This is a SUPER easy guide on Copper element.
In fact, the table mentioned below is the perfect information box (Which gives you every single detail about the Copper element in Periodic table.)
So if you want to know anything about Copper element, then this guide is for you.
Let’s finish this very quickly.
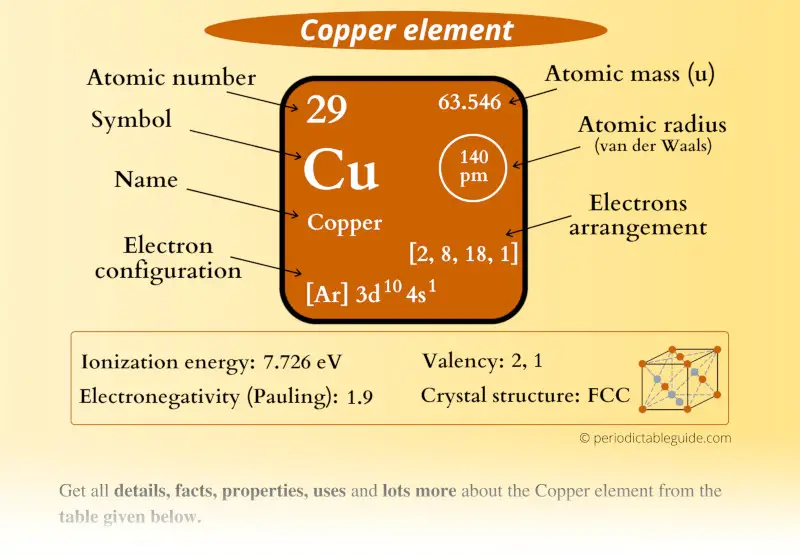
Copper Element (Cu) Information
| Appearance |  Reddish orange metallic luster |
| State (at STP) | Solid |
| Position in Periodic table | 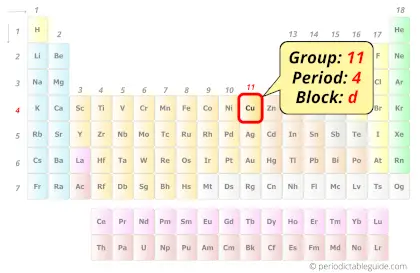 Group: 11, Period: 4, Block: d |
| Category | 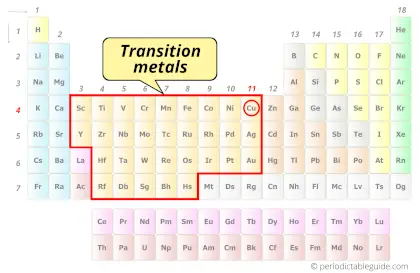 Transition metals |
| Atomic number or Protons | 29 |
| Neutrons | 35 |
| Electrons | 29 |
| Symbol | Cu |
| Atomic mass |  63.546 u |
| Electrons arrangement or Bohr model | 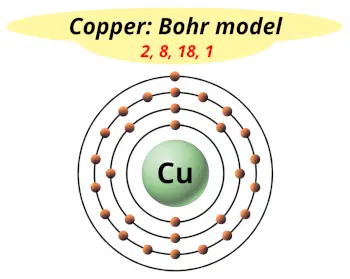 2, 8, 18, 1 |
| Electronic configuration | [Ar] 3d10 4s1 |
| Atomic radius | 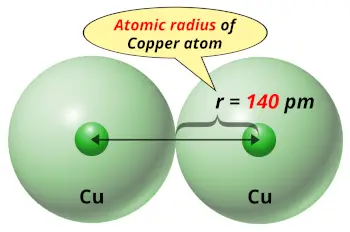 140 picometers (van der Waals radius) |
| 1st Ionization energy | 7.726 eV |
| Electronegativity | 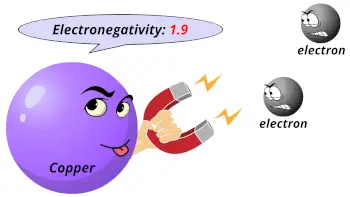 1.9 (Pauling scale) |
| Crystal structure | 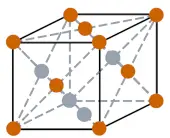 FCC (Face centered cubic) |
| Melting point | 1357.7 K or 1084.6 °C or 1984.3 °F |
| Boiling point | 2835 K or 2562 °C or 4643 °F |
| Density | 8.96 g/cm3 |
| Main isotope | 63Cu (69.1%) and 65Cu (30.8%) |
| Who discovered Copper and when? | Carl Wilhelm Scheele in 1771 |
| CAS number | 7440-50-8 |
Copper in Periodic table
Copper element is in group 11 and period 4 of the Periodic table. Copper is the d-block element and it belongs to transition metals group.
