This is a SUPER easy guide on Silver element.
In fact, the table mentioned below is the perfect information box (Which gives you every single detail about the Silver element in Periodic table.)
So if you want to know anything about Silver element, then this guide is for you.
Let’s finish this very quickly.
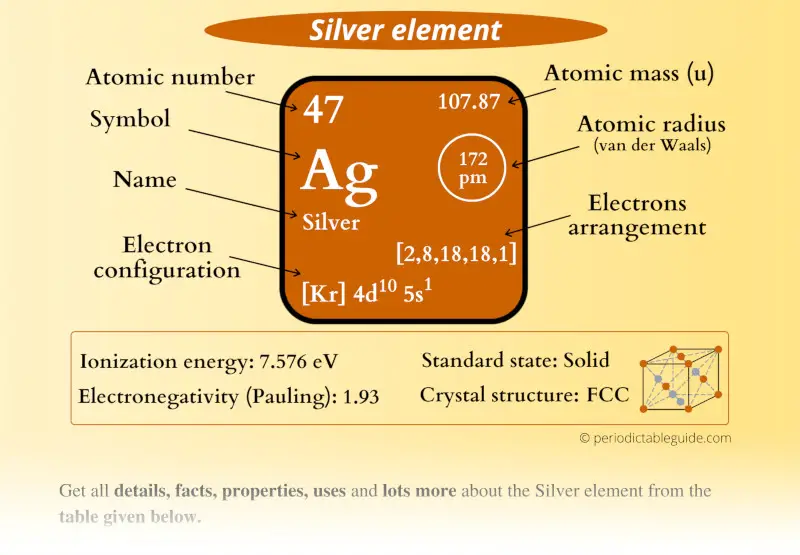
Silver Element (Ag) Information
| Appearance |  White metallic luster |
| State (at STP) | Solid |
| Position in Periodic table | 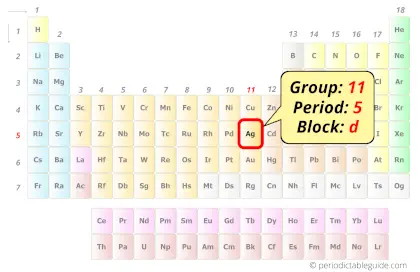 Group: 11, Period: 5, Block: d |
| Category | 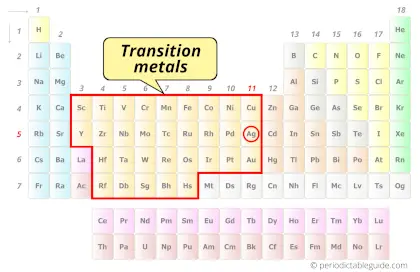 Transition metals |
| Atomic number or Protons | 47 |
| Neutrons | 61 |
| Electrons | 47 |
| Symbol | Ag |
| Atomic mass |  107.87 u |
| Electrons arrangement or Bohr model | 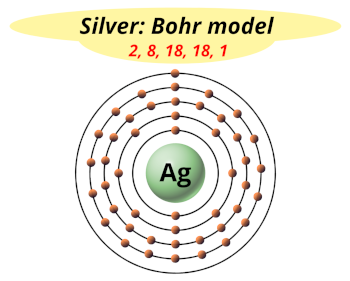 2, 8, 18, 18, 1 |
| Electronic configuration | [Kr] 4d10 5s1 |
| Atomic radius | 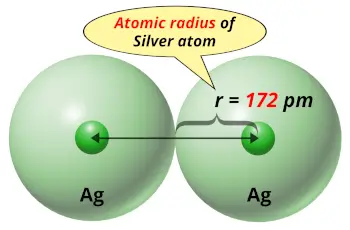 172 picometers (van der Waals radius) |
| 1st Ionization energy | 7.576 eV |
| Electronegativity | 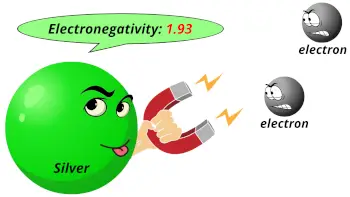 1.93 (Pauling scale) |
| Crystal structure | 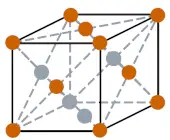 FCC (Face centered cubic) |
| Melting point | 1234.9 K or 961.7 °C or 1763.2 °F |
| Boiling point | 2435 K or 2162 °C or 3924 °F |
| Density | 10.5 g/cm3 |
| Main isotope | 107Ag (51.8%) and 109Ag (48.1%) |
| CAS number | 7440-22-4 |
Silver in Periodic table
Silver element is in group 11 and period 5 of the Periodic table. Silver is the d-block element and it belongs to transition metals group.
