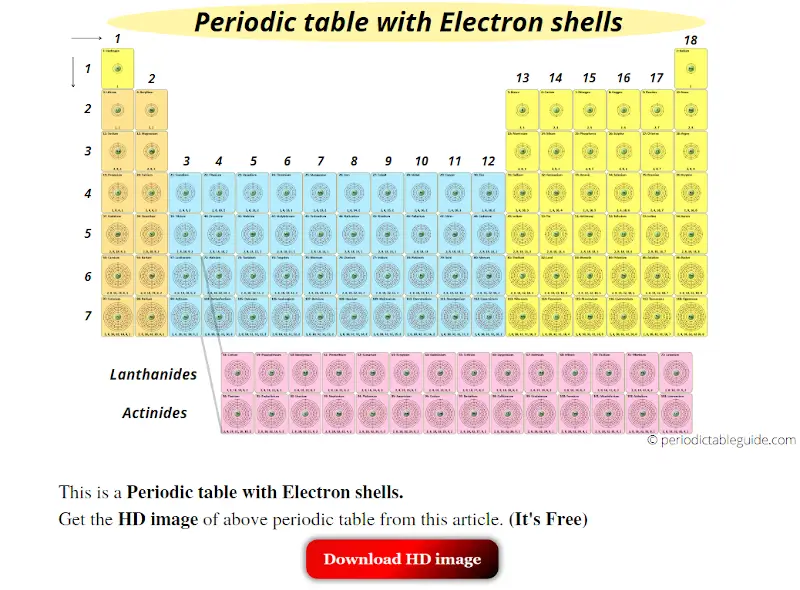
This is a Periodic table with Electrons per shell.
In the above Periodic table you can find all the elements with their electron shell configuration.
Also you can see their electron shells 2, 8, 18, … in the Periodic table itself.
Now, if you want to know the electron configuration of all these elements, then see the below Periodic table.
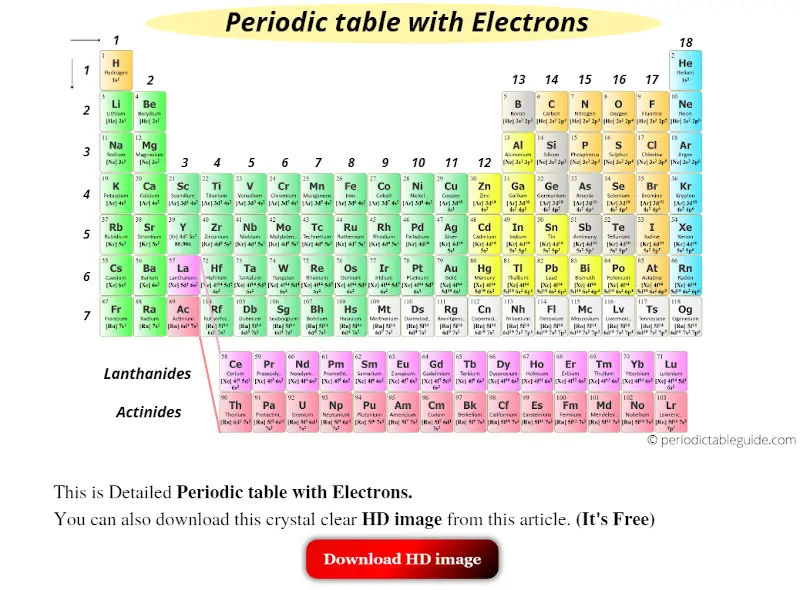
So this is a Periodic table with electron shell configuration.
But, I want to ask you a simple question.
- Do you know how the electrons are arranged around the nucleus of an atom?
- What are the energy shells (K, L, M, N, etc…)?
- How many electrons can accommodate in 1st, 2nd, 3rd, 4th, … orbits?
I’ll clearly explain this to you in just a few seconds.
+
I’ll also give you a complete list of elements with electrons per shell.
So let’s dive straight into it.
How are electrons arranged around the nucleus of an atom?
Just like the moon revolving around the earth, the electrons also revolve around the nucleus.
