This is a SUPER easy guide on Nickel element.
In fact, the table mentioned below is the perfect information box (Which gives you every single detail about the Nickel element in Periodic table.)
So if you want to know anything about Nickel element, then this guide is for you.
Let’s finish this very quickly.
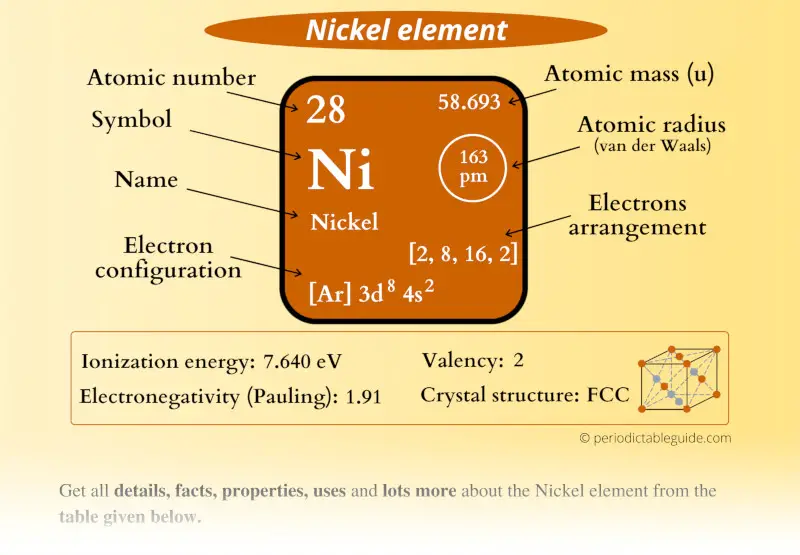
Nickel Element (Ni) Information
| Appearance |  Lustrous silvery metallic surface |
| State (at STP) | Solid |
| Position in Periodic table | 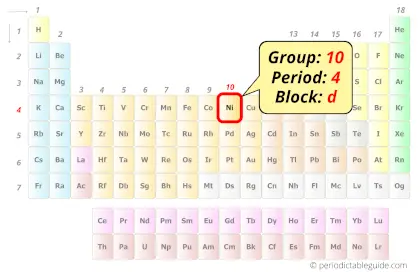 Group: 10, Period: 4, Block: d |
| Category | 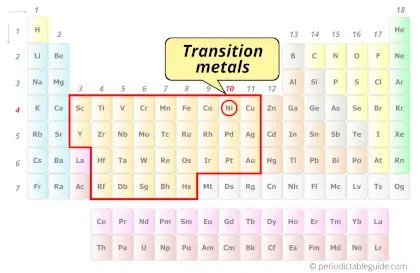 Transition metals |
| Atomic number or Protons | 28 |
| Neutrons | 31 |
| Electrons | 28 |
| Symbol | Ni |
| Atomic mass | 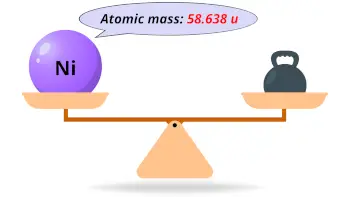 58.638 u |
| Electrons arrangement or Bohr model | 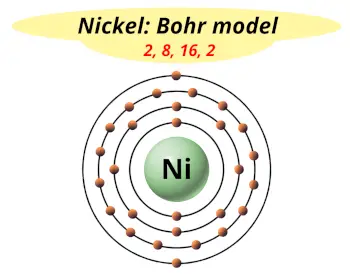 2, 8, 16, 2 |
| Electronic configuration | [Ar] 3d8 4s2 |
| Atomic radius | 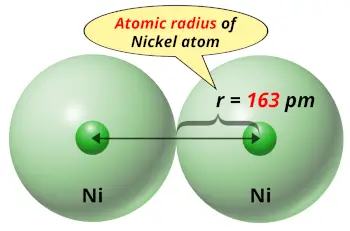 163 picometers (van der Waals radius) |
| 1st Ionization energy | 7.64 eV |
| Electronegativity | 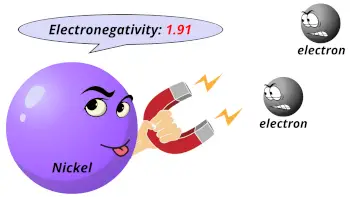 1.91 (Pauling scale) |
| Crystal structure | 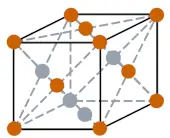 FCC (Face centered cubic) |
| Melting point | 1728 K or 1455 °C or 2651 °F |
| Boiling point | 3003 K or 2730 °C or 4946 °F |
| Density | 8.908 g/cm3 |
| Main isotope | 58Ni (68% abundance) and 60Ni (26.2% abundance) |
| Who discovered Nickel and when? |  Axel Fredrik Cronstedt in 1751 |
| CAS number | 7440-02-0 |
Nickel in Periodic table
Nickel element is in group 10 and period 4 of the Periodic table. Nickel is the d-block element and it belongs to transition metals group.
