This is a SUPER easy guide on Technetium element.
In fact, the table mentioned below is the perfect information box (Which gives you every single detail about the Technetium element in Periodic table.)
So if you want to know anything about Technetium element, then this guide is for you.
Let’s finish this very quickly.
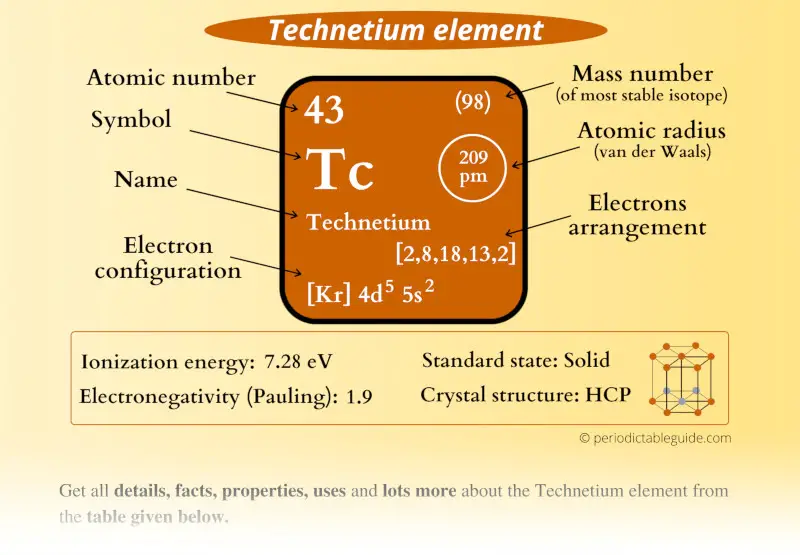
Technetium Element (Tc) Information
| Appearance |  Shiny gray metallic luster |
| State (at STP) | Solid |
| Position in Periodic table | 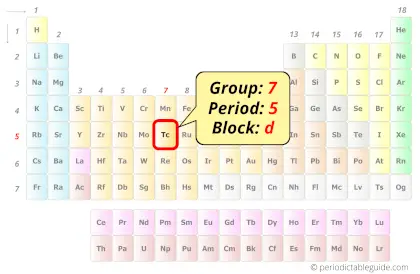 Group: 7, Period: 5, Block: d |
| Category | 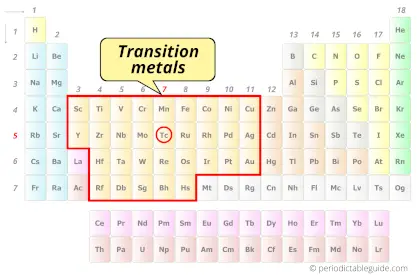 Transition metals |
| Atomic number or Protons | 43 |
| Neutrons | 55 |
| Electrons | 43 |
| Symbol | Tc |
| Atomic mass of Technetium (most stable isotope) | 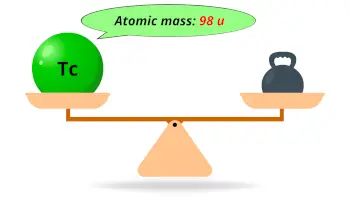 98 u |
| Electrons arrangement or Bohr model | 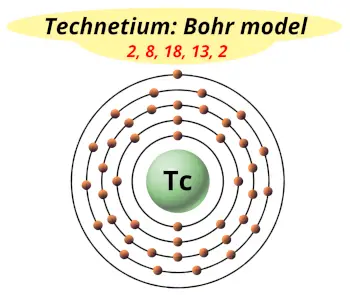 2, 8, 18, 13, 2 |
| Electronic configuration | [Kr] 4d5 5s2 |
| Atomic radius | 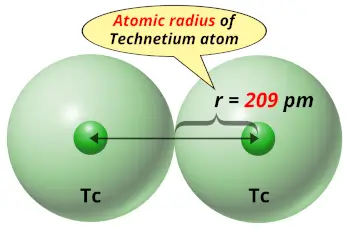 209 picometers (van der Waals radius) |
| 1st Ionization energy | 7.28 eV |
| Electronegativity | 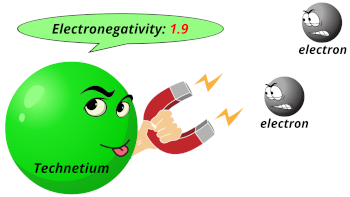 1.9 (Pauling scale) |
| Crystal structure | 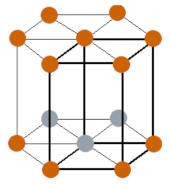 HCP (Hexagonal close packing) |
| Melting point | 2430 K or 2157 °C or 3915 °F |
| Boiling point | 4538 K or 4265 °C or 7709 °F |
| Density | 11.5 g/cm3 |
| Who discovered Technetium and when? | Carlo Perrier and Emilio Segrè in 1973 |
| CAS number | 7440-26-8 |
Technetium in Periodic table
Technetium element is in group 7 and period 5 of the Periodic table. Technetium is the d-block element and it belongs to Transition metals group.
