Valence electrons:
- For main group elements (i.e s-block and p-block elements), the valence electrons are the electrons present in the outermost orbit.
- But for most of the transition and inner transition elements, the valence electrons are the electrons present in the shells outside the noble gas core.
If you want a Periodic table with Valence electrons, then visit Periodic table with Valence electrons labeled in it. (Where you will get the HD images along with the explanation).
Valence Electrons Chart for All Elements
| Atomic number | Elements | Valence electrons |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Hydrogen (H) | 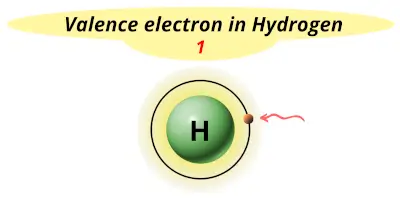 1 |
| 2 | Helium (He) | 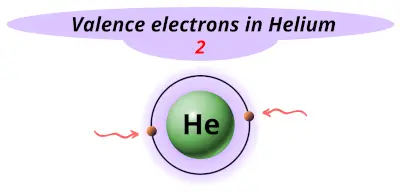 2 |
| 3 | Lithium (Li) | 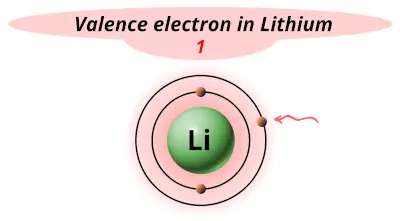 1 |
| 4 | Beryllium (Be) | 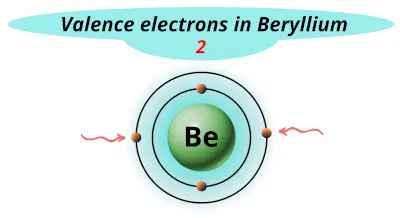 2 |
| 5 | Boron (B) | 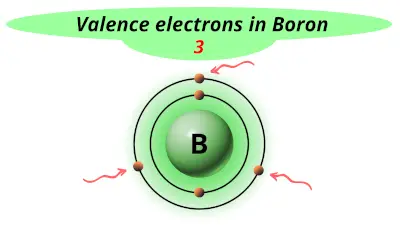 3 |
| 6 | Carbon (C) | 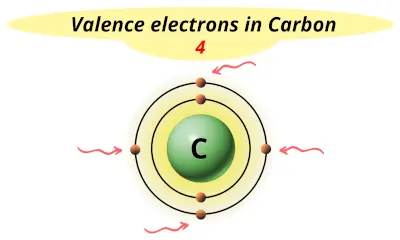 4 |
| 7 | Nitrogen (N) | 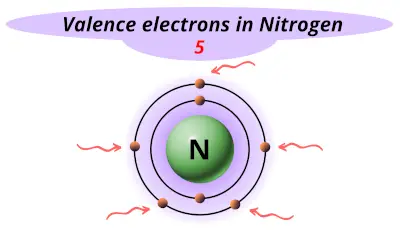 5 |
| 8 | Oxygen (O) | 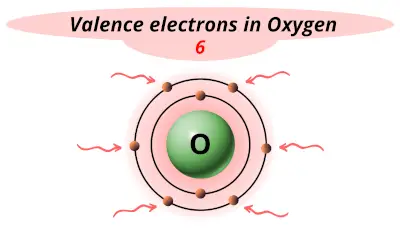 6 |
| 9 | Fluorine (F) | 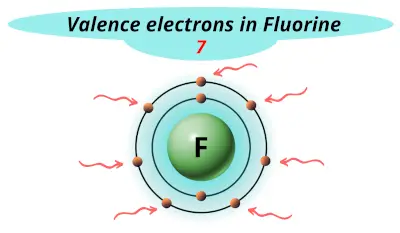 7 |
| 10 | Neon (Ne) | 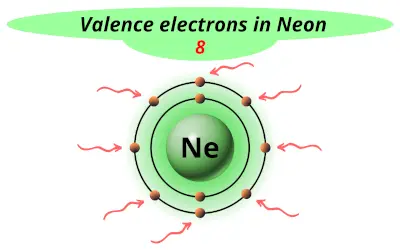 8 |
| 11 | Sodium (Na) | 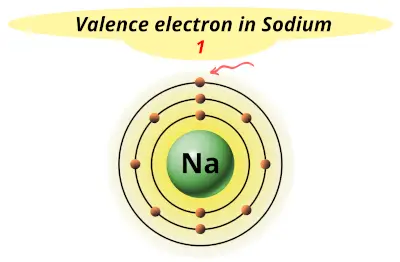 1 |
| 12 | Magnesium (Mg) | 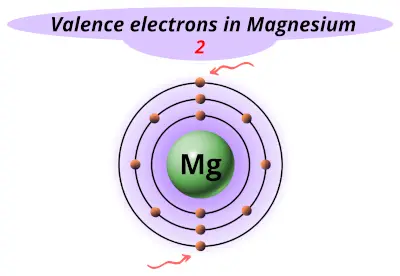 2 |
| 13 | Aluminum (Al) | 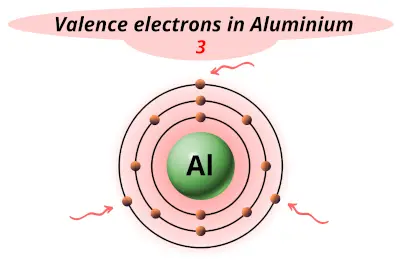 3 |
| 14 | Silicon (Si) | 4 |
| 15 | Phosphorus (P) | 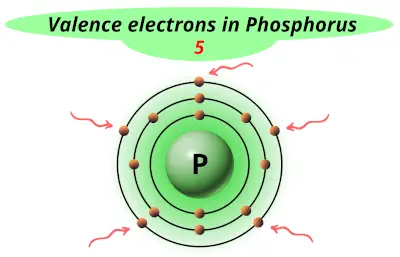 5 |
| 16 | Sulfur (S) | 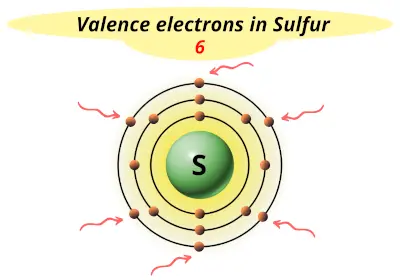 6 |
| 17 | Chlorine (Cl) | 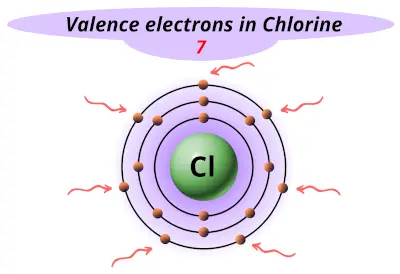 7 |