| H | He | ||||||||||||||||
| Li | Be | B | C | N | O | F | Ne | ||||||||||
| Na | Mg | Al | Si | P | S | Cl | Ar | ||||||||||
| K | Ca | Sc | Ti | V | Cr | Mn | Fe | Co | Ni | Cu | Zn | Ga | Ge | As | Se | Br | Kr |
| Rb | Sr | Y | Zr | Nb | Mo | Tc | Ru | Rh | Pd | Ag | Cd | In | Sn | Sb | Te | I | Xe |
| Cs | Ba | La* | Hf | Ta | W | Re | Os | Ir | Pt | Au | Hg | Tl | Pb | Bi | Po | At | Rn |
| Fr | Ra | Ac** | Rf | Db | Sg | Bh | Hs | Mt | Ds | Rg | Cn | Nh | Fl | Mc | Lv | Ts | Og |
| *Ce | Pr | Nd | Pm | Sm | Eu | Gd | Tb | Dy | Ho | Er | Tm | Yb | Lu | ||||
| **Th | Pa | U | Np | Pu | Am | Cm | Bk | Cf | Es | Fm | Md | No | Lr |
←Move to: Cobalt (Co) element – Periodic Table
→Move to: Copper (Cu) element – Periodic Table
Why is Nickel in Period 4?
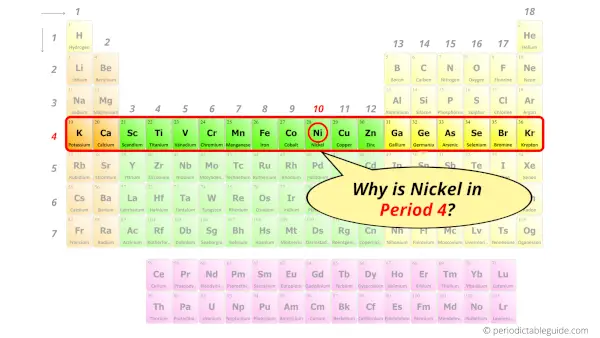
Let me ask you a question.
How many shells does nickel have?
It’s 4. Right?
You have already seen the bohr model of nickel atom in the above table.
From the Bohr model, it can be found that the number of orbits or shells in nickel is 4. Hence, as nickel has 4 orbits, it lies in period 4 of the Periodic table.
Why is Nickel in d-block?
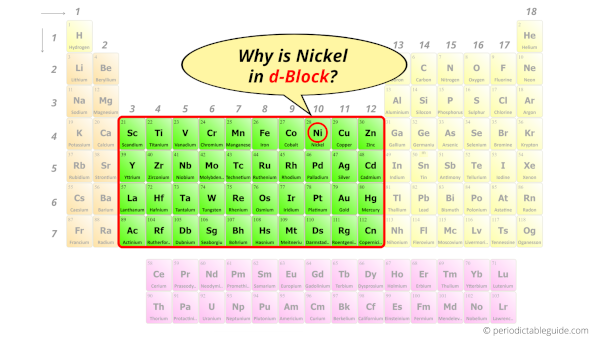
Before knowing this reason, first of all I want to ask you a simple question.
How can you determine the blocks-wise position of elements?
The simple answer: The elements will lie in the s, p, d or f block will completely depend upon the subshell in which the last electron will enter.
For example; the electron configuration of nickel is [Ar] 4s2 3d8.
So the last electron of nickel enters the d-subshell or d-orbital.
Hence, nickel is the d-block element.
Is Nickel a Transition Metal? Why?
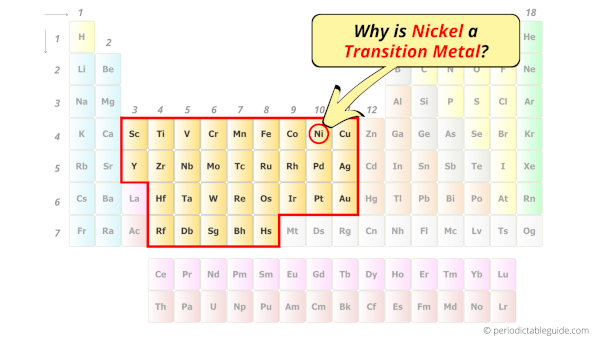
Yes, Nickel is a transition metal because it has incompletely filled d-orbital in its ground state.
Let me explain the exact meaning of this.
According to the definition of transition metals;
The element should compulsorily have incomplete d-orbitals, either in their ground state (M) or most common oxidation states (M1+, M2+, etc) then only they are called transition metals.
