This is a SUPER easy guide on Scandium element.
In fact, the table mentioned below is the perfect information box (Which gives you every single detail about the Scandium element on Periodic table.)
So if you want to know anything about Scandium element, then this guide is for you.
Let’s finish this very quickly.
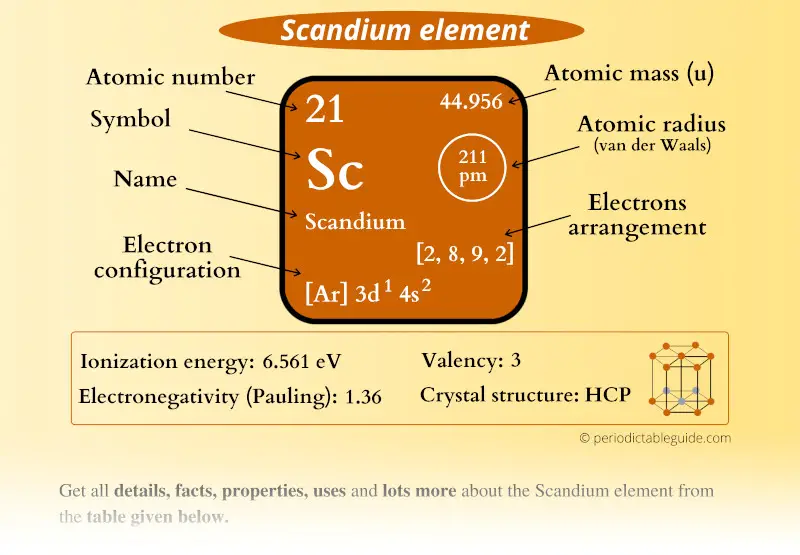
Scandium Element (Sc) Information
| Appearance |  Silvery white |
| State (at STP) | Solid |
| Position in Periodic table | 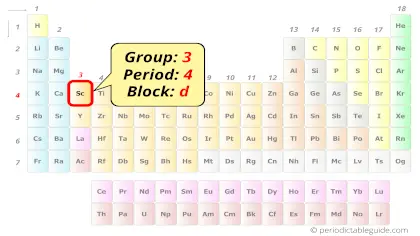 Group: 3, Period: 4, Block: d |
| Category | 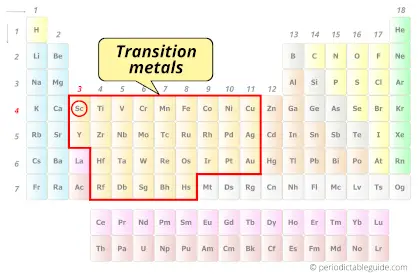 Transition metals |
| Atomic number or Protons | 21 |
| Neutrons | 24 |
| Electrons | 21 |
| Symbol | Sc |
| Atomic mass |  44.956 u |
| Electrons arrangement or Bohr model | 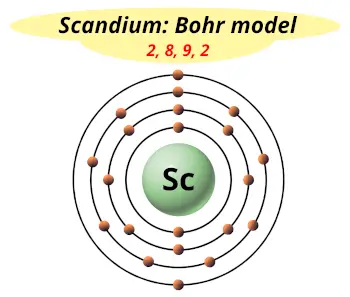 2, 8, 9, 2 |
| Electronic configuration | [Ar] 3d1 4s2 |
| Atomic radius | 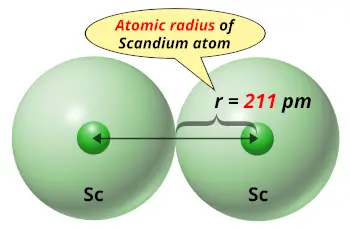 211 picometers (van der Waals radius) |
| Valence electrons | 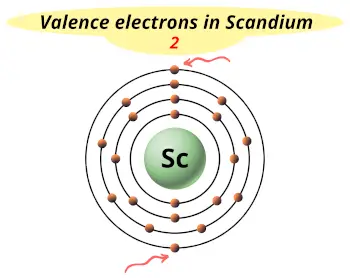 2 |
| 1st Ionization energy | 6.56 eV |
| Electronegativity | 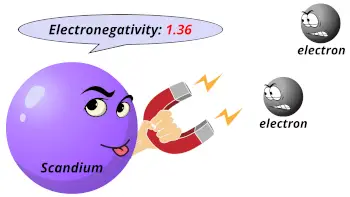 1.36 (Pauling scale) |
| Crystal structure | 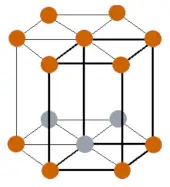 HCP (Hexagonal closed packing) |
| Melting point | 1814 K or 1541 °C or 2806 °F |
| Boiling point | 3109 K or 2836 °C or 5136 °F |
| Density | 2.985 g/cm3 |
| Main isotope | 45Sc |
| Who discovered Scandium and when? |  Lars Frederik Nilson in 1879 |
| CAS number | 7440-20-2 |
Scandium on Periodic table
Scandium element is in group 3 and period 4 of the Periodic table. Scandium is the d-block element and it belongs to transition metals group.