| 18 | Argon (Ar) | 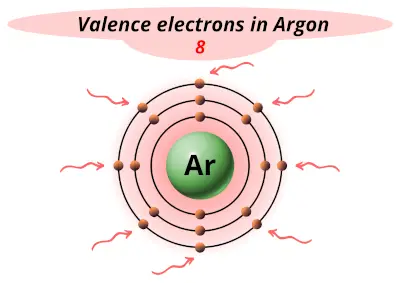 8 |
| 19 | Potassium (K) | 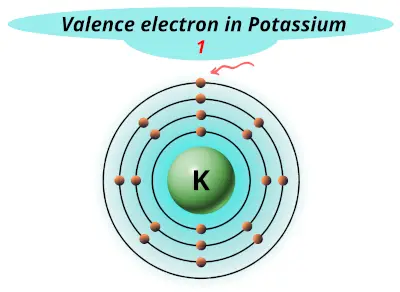 1 |
| 20 | Calcium (Ca) | 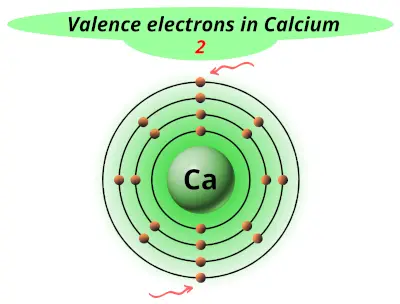 2 |
| 21 | Scandium (Sc) | 3 |
| 22 | Titanium (Ti) | 4 |
| 23 | Vanadium (V) | 5 |
| 24 | Chromium (Cr) | 6 |
| 25 | Manganese (Mn) | 7 |
| 26 | Iron (Fe) | 8 |
| 27 | Cobalt (Co) | 9 |
| 28 | Nickel (Ni) | 10 |
| 29 | Copper (Cu) | 11 |
| 30 | Zinc (Zn) | 12 |
| 31 | Gallium (Ga) | 3 |
| 32 | Germanium (Ge) | 4 |
| 33 | Arsenic (As) | 5 |
| 34 | Selenium (Se) | 6 |
| 35 | Bromine (Br) | 7 |
| 36 | Krypton (Kr) | 8 |
| 37 | Rubidium (Rb) | 1 |
| 38 | Strontium (Sr) | 2 |
| 39 | Yttrium (Y) | 3 |
| 40 | Zirconium (Zr) | 4 |
| 41 | Niobium (Nb) | 5 |
| 42 | Molybdenum (Mo) | 6 |
| 43 | Technetium (Tc) | 7 |
| 44 | Ruthenium (Ru) | 8 |
| 45 | Rhodium (Rh) | 9 |
| 46 | Palladium (Pd) | 10 |
| 47 | Silver (Ag) | 11 |
| 48 | Cadmium (Cd) | 12 |
| 49 | Indium (In) | 3 |
| 50 | Tin (Sn) | 4 |
| 51 | Antimony (Sb) | 5 |
| 52 | Tellurium (Te) | 6 |
| 53 | Iodine (I) | 7 |
| 54 | Xenon (Xe) | 8 |
| 55 | Cesium (Cs) | 1 |
| 56 | Barium (Ba) | 2 |
| 57 | Lanthanum (La) | 3 |
| 58 | Cerium (Ce) | 4 |
| 59 | Praseodymium (Pr) | 5 |
| 60 | Neodymium (Nd) | 6 |
| 61 | Promethium (Pm) | 7 |
| 62 | Samarium (Sm) | 8 |
| 63 | Europium (Eu) | 9 |
| 64 | Gadolinium (Gd) | 10 |
| 65 | Terbium (Tb) | 11 |
| 66 | Dysprosium (Dy) | 12 |
| 67 | Holmium (Ho) | 13 |
| 68 | Erbium (Er) | 14 |
| 69 | Thulium (Tm) | 15 |
| 70 | Ytterbium (Yb) | 16 |
| 71 | Lutetium (Lu) | 3 |
| 72 | Hafnium (Hf) | 4 |
| 73 | Tantalum (Ta) | 5 |
| 74 | Tungsten (W) | 6 |