Now, the ground state of Nickel means its normal state in which it has neither gained nor lost any electron/s.
So the ground state of Nickel is Ni.
And the ground state electronic configuration of Nickel is [Ar] 4s2 3d8.
In this state, if we see the electron configuration of Nickel, then it possesses incomplete d-orbitals.
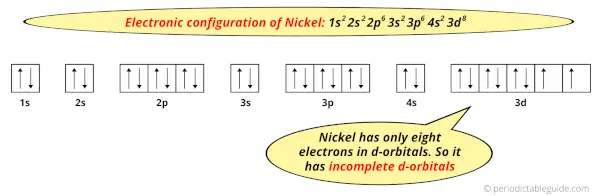
Because, there are only eight electrons in the d-orbitals.
In order to have the complete d-orbitals, there must be 10 electrons in it.
But in the ground state electronic configuration of nickel, you can see that it has only 8 electrons in d-orbitals.
Thus, Nickel has incomplete d-orbitals.
And hence, as Nickel has incomplete d-orbitals, it is considered as a transition metal.
Also see: Location of transition metals on periodic table (Image)
7 Interesting facts about Nickel
Interesting facts about nickel element are mentioned below.
- Nickel is the 5th most abundant element found in the earth. And it is only the 22nd most abundant element in the earth’s crust.
- If we talk about its proportion is earth’s inner core, then nickel is the 2nd most abundant element after iron.
- Out of the total nickel produced in the world, around 65% of it is used in manufacturing of stainless steels.
- The first coin of pure nickel was made in Switzerland (in 1881).
- Canada is the world’s largest producer of nickel [1]. It is believed that the large meteorite containing nickel might have crashed into the earth near Canada (thousands of years ago.)
- 1 kg of nickel metal can be drawn into approximately 300 km of wire. [2]
- Nickel metal has magnetic properties and it can retain its magnetic properties even at high temperatures.
Properties of Nickel
The physical and chemical properties of nickel element are mentioned below.
Physical properties of Nickel
Physical properties of nickel are mentioned below.
- Nickel is a hard and malleable metal having a lustrous silvery metallic surface.
- Nickel has many isotopes, but out of those isotopes, 58Ni and 60Ni are stable and they have an abundance of 68% and 26% respectively.
- The melting point of nickel is 1455 °C and its boiling point is 2730 °C.
- The atomic mass of nickel is 58.638 u and its density is 8.908 g/cm3.
- Nickel is also a good conductor of heat and electricity.
- Nickel is a metal that shows magnetic properties.
Chemical properties of Nickel
Chemical properties of nickel are mentioned below.
- Nickel is not a very reactive metal. It shows very less reactivity with other elements.
- Nickel atom have incomplete d-orbitals, hence it is classified as a transition metal on the periodic table.
- Nickel metal is resistant to corrosion.
- The greenish tint in a glass is due to the presence of nickel in it.
Uses of Nickel
Uses of nickel are mentioned below.
- The nickel metal is generally used to provide an outer protective coating on the softer metals.
- Nickel is als0 used as a super alloy as it has an ability to withstand at higher temperatures.
- In industries, nickel is used in manufacturing stainless steels, as well as in military applications and aerospace applications.
- As nickel is a corrosion resistance material, around 6% of nickel is used in applications like coins, batteries (nickel-cadmium batteries) and other electronics.
- Nickel is also used in making guitar strings.
- As nickel is difficult to oxidise, it is also used in electroplating of other metals.
Explore our New Interactive Periodic Table (with Rotating Bohr Models and More)

Details about this Periodic table:
- Access detailed info on all elements: atomic mass, electron configurations, charges, and more.
- View rotating Bohr models for all 118 elements.
- Get a free HD image of the Periodic Table.
Note: For future use, bookmark this Periodic table or visit “PeriodicTableGuide.com”
External resources:
- Nickel Statistics and Information | U.S. Geological Survey. (n.d.). Nickel Statistics and Information | U.S. Geological Survey. https://www.usgs.gov/centers/national-minerals-information-center/nickel-statistics-and-information
- Periodic Table of Elements: Los Alamos National Laboratory. (n.d.). Periodic Table of Elements: Los Alamos National Laboratory. https://periodic.lanl.gov/28.shtml
- Nickel – Wikipedia. (2016, March 2). Nickel – Wikipedia. https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Nickel
- Nickel – Element information, properties and uses | Periodic Table. (n.d.). Nickel – Element Information, Properties and Uses | Periodic Table. https://www.rsc.org/periodic-table/element/28/nickel
- P. (n.d.). Nickel | Ni (Element) – PubChem. Nickel | Ni (Element) – PubChem. https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/element/Nickel