| H | He | ||||||||||||||||
| Li | Be | B | C | N | O | F | Ne | ||||||||||
| Na | Mg | Al | Si | P | S | Cl | Ar | ||||||||||
| K | Ca | Sc | Ti | V | Cr | Mn | Fe | Co | Ni | Cu | Zn | Ga | Ge | As | Se | Br | Kr |
| Rb | Sr | Y | Zr | Nb | Mo | Tc | Ru | Rh | Pd | Ag | Cd | In | Sn | Sb | Te | I | Xe |
| Cs | Ba | La* | Hf | Ta | W | Re | Os | Ir | Pt | Au | Hg | Tl | Pb | Bi | Po | At | Rn |
| Fr | Ra | Ac** | Rf | Db | Sg | Bh | Hs | Mt | Ds | Rg | Cn | Nh | Fl | Mc | Lv | Ts | Og |
| *Ce | Pr | Nd | Pm | Sm | Eu | Gd | Tb | Dy | Ho | Er | Tm | Yb | Lu | ||||
| **Th | Pa | U | Np | Pu | Am | Cm | Bk | Cf | Es | Fm | Md | No | Lr |
←Move to: Calcium (Ca) element – Periodic Table
→Move to: Titanium (Ti) element – Periodic Table
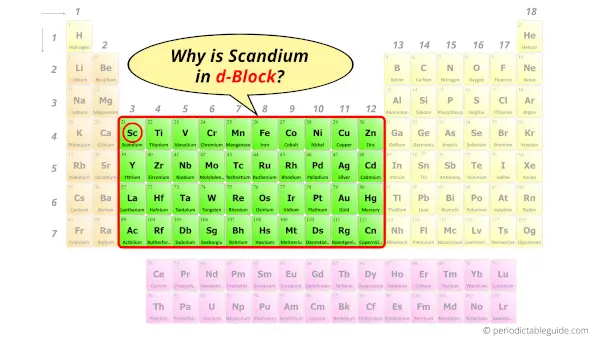
Why is Scandium in the d block?
Before knowing this reason, first of all a simple question to you.
How can you determine the blocks wise position of elements?
The simple answer: The elements will lie in the s, p, d or f block will completely depend upon the subshell in which the last electron will enter.
For example; the electron configuration of Scandium is [Ar] 4s2 3d1.
So the last electron of Scandium enters the d-subshell or d-orbital.
Hence, scandium is the d-block element.
Is Scandium a Metal, Nonmetal or Metalloid?
Scandium is a Metal. It’s a silvery white colored moderately soft metal. When it is kept open in the air, it reacts very slowly with oxygen to form Sc2O3 and its color changes from silvery white to yellowish color.

But do you know what exactly the metals are?
- Metals are the elements which lose electron/s during a chemical reaction.