The electrons revolve around the nucleus in the specific paths which are known as orbits or shells.
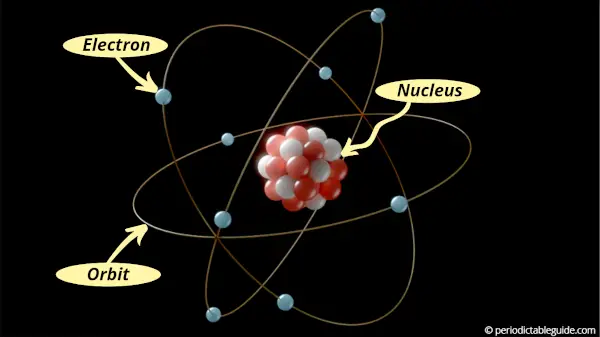
Now the question is,
How many electrons can be accommodated in each shell?
Here is a table showing electrons in each shell.
Number of electrons in each shell.
| Orbit / Shell (n) | Maximum no. of electrons this orbit can hold |
| K shell, n = 1 | 2 × 1² = 2 |
| L shell, n = 2 | 2 × 2² = 8 |
| M shell, n = 3 | 2 × 3² = 18 |
| N shell, n = 4 | 2 × 4² = 32 |
Thus,
- 1st shell can hold 2 electrons.
- 2nd shell can hold 8 electrons.
- 3rd shell can hold 18 electrons.
- 4th shell can hold 32 electrons.
Now I’ll show you the complete list of elements with electrons per shell.
List of elements with electrons per shell
| List of elements | Electrons per shell |
| 1 | Hydrogen (H) | 1 |
| 2 | Helium (He) | 2 |
| 3 | Lithium (Li) | 2, 1 |
| 4 | Beryllium (Be) | 2, 2 |
| 5 | Boron (B) | 2, 3 |
| 6 | Carbon (C) | 2, 4 |
| 7 | Nitrogen (N) | 2, 5 |
| 8 | Oxygen (O) | 2, 6 |
| 9 | Fluorine (F) | 2, 7 |
| 10 | Neon (Ne) | 2, 8 |
| 11 | Sodium (Na) | 2, 8 , 1 |
| 12 | Magnesium (Mg) | 2, 8 , 2 |
| 13 | Aluminum (Al) | 2, 8 , 3 |
| 14 | Silicon (Si) | 2, 8 , 4 |
| 15 | Phosphorus (P) | 2, 8 , 5 |
| 16 | Sulfur (S) | 2, 8 , 6 |
| 17 | Chlorine (Cl) | 2, 8 , 7 |
| 18 | Argon (Ar) | 2, 8 , 8 |
| 19 | Potassium (K) | 2, 8, 8, 1 |
| 20 | Calcium (Ca) | 2, 8, 8, 2 |
| 21 | Scandium (Sc) | 2, 8, 9, 2 |
| 22 | Titanium (Ti) | 2, 8, 10, 2 |
| 23 | Vanadium (V) | 2, 8, 11, 2 |
| 24 | Chromium (Cr) | 2, 8, 13, 1 |
| 25 | Manganese (Mn) | 2, 8, 13, 2 |
| 26 | Iron (Fe) | 2, 8, 14, 2 |
| 27 | Cobalt (Co) | 2, 8, 15, 2 |
| 28 | Nickel (Ni) | 2, 8, 16, 2 |
| 29 | Copper (Cu) | 2, 8, 18, 1 |
| 30 | Zinc (Zn) | 2, 8, 18, 2 |
| 31 | Gallium (Ga) | 2, 8, 18, 3 |
| 32 | Germanium (Ge) | 2, 8, 18, 4 |
| 33 | Arsenic (As) | 2, 8, 18, 5 |
| 34 | Selenium (Se) | 2, 8, 18, 6 |
| 35 | Bromine (Br) | 2, 8, 18, 7 |
| 36 | Krypton (Kr) | 2, 8, 18, 8 |
| 37 | Rubidium (Rb) | 2, 8, 18, 8, 1 |
| 38 | Strontium (Sr) | 2, 8, 18, 8, 2 |
| 39 | Yttrium (Y) | 2, 8, 18, 9, 2 |
| 40 | Zirconium (Zr) | 2, 8, 18, 10, 2 |
| 41 | Niobium (Nb) | 2, 8, 18, 12, 1 |
| 42 | Molybdenum (Mo) | 2, 8, 18, 13, 1 |
| 43 | Technetium (Tc) | 2, 8, 18, 13, 2 |