| H | He | ||||||||||||||||
| Li | Be | B | C | N | O | F | Ne | ||||||||||
| Na | Mg | Al | Si | P | S | Cl | Ar | ||||||||||
| K | Ca | Sc | Ti | V | Cr | Mn | Fe | Co | Ni | Cu | Zn | Ga | Ge | As | Se | Br | Kr |
| Rb | Sr | Y | Zr | Nb | Mo | Tc | Ru | Rh | Pd | Ag | Cd | In | Sn | Sb | Te | I | Xe |
| Cs | Ba | La* | Hf | Ta | W | Re | Os | Ir | Pt | Au | Hg | Tl | Pb | Bi | Po | At | Rn |
| Fr | Ra | Ac** | Rf | Db | Sg | Bh | Hs | Mt | Ds | Rg | Cn | Nh | Fl | Mc | Lv | Ts | Og |
| *Ce | Pr | Nd | Pm | Sm | Eu | Gd | Tb | Dy | Ho | Er | Tm | Yb | Lu | ||||
| **Th | Pa | U | Np | Pu | Am | Cm | Bk | Cf | Es | Fm | Md | No | Lr |
←Move to: Palladium (Pd) element – Periodic Table
→Move to: Cadmium (Cd) element – Periodic Table
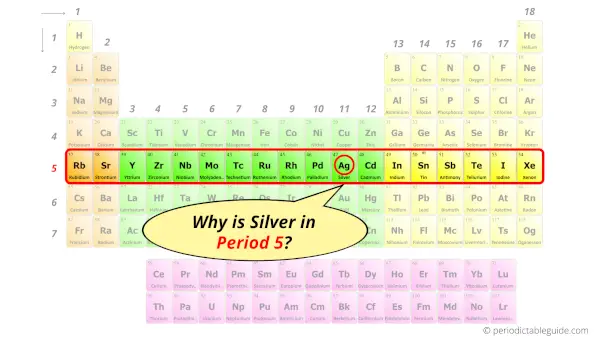
Why is Silver in Period 5?
Let me ask you a question.
How many shells does silver have?
It’s 5. Right?
You have already seen the bohr model of silver atom in the above table.
From the Bohr model, it can be found that the number of orbits or shells in silver is 5. Hence, as silver has 5 orbits, it lies in period 5 of the Periodic table.
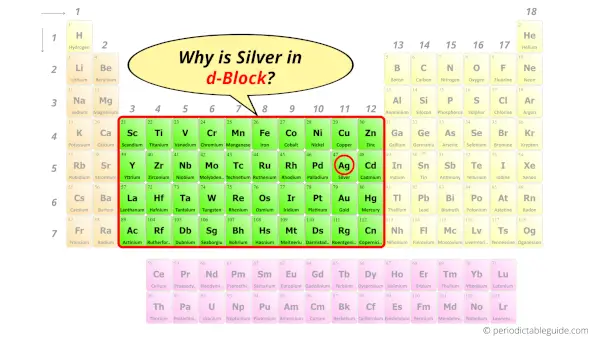
Why is Silver in d-block?
Before knowing this reason, first of all I want to ask you a simple question.
How can you determine the blocks-wise position of elements?
The simple answer: The elements will lie in the s, p, d or f block will completely depend upon the subshell in which the last electron will enter.
For example; the electron configuration of silver is [Kr] 5s1 4d10.
So the last electron of silver enters the d-subshell or d-orbital.
Hence, silver is the d-block element.
Is Silver a Transition Metal? Why?
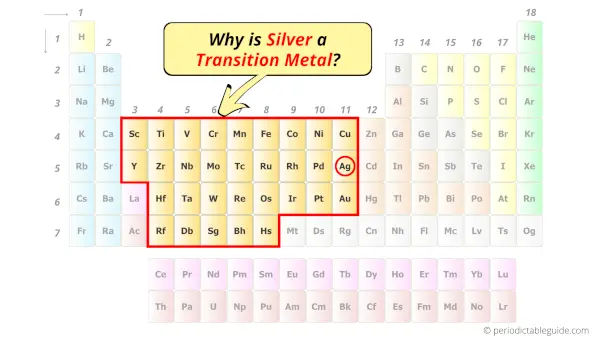
Yes, Silver is a transition metal because it has incompletely filled d-orbital in its common oxidation state (Ag2+).
Let me explain the exact meaning of this.
According to the definition of transition metals;
The element should compulsorily have incomplete d-orbitals, either in their ground state (M) or most common oxidation states (M1+, M2+, etc) then only they are called transition metals.