In other words, metals are electron donors.
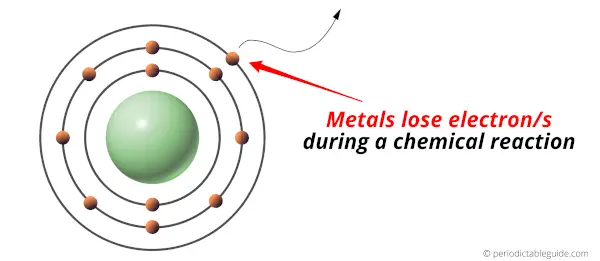
Metals are found on the left side of the Periodic table.
For more clarification, see the location of metals on the Periodic table (Image).
Is Scandium a Transition Metal? Why?
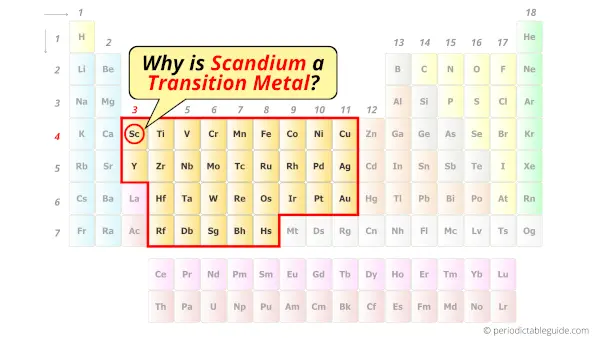
Yes, Scandium element is a transition metal. Because it has incompletely filled d-orbital in its ground state.
Let me explain the exact meaning of this.
According to the definition of transition metals;
The element should compulsorily have incomplete d-orbitals, either in their ground state (M) or most common oxidation states (M1+, M2+, etc) then only they are called transition metals.
Now, the ground state of scandium means its normal state in which it has neither gained nor lost any electron/s.
So the ground state of scandium is Sc.
And the ground state electronic configuration of Scandium is [Ar] 4s2 3d1.
In this state, if we see the electron configuration of Scandium, then it possesses incomplete d-orbitals.
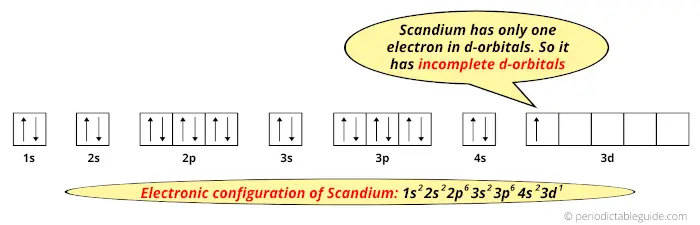
Because, there is only one electron in the d-orbitals.
In order to have the complete d-orbitals, there must be 10 electrons in it.
But in the ground state electronic configuration of scandium, you can see that it has only 1 electron in d-orbital.
Thus, scandium has incomplete d-orbitals.
And hence, as scandium has incomplete d-orbitals, it is considered as a transition metal.
Also see: Location of transition metals on periodic table (image)
Is Scandium bigger than Calcium?
No, Scandium is not bigger than Calcium. The van der Waals radius of the scandium atom is 211 picometers, while the van der Waals radius of calcium atom is 231 picometers.
Hence, Scandium atom is smaller than calcium atom.
Let me tell you the exact reason behind this.
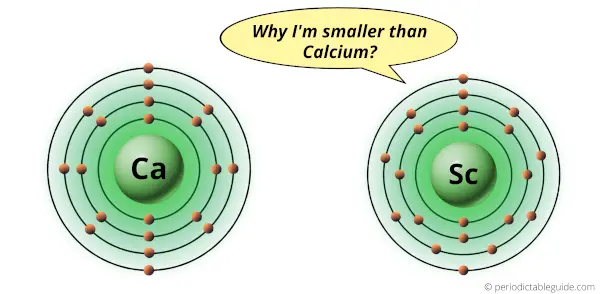
Scandium and calcium are the elements in the same period (i.e period 4).
