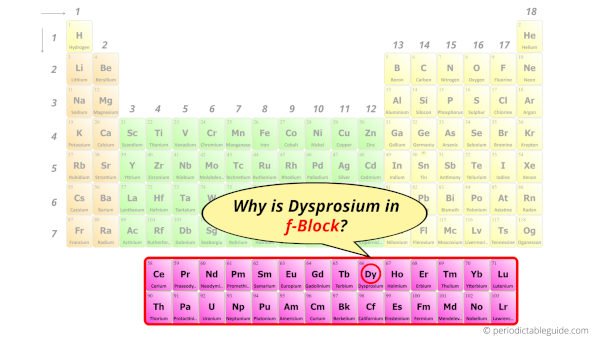
Before knowing this reason, first of all I want to ask you a simple question.
How can you determine the blocks-wise position of elements?
The simple answer: The elements will lie in the s, p, d or f block will completely depend upon the subshell in which the last electron will enter.
For example; the electron configuration of dysprosium is [Xe] 6s2 4f10.
So the last electron of dysprosium enters the f-subshell or f-orbital.
Hence, dysprosium is the f-block element.
5 Interesting facts about Dysprosium
Interesting facts about dysprosium element are mentioned below.
- The name dysprosium is derived from the Greek word “dysprositos”, which means “difficult to get at”.
- Dysprosium was discovered by Lecoq de Boisbaudran in 1886.
- The concentration of dysprosium metal in the earth’s crust is approximately 6 ppm by weight. [1]
- Dysprosium is classified as a rare earth metal on the periodic table, but actually they are not rare. These elements are spread evenly on the earth and it is difficult to find them in one place. Hence they are rare in the context of available resources.
- The most common mineral ores of dysprosium are monazite and bastnaesite.
Properties of Dysprosium
The physical and chemical properties of dysprosium element are mentioned below.
Physical properties of Dysprosium
Physical properties of dysprosium are mentioned below.
- Dysprosium is a solid metal having a silvery white metallic surface.
- Dysprosium is a soft metal and it can be cut even with a kitchen knife.
- The melting point of dysprosium is 1407 °C and its boiling point is 2562 °C.
- Dysprosium has a HCP (hexagonal close packed) crystal structure.
- The atomic mass of dysprosium is 162.50 u and its density is 8.55 g/cm3.
- Dysprosium has many isotopes, but out of those isotopes, the most abundant isotope is 164Dy (which has an abundance of approximately 28%).
Chemical properties of Dysprosium
Chemical properties of dysprosium are mentioned below.
- At room temperature, when dysprosium is kept open in air, it starts tarnishing.
- As dysprosium is a reactive metal, it is not found in free state in the earth’s crust. But it exists as a compound with other elements.
- The most common oxidation state of dysprosium is +3. That means, it exists as Dy3+ in its mineral ores.
- The electronic configuration of dysprosium ([Xe] 4f10 6s2) shows that its last electron enters f-orbital. Because of this reason, it is f-block element.
- The first ionization energy of dysprosium is 5.939 eV.
Uses of Dysprosium
Uses of dysprosium are mentioned below.
- Dysprosium can be used as a neutron absorber in nuclear reactors.
- The alloy made from dysprosium, iron and terbium has a property to expand and contract in presence of magnetic field. Because of this property, it is used in sonar systems.
- Data storage devices like hard discs as well as compact discs also used dysprosium.
Explore our New Interactive Periodic Table (with Rotating Bohr Models and More)

Details about this Periodic table:
- Access detailed info on all elements: atomic mass, electron configurations, charges, and more.
- View rotating Bohr models for all 118 elements.
- Get a free HD image of the Periodic Table.
Note: For future use, bookmark this Periodic table or visit “PeriodicTableGuide.com”
External resources:
- Dysprosium – Element information, properties and uses | Periodic Table. (n.d.). Dysprosium – Element Information, Properties and Uses | Periodic Table. https://www.rsc.org/periodic-table/element/66/dysprosium
- Dysprosium – Wikipedia. (2009, May 3). Dysprosium – Wikipedia. https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Dysprosium
- P. (n.d.). Dysprosium | Dy (Element) – PubChem. Dysprosium | Dy (Element) – PubChem. https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/element/Dysprosium
- It’s Elemental – The Element Dysprosium. (n.d.). It’s Elemental – the Element Dysprosium. https://education.jlab.org/itselemental/ele066.html
- Dysprosium (Dy) | AMERICAN ELEMENTS ® (n.d.). American Elements: The Materials Science Company. https://www.americanelements.com/dy.html