| H | He | ||||||||||||||||
| Li | Be | B | C | N | O | F | Ne | ||||||||||
| Na | Mg | Al | Si | P | S | Cl | Ar | ||||||||||
| K | Ca | Sc | Ti | V | Cr | Mn | Fe | Co | Ni | Cu | Zn | Ga | Ge | As | Se | Br | Kr |
| Rb | Sr | Y | Zr | Nb | Mo | Tc | Ru | Rh | Pd | Ag | Cd | In | Sn | Sb | Te | I | Xe |
| Cs | Ba | La* | Hf | Ta | W | Re | Os | Ir | Pt | Au | Hg | Tl | Pb | Bi | Po | At | Rn |
| Fr | Ra | Ac** | Rf | Db | Sg | Bh | Hs | Mt | Ds | Rg | Cn | Nh | Fl | Mc | Lv | Ts | Og |
| *Ce | Pr | Nd | Pm | Sm | Eu | Gd | Tb | Dy | Ho | Er | Tm | Yb | Lu | ||||
| **Th | Pa | U | Np | Pu | Am | Cm | Bk | Cf | Es | Fm | Md | No | Lr |
←Move to: Molybdenum (Mo) element – Periodic Table
→Move to: Ruthenium (Ru) element – Periodic Table
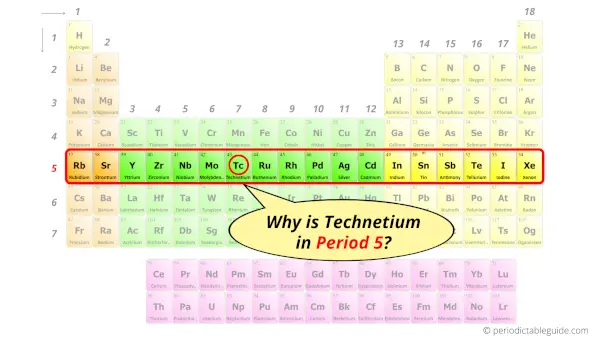
Why is Technetium in Period 5?
Let me ask you a question.
How many shells does technetium have?
It’s 5. Right?
You have already seen the bohr model of technetium atom in the above table.
From the Bohr model, it can be found that the number of orbits or shells in technetium is 5. Hence, as technetium has 5 orbits, it lies in period 5 of the Periodic table.
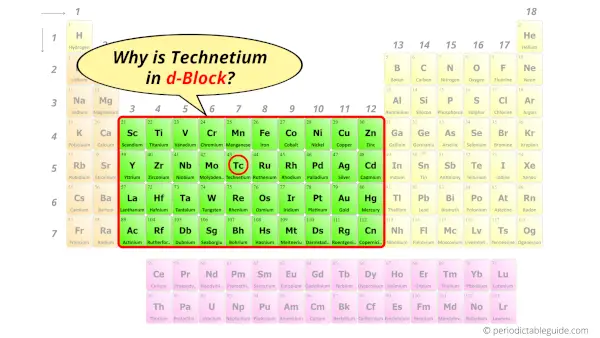
Why is Technetium in d-block?
Before knowing this reason, first of all I want to ask you a simple question.
How can you determine the blocks-wise position of elements?
The simple answer: The elements will lie in the s, p, d or f block will completely depend upon the subshell in which the last electron will enter.
For example; the electron configuration of technetium is [Kr] 5s2 4d5.
So the last electron of technetium enters the d-subshell or d-orbital.
Hence, technetium is the d-block element.
Is Technetium a Transition Metal? Why?
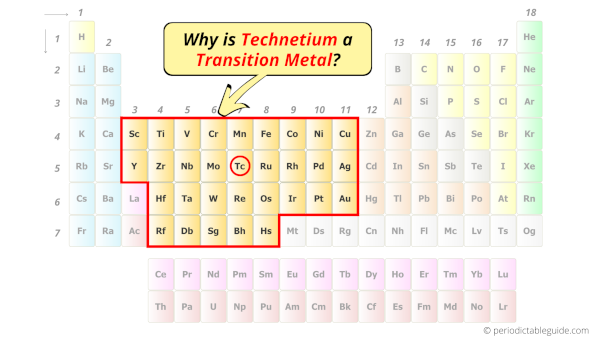
Yes, Titanium is a transition metal because it has incompletely filled d-orbital in its ground state.