| 75 | Rhenium (Re) | 7 |
| 76 | Osmium (Os) | 8 |
| 77 | Iridium (Ir) | 9 |
| 78 | Platinum (Pt) | 10 |
| 79 | Gold (Au) | 11 |
| 80 | Mercury (Hg) | 12 |
| 81 | Thallium (Tl) | 3 |
| 82 | Lead (Pb) | 4 |
| 83 | Bismuth (Bi) | 5 |
| 84 | Polonium (Po) | 6 |
| 85 | Astatine (At) | 7 |
| 86 | Radon (Rn) | 8 |
| 87 | Francium (Fr) | 1 |
| 88 | Radium (Ra) | 2 |
| 89 | Actinium (Ac) | 3 |
| 90 | Thorium (Th) | 4 |
| 91 | Protactinium (Pa) | 5 |
| 92 | Uranium (U) | 6 |
| 93 | Neptunium (Np) | 7 |
| 94 | Plutonium (Pu) | 8 |
| 95 | Americium (Am) | 9 |
| 96 | Curium (Cm) | 10 |
| 97 | Berkelium (Bk) | 11 |
| 98 | Californium (Cf) | 12 |
| 99 | Einsteinium (Es) | 13 |
| 100 | Fermium (Fm) | 14 |
| 101 | Mendelevium (Md) | 15 |
| 102 | Nobelium (No) | 16 |
| 103 | Lawrencium (Lr) | 3 |
| 104 | Rutherfordium (Rf) | 4 |
| 105 | Dubnium (Db) | 5 |
| 106 | Seaborgium (Sg) | 6 |
| 107 | Bohrium (Bh) | 7 |
| 108 | Hassium (Hs) | 8 |
| 109 | Meitnerium (Mt) | 9 |
| 110 | Darmstadtium (Ds) | 10 |
| 111 | Roentgenium (Rg) | 11 |
| 112 | Copernicium (Cn) | 12 |
| 113 | Nihonium (Nh) | 3 |
| 114 | Flerovium (Fl) | 4 |
| 115 | Moscovium (Mc) | 5 |
| 116 | Livermorium (Lv) | 6 |
| 117 | Tennessine (Ts) | 7 |
| 118 | Oganesson (Og) | 8 |
Explore our New Interactive Periodic Table (with Rotating Bohr Models and More)

Details about this Periodic table:
- Access detailed info on all elements: atomic mass, electron configurations, charges, and more.
- View rotating Bohr models for all 118 elements.
- Get a free HD image of the Periodic Table.
Note: For future use, bookmark this Periodic table or visit “PeriodicTableGuide.com”
External links:
Valence electrons of elements
