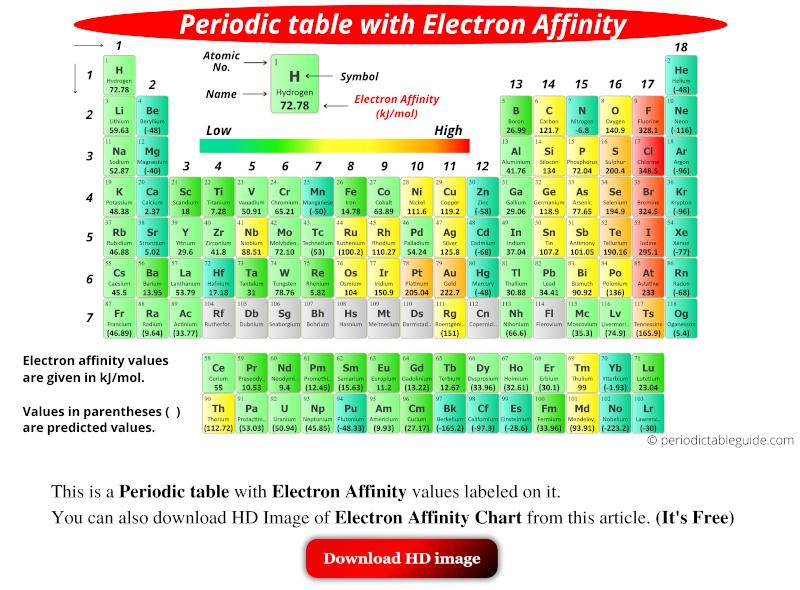
Periodic table with electron affinity values is shown above. The values of electron affinity are given in kJ/mol. Values in parentheses ( ) are predicted values.
Electron affinity is the amount of energy change (ΔE) that occurs when an electron is added in the outermost shell of an isolated gaseous atom.
In other words, when the electron is added to a neutral atom, the energy is either released or absorbed. And this amount of energy change (ΔE) is called electron affinity.
This energy change (ΔE) can be positive, negative or zero.
And the sign of Electron Affinity (EEA) is opposite to the sign of energy change (ΔE).
EEA = – (ΔE)
In simple words, if ΔE is positive, then EEA will be negative. And if ΔE is negative, then EEA will be positive.
Points to remember:
- For exothermic reaction (i.e when energy is released), the change in energy (ΔE) is negative. Hence the sign of Electron Affinity (EEA) will be positive.
- For endothermic reaction (i.e when energy is absorbed), the change in energy (ΔE) is positive. Hence the sign of Electron Affinity (EEA) will be negative.
- For neutral process (i.e when energy is neither absorbed nor released), the value of Electron Affinity (EEA) will be zero.
More the positive values of Electron Affinity (EEA), more is the energy released.
Halogens on the periodic table shows more positive values of Electron Affinity (EEA). Hence they indicate that more energy is released when an electron is added to the neutral atom.
Electron Affinity Values of All Elements
| Atomic number | Elements | Electron affinity (kJ/mol) |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Hydrogen (H) | 72.78 |
| 2 | Helium (He) | (-48) |
| 3 | Lithium (Li) | 59.63 |
| 4 | Beryllium (Be) | (-48) |
| 5 | Boron (B) | 26.99 |
| 6 | Carbon (C) | 121.77 |
| 7 | Nitrogen (N) | -6.8 |
| 8 | Oxygen (O) | 140.98 |
| 9 | Fluorine (F) | 328.16 |
| 10 | Neon (Ne) | (-116) |
| 11 | Sodium (Na) | 52.87 |
| 12 | Magnesium (Mg) | (-40) |
| 13 | Aluminum (Al) | 41.76 |
| 14 | Silicon (Si) | 134.06 |
| 15 | Phosphorus (P) | 72.04 |
| 16 | Sulfur (S) | 200.4 |
| 17 | Chlorine (Cl) | 348.57 |
| 18 | Argon (Ar) | (-96) |
| 19 | Potassium (K) | 48.38 |
| 20 | Calcium (Ca) | 2.37 |
| 21 | Scandium (Sc) | 18 |
| 22 | Titanium (Ti) | 7.28 |
| 23 | Vanadium (V) | 50.91 |
| 24 | Chromium (Cr) | 65.21 |
| 25 | Manganese (Mn) | (-50) |
| 26 | Iron (Fe) | 14.78 |
| 27 | Cobalt (Co) | 63.89 |
| 28 | Nickel (Ni) | 111.65 |
| 29 | Copper (Cu) | 119.23 |
| 30 | Zinc (Zn) | (-58) |
| 31 | Gallium (Ga) | 29.06 |
| 32 | Germanium (Ge) | 118.93 |
| 33 | Arsenic (As) | 77.65 |
| 34 | Selenium (Se) | 194.95 |
| 35 | Bromine (Br) | 324.53 |
| 36 | Krypton (Kr) | (-96) |
| 37 | Rubidium (Rb) | 46.88 |
| 38 | Strontium (Sr) | 5.02 |
| 39 | Yttrium (Y) | 29.6 |
| 40 | Zirconium (Zr) | 41.8 |
| 41 | Niobium (Nb) | 88.51 |
| 42 | Molybdenum (Mo) | 72.10 |