Let me explain the exact meaning of this.
According to the definition of transition metals;
The element should compulsorily have incomplete d-orbitals, either in their ground state (M) or most common oxidation states (M1+, M2+, etc) then only they are called transition metals.
Now, the ground state of Technetium means its normal state in which it has neither gained nor lost any electron/s.
So the ground state of Technetium is Tc.
And the ground state electronic configuration of Technetium is [Kr] 5s2 4d5.
In this state, if we see the electron configuration of Technetium, then it possesses incomplete d-orbitals.
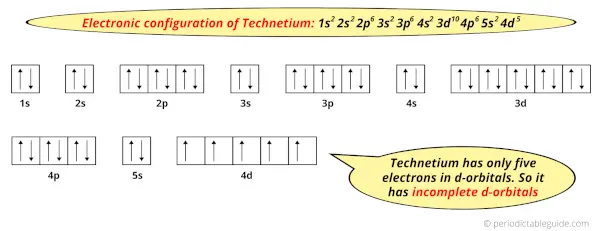
Because, there are only five electrons in the d-orbitals.
In order to have the complete d-orbitals, there must be 10 electrons in it.
But in the ground state electronic configuration of technetium, you can see that it has only 5 electrons in d-orbitals.
Thus, technetium has incomplete d-orbitals.
And hence, as technetium has incomplete d-orbitals, it is considered as a transition metal.
5 Interesting facts about Technetium
Interesting facts about technetium element are mentioned below.
- The name technetium was derived from the Greek word “technetos” meaning artificial.
- Technetium is a radioactive element and it is artificially prepared by humans.
- Initially, this element was named as masurium. But later on it was named technetium.
- Technetium is a very rare element and it is believed to be found in different types of stars.
- Technetium is the first artificially made element present in the periodic table.
Properties of Technetium
The physical and chemical properties of technetium element are mentioned below.
Physical properties of Technetium
Physical properties of technetium are mentioned below.
- Technetium is a solid metal having silvery grey metallic lustre.
- The melting point of technetium is 2157 °C and its boiling point is 4265 °C.
- The atomic mass of the most stable isotope of technetium is 98 u and its density is 11.5 g/cm3.
- The crystal structure of technetium is HCP (Hexagonal close packing).
Chemical properties of Technetium
Chemical properties of technetium are mentioned below.
- Technetium has incomplete d-orbitals, and hence it is classified as a transition metal on periodic table.
- Technetium has some isotopes whose half-life is only a few hours, while some isotopes have a half-life of 200,000 years to over a million years.
- Most common oxidation states of technetium are +7, +5 and +4.
- Technetium is soluble in nitric acid as well as concentrated sulphuric acid, but it is not soluble in hydrochloric acid.
Uses of Technetium
Uses of technetium are mentioned below.
- Technetium acts as a very good super conductor at the temperature below 11 K.
- The isotope 99Tc is used in medical radioactive isotope tests.
- The technetium is also used in small proportions in manufacturing of steels, which protects steel from corrosion.
Explore our New Interactive Periodic Table (with Rotating Bohr Models and More)

Details about this Periodic table:
- Access detailed info on all elements: atomic mass, electron configurations, charges, and more.
- View rotating Bohr models for all 118 elements.
- Get a free HD image of the Periodic Table.
Note: For future use, bookmark this Periodic table or visit “PeriodicTableGuide.com”
External resources:
- Technetium – Element information, properties and uses | Periodic Table. (n.d.). Technetium – Element Information, Properties and Uses | Periodic Table. https://www.rsc.org/periodic-table/element/43/technetium
- It’s Elemental – The Element Technetium. (n.d.). It’s Elemental – the Element Technetium. https://education.jlab.org/itselemental/ele043.html
- Armstrong, J. T. (2008, October 16). Technetium: The Element That Was Discovered Twice. NIST. https://www.nist.gov/publications/technetium-element-was-discovered-twice
- Radionuclide Basics: Technetium-99 | US EPA. (2015, April 14). US EPA. https://www.epa.gov/radiation/radionuclide-basics-technetium-99
- Hackney, J. C. (1951, April). Technetium—Element 43. Journal of Chemical Education, 28(4), 186. https://doi.org/10.1021/ed028p186