But there is a slight difference in their atomic size.
The Scandium atom is slightly smaller in size than the calcium atom.
Here is the reason behind this.
You might be knowing about the atomic size trend in Periodic table.
According to the atomic size trend, as we move across a period (from left to right in the Periodic table), the atomic size of the elements decreases.
This is because of the increase in attractive force between the positively charged nucleus and negativity charges electrons.
Let me explain this with an example.
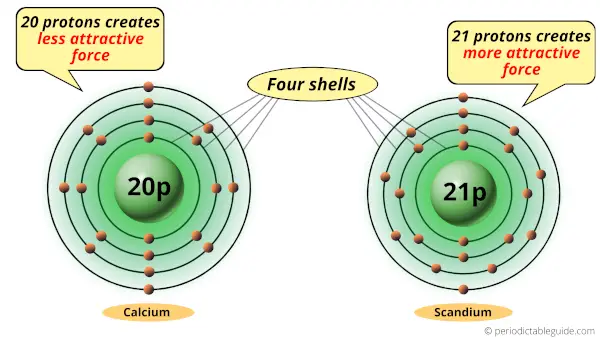
As you can see, calcium and scandium atoms have 4 shells or orbits.
But the difference is the number of protons present in their nucleus.
Calcium atom has 20 protons while the scandium atom has 21 protons.
Protons are the positively charged particles which attract the negatively charged electrons.
Now, the scandium atom has 21 protons, so it generates more attractive force compared to that of calcium.
So if we compare calcium atom and scandium atom, then they have same number of shells but the scandium atom has more positive charge which attracts the electrons towards the nucleus.
Thus, because of this attractive force, the scandium atom shrinks.
Hence, Scandium is smaller than calcium.
Also see: Periodic table with atomic size labeled on it (Image)
Interesting facts about scandium
Facts about scandium element are mentioned below.
- Scandium is a silvery white colored moderately soft metal. When it is kept open in the air, it reacts very slowly with oxygen to form Sc2O3 and its color changes from silvery white to yellowish color.
- Density of scandium is approximately 3 times that of water.
- Scandium is a transition metal, but it is also called Rare Earth metal. (Because scandium is spread evenly on the earth and it is very difficult to find it at one place on the earth). (Source)
- Just like aluminum, scandium is also a lighter metal. But Scandium has much higher melting point than aluminum. (Melting point of aluminum is 660 °C, while melting point of scandium is 1541 °C)
- Scandium element is more abundant on moon and sun, than on earth. (Sources: [1], [2])
- The existence of scandium was predicted by Mendeleev 10 years before it was actually discovered. Before 10 years of discovery, Mendeleev had predicted this element as eka-boron.
Explore our New Interactive Periodic Table (with Rotating Bohr Models and More)

Details about this Periodic table:
- Access detailed info on all elements: atomic mass, electron configurations, charges, and more.
- View rotating Bohr models for all 118 elements.
- Get a free HD image of the Periodic Table.
Note: For future use, bookmark this Periodic table or visit “PeriodicTableGuide.com”
External resources:
- It’s Elemental – The Element Scandium. (n.d.). It’s Elemental – the Element Scandium. https://education.jlab.org/itselemental/ele021.html
- P. (n.d.). Scandium | Sc (Element) – PubChem. Scandium | Sc (Element) – PubChem. https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/element/Scandium
- C&EN: IT’S ELEMENTAL: THE PERIODIC TABLE – SCANDIUM. (n.d.). C&EN: IT’S ELEMENTAL: THE PERIODIC TABLE – SCANDIUM. https://pubsapp.acs.org/cen/80th/print/scandium.html?
- Scandium – Element information, properties and uses | Periodic Table. (n.d.). Scandium – Element Information, Properties and Uses | Periodic Table. https://www.rsc.org/periodic-table/element/21/scandium