| 43 | Technetium (Tc) | (53) |
| 44 | Ruthenium (Ru) | (100.27) |
| 45 | Rhodium (Rh) | 110.27 |
| 46 | Palladium (Pd) | 54.24 |
| 47 | Silver (Ag) | 125.86 |
| 48 | Cadmium (Cd) | (-68) |
| 49 | Indium (In) | 37.04 |
| 50 | Tin (Sn) | 107.29 |
| 51 | Antimony (Sb) | 101.05 |
| 52 | Tellurium (Te) | 190.16 |
| 53 | Iodine (I) | 295.15 |
| 54 | Xenon (Xe) | (-77) |
| 55 | Cesium (Cs) | 45.5 |
| 56 | Barium (Ba) | 13.95 |
| 57 | Lanthanum (La) | 53.79 |
| 58 | Cerium (Ce) | 55 |
| 59 | Praseodymium (Pr) | 10.53 |
| 60 | Neodymium (Nd) | 9.4 |
| 61 | Promethium (Pm) | (12.45) |
| 62 | Samarium (Sm) | (15.63) |
| 63 | Europium (Eu) | 11.2 |
| 64 | Gadolinium (Gd) | (13.22) |
| 65 | Terbium (Tb) | 12.67 |
| 66 | Dysprosium (Dy) | (33.96) |
| 67 | Holmium (Ho) | (32.61) |
| 68 | Erbium (Er) | (30.1) |
| 69 | Thulium (Tm) | 99 |
| 70 | Ytterbium (Yb) | (-1.93) |
| 71 | Lutetium (Lu) | 23.04 |
| 72 | Hafnium (Hf) | 17.18 |
| 73 | Tantalum (Ta) | 31 |
| 74 | Tungsten (W) | 78.76 |
| 75 | Rhenium (Re) | 5.82 |
| 76 | Osmium (Os) | 104 |
| 77 | Iridium (Ir) | 150.94 |
| 78 | Platinum (Pt) | 205.04 |
| 79 | Gold (Au) | 222.75 |
| 80 | Mercury (Hg) | (-48) |
| 81 | Thallium (Tl) | 30.88 |
| 82 | Lead (Pb) | 34.41 |
| 83 | Bismuth (Bi) | 90.92 |
| 84 | Polonium (Po) | (136) |
| 85 | Astatine (At) | 233 |
| 86 | Radon (Rn) | (-68) |
| 87 | Francium (Fr) | (46.89) |
| 88 | Radium (Ra) | (9.64) |
| 89 | Actinium (Ac) | (33.77) |
| 90 | Thorium (Th) | (112.72) |
| 91 | Protactinium (Pa) | (53.03) |
| 92 | Uranium (U) | (50.94) |
| 93 | Neptunium (Np) | (45.85) |
| 94 | Plutonium (Pu) | (-48.33) |
| 95 | Americium (Am) | (9.93) |
| 96 | Curium (Cm) | (27.17) |
| 97 | Berkelium (Bk) | (-165.24) |
| 98 | Californium (Cf) | (-97.31) |
| 99 | Einsteinium (Es) | (-28.6) |
| 100 | Fermium (Fm) | (33.96) |
| 101 | Mendelevium (Md) | (93.91) |
| 102 | Nobelium (No) | (-223.22) |
| 103 | Lawrencium (Lr) | (-30.04) |
| 104 | Rutherfordium (Rf) | unknown |
| 105 | Dubnium (Db) | unknown |
| 106 | Seaborgium (Sg) | unknown |
| 107 | Bohrium (Bh) | unknown |
| 108 | Hassium (Hs) | unknown |
| 109 | Meitnerium (Mt) | unknown |
| 110 | Darmstadtium (Ds) | unknown |
| 111 | Roentgenium (Rg) | (151) |
| 112 | Copernicium (Cn) | unknown |
| 113 | Nihonium (Nh) | (66.6) |
| 114 | Flerovium (Fl) | unknown |
| 115 | Moscovium (Mc) | (35.3) |
| 116 | Livermorium (Lv) | (74.9) |
| 117 | Tennessine (Ts) | (165.9) |
| 118 | Oganesson (Og) | (5.403) |
Explore our New Interactive Periodic Table (with Rotating Bohr Models and More)

Details about this Periodic table:
- Access detailed info on all elements: atomic mass, electron configurations, charges, and more.
- View rotating Bohr models for all 118 elements.
- Get a free HD image of the Periodic Table.
Note: For future use, bookmark this Periodic table or visit “PeriodicTableGuide.com”
External links:
Electron affinity of elements: Wikipedia