| 44 | Ruthenium (Ru) | 2, 8, 18, 15, 1 |
| 45 | Rhodium (Rh) | 2, 8, 18, 16, 1 |
| 46 | Palladium (Pd) | 2, 8, 18, 18 |
| 47 | Silver (Ag) | 2, 8, 18, 18, 1 |
| 48 | Cadmium (Cd) | 2, 8, 18, 18, 2 |
| 49 | Indium (In) | 2, 8, 18, 18, 3 |
| 50 | Tin (Sn) | 2, 8, 18, 18, 4 |
| 51 | Antimony (Sb) | 2, 8, 18, 18, 5 |
| 52 | Tellurium (Te) | 2, 8, 18, 18, 6 |
| 53 | Iodine (I) | 2, 8, 18, 18, 7 |
| 54 | Xenon (Xe) | 2, 8, 18, 18, 8 |
| 55 | Caesium (Cs) | 2, 8, 18, 18, 8, 1 |
| 56 | Barium (Ba) | 2, 8, 18, 18, 8, 2 |
| 57 | Lanthanum (La) | 2, 8, 18, 18, 9, 2 |
| 58 | Cerium (Ce) | 2, 8, 18, 19, 9, 2 |
| 59 | Praseodymium (Pr) | 2, 8, 18, 21, 8, 2 |
| 60 | Neodymium (Nd) | 2, 8, 18, 22, 8, 2 |
| 61 | Promethium (Pm) | 2, 8, 18, 23, 8, 2 |
| 62 | Samarium (Sm) | 2, 8, 18, 24, 8, 2 |
| 63 | Europium (Eu) | 2, 8, 18, 25, 8, 2 |
| 64 | Gadolinium (Gd) | 2, 8, 18, 25, 9, 2 |
| 65 | Terbium (Tb) | 2, 8, 18, 27, 8, 2 |
| 66 | Dysprosium (Dy) | 2, 8, 18, 28, 8, 2 |
| 67 | Holmium (Ho) | 2, 8, 18, 29, 8, 2 |
| 68 | Erbium (Er) | 2, 8, 18, 30, 8, 2 |
| 69 | Thulium (Tm) | 2, 8, 18, 31, 8, 2 |
| 70 | Ytterbium (Yb) | 2, 8, 18, 32, 8, 2 |
| 71 | Lutetium (Lu) | 2, 8, 18, 32, 9, 2 |
| 72 | Hafnium (Hf) | 2, 8, 18, 32, 10, 2 |
| 73 | Tantalum (Ta) | 2, 8, 18, 32, 11, 2 |
| 74 | Tungsten (W) | 2, 8, 18, 32, 12, 2 |
| 75 | Rhenium (Re) | 2, 8, 18, 32, 13, 2 |
| 76 | Osmium (Os) | 2, 8, 18, 32, 14, 2 |
| 77 | Iridium (Ir) | 2, 8, 18, 32, 15, 2 |
| 78 | Platinum (Pt) | 2, 8, 18, 32, 17, 1 |
| 79 | Gold (Au) | 2, 8, 18, 32, 18, 1 |
| 80 | Mercury (Hg) | 2, 8, 18, 32, 18, 2 |
| 81 | Thallium (Tl) | 2, 8, 18, 32, 18, 3 |
| 82 | Lead (Pb) | 2, 8, 18, 32, 18, 4 |
| 83 | Bismuth (Bi) | 2, 8, 18, 32, 18, 5 |
| 84 | Polonium (Po) | 2, 8, 18, 32, 18, 6 |
| 85 | Astatine (At) | 2, 8, 18, 32, 18, 7 |
| 86 | Radon (Rn) | 2, 8, 18, 32, 18, 8 |
| 87 | Francium (Fr) | 2, 8, 18, 32, 18, 8, 1 |
| 88 | Radium (Ra) | 2, 8, 18, 32, 18, 8, 2 |
| 89 | Actinium (Ac) | 2, 8, 18, 32, 18, 9, 2 |
| 90 | Thorium (Th) | 2, 8, 18, 32, 18, 10, 2 |
| 91 | Protactinium (Pa) | 2, 8, 18, 32, 20, 9, 2 |
| 92 | Uranium (U) | 2, 8, 18, 32, 21, 9, 2 |
| 93 | Neptunium (Np) | 2, 8, 18, 32, 22, 9, 2 |
| 94 | Plutonium (Pu) | 2, 8, 18, 32, 24, 8, 2 |
| 95 | Americium (Am) | 2, 8, 18, 32, 25, 8, 2 |