Now, the ground state of silver means its normal state in which it has neither gained nor lost any electron/s (i.e Ag).
And the common oxidation states of silver are Ag+, Ag2+, as well as Ag3+.
Now, let’s see the example of silver with oxidation state +2. So,
The electron configuration of Ag is: [Kr] 4d10 5s1 and
The electron configuration of Ag2+ is: [Kr] 4d9
So, in this +2 oxidation state of silver (Ag2+), if we see the electron configuration, then it possesses incomplete d-orbitals.
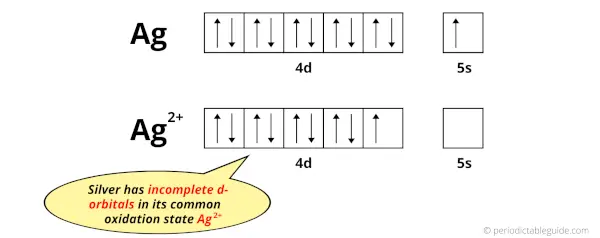
You can see that all the d-orbitals are completely filled (all the 10 electrons are present) in the elemental state (Ag) but they are incomplete (only 9 electrons are present) in its oxidation state (Ag2+).
In short, silver element have incomplete d-orbitals in its oxidation state (Ag2+).
Hence, according to the definition mentioned above, silver is a transition metal.
7 Interesting facts about Silver
Interesting facts about silver element are mentioned below.
- The name silver was derived from the Anglo-Saxon word “seolfor”.
- Mexico is the leading producer of silver in the world.
- In ancient times, the silver metal was used as a currency. And in ancient Egypt, once it was valued more than gold.
- Silver is so ductile metal that one ounce of silver can be drawn into around 8000 feet long wire.
- Silver is generally obtained as a byproduct during the mining of copper, zinc and lead.
- For a long time, silver has been known as “poor man’s gold”.
- The official currency of United Kingdom (i.e Pound Sterling) was initially equal in value to one pound of silver.
Properties of Silver
The physical and chemical properties of silver element are mentioned below.
Physical properties of Silver
Physical properties of silver are mentioned below.
- Silver is a solid metal having a lustrous white surface.
- Out of all the metals on the periodic table, pure silver is the best conductor of heat and electricity.
- Silver is a ductile as well as malleable metal.
- The atomic mass of silver is 107.87 u and its density is 10.5 g/cm3.
- The melting point of silver is 961.7 °C and its boiling point is 2162 °C.
- Silver has a FCC (Face centered cubic) crystal structure.
- Silver has natural isotopes as well as artificial isotopes. Out of them, the stable isotopes are 107Ag and 109Ag having an abundance of 51.8% and 48.1% respectively.
Chemical properties of Silver
Chemical properties of silver are mentioned below.
- Silver is a transition metal having incomplete d-orbitals.
- When silver is kept open in the air for a longer time, it tarnishes and turns dark grey in color. Hence it requires polishing.
- When silver is exposed to hydrogen sulfide it reacts with sulfur and forms a black sulfide layer on it.
- Silver does not show any chemical reaction with water, acids, as well as other compounds.
Uses of Silver
Uses of silver are mentioned below.
- Silver is a precious and nonreactive metal and hence it is used in making jewelry.
- Silver has an ability to reflect the visible light, and hence it is used in manufacturing mirrors.
- As silver is a good conductor of electricity, it is used in manufacturing battery components as well as other electronic devices.
- In ancient times, silver bottles were used to store water, wine, vinegar etc to protect them from bacteria contamination.
- In India, sweets are decorated with a very thin layer of silver (which we can eat).
- Silver was also used by dentists as a material for filling cavities.
Explore our New Interactive Periodic Table (with Rotating Bohr Models and More)

Details about this Periodic table:
- Access detailed info on all elements: atomic mass, electron configurations, charges, and more.
- View rotating Bohr models for all 118 elements.
- Get a free HD image of the Periodic Table.
Note: For future use, bookmark this Periodic table or visit “PeriodicTableGuide.com”
External resources:
- Silver – Element information, properties and uses | Periodic Table. (n.d.). Silver – Element Information, Properties and Uses | Periodic Table. https://www.rsc.org/periodic-table/element/47/silver
- Silver – Wikipedia. (2017, December 17). Silver – Wikipedia. https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Silver
- P. (n.d.). Silver | Ag (Element) – PubChem. Silver | Ag (Element) – PubChem. https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/element/Silver
- It’s Elemental – The Element Silver. (n.d.). It’s Elemental – the Element Silver. https://education.jlab.org/itselemental/ele047.html