| 96 | Curium (Cm) | 2, 8, 18, 32, 25, 9, 2 |
| 97 | Berkelium (Bk) | 2, 8, 18, 32, 27, 8, 2 |
| 98 | Californium (Cf) | 2, 8, 18, 32, 28, 8, 2 |
| 99 | Einsteinium (Es) | 2, 8, 18, 32, 29, 8, 2 |
| 100 | Fermium (Fm) | 2, 8, 18, 32, 30, 8, 2 |
| 101 | Mendelevium (Md) | 2, 8, 18, 32, 31, 8, 2 |
| 102 | Nobelium (No) | 2, 8, 18, 32, 32, 8, 2 |
| 103 | Lawrencium (Lr) | 2, 8, 18, 32, 32, 8, 3 |
| 104 | Rutherfordium (Rf) | 2, 8, 18, 32, 32, 10, 2 |
| 105 | Dubnium (Db) | 2, 8, 18, 32, 32, 11, 2 |
| 106 | Seaborgium (Sg) | 2, 8, 18, 32, 32, 12, 2 |
| 107 | Bohrium (Bh) | 2, 8, 18, 32, 32, 13, 2 |
| 108 | Hassium (Hs) | 2, 8, 18, 32, 32, 14, 2 |
| 109 | Meitnerium (Mt) | 2, 8, 18, 32, 32, 15, 2 |
| 110 | Darmstadtium (Ds) | 2, 8, 18, 32, 32, 17, 1 |
| 111 | Roentgenium (Rg) | 2, 8, 18, 32, 32, 17, 2 |
| 112 | Copernicium (Cn) | 2, 8, 18, 32, 32, 18, 2 |
| 113 | Nihonium (Nh) | 2, 8, 18, 32, 32, 18, 3 |
| 114 | Flerovium (Fl) | 2, 8, 18, 32, 32, 18, 4 |
| 115 | Moscovium (Mc) | 2, 8, 18, 32, 32, 18, 5 |
| 116 | Livermorium (Lv) | 2, 8, 18, 32, 32, 18, 6 |
| 117 | Tennessine (Ts) | 2, 8, 18, 32, 32, 18, 7 |
| 118 | Oganesson (Og) | 2, 8, 18, 32, 32, 18, 8 |
So this is it for this article.
I hope you have clearly understood the Periodic table with electrons per shell.
If you have any questions, ask me in the comments below.
Also let me know, has this article helped you or not?
Explore our New Interactive Periodic Table (with Rotating Bohr Models and More)

Details about this Periodic table:
- Access detailed info on all elements: atomic mass, electron configurations, charges, and more.
- View rotating Bohr models for all 118 elements.
- Get a free HD image of the Periodic Table.
Note: For future use, bookmark this Periodic table or visit “PeriodicTableGuide.com”
Suggested Important articles for you:
- Periodic table of elements (Detailed guide + HD image)
- Periodic table with metals
- Periodic table with nonmetals
- Periodic table with metalloids
- Periodic table with halogens
- Periodic table with noble gases
- Periodic table showing alkali metals
- Periodic table showing alkaline earth metals
- Periodic table with transition metals
- Periodic table with inner transition metals
- Periodic trends (Trends in periodic table)