| H | He | ||||||||||||||||
| Li | Be | B | C | N | O | F | Ne | ||||||||||
| Na | Mg | Al | Si | P | S | Cl | Ar | ||||||||||
| K | Ca | Sc | Ti | V | Cr | Mn | Fe | Co | Ni | Cu | Zn | Ga | Ge | As | Se | Br | Kr |
| Rb | Sr | Y | Zr | Nb | Mo | Tc | Ru | Rh | Pd | Ag | Cd | In | Sn | Sb | Te | I | Xe |
| Cs | Ba | La* | Hf | Ta | W | Re | Os | Ir | Pt | Au | Hg | Tl | Pb | Bi | Po | At | Rn |
| Fr | Ra | Ac** | Rf | Db | Sg | Bh | Hs | Mt | Ds | Rg | Cn | Nh | Fl | Mc | Lv | Ts | Og |
| *Ce | Pr | Nd | Pm | Sm | Eu | Gd | Tb | Dy | Ho | Er | Tm | Yb | Lu | ||||
| **Th | Pa | U | Np | Pu | Am | Cm | Bk | Cf | Es | Fm | Md | No | Lr |
←Move to: Nickel (Ni) element – Periodic Table
→Move to: Zinc (Zn) element – Periodic Table
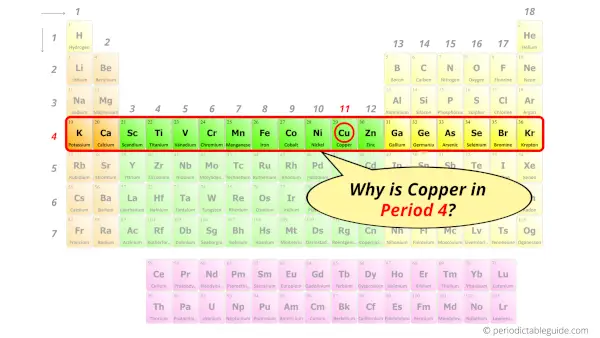
Why is Copper in Period 4?
Let me ask you a question.
How many shells does copper atom have?
It’s 4. Right?
You have already seen the bohr model of copper atom in the above table.
From the Bohr model, it can be found that the number of orbits or shells in copper is 4. Hence, as copper has 4 orbits, it lies in period 4 of the Periodic table.
Is Copper a Transition Metal? Why?
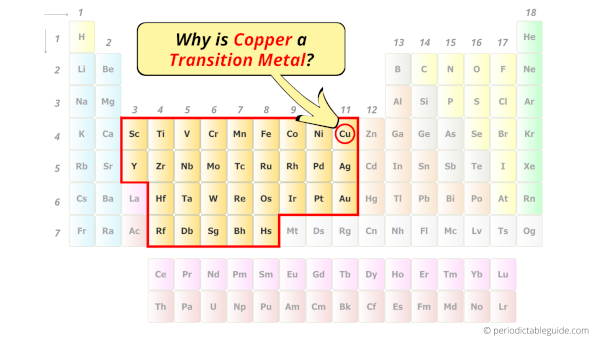
Yes, Copper is a transition metal because it has incompletely filled d-orbital in its most common oxidation state (Cu2+).
Let me explain the exact meaning of this.
According to the definition of transition metals;
The element should compulsorily have incomplete d-orbitals, either in their ground state (M) or most common oxidation states (M1+, M2+, etc) then only they are called transition metals.
Now, the ground state of copper means its normal state in which it has neither gained nor lost any electron/s (i.e Cu).
And the most common oxidation state of copper is Cu2+, because most commonly copper loses 2 electrons during a chemical reaction.
Now,
The electron configuration of Cu is: [Ar] 3d10 4s1 and
The electron configuration of Cu2+ is: [Ar] 3d9
So, in this most common oxidation state of copper (Cu2+), if we see the electron configuration, then it possesses incomplete d-orbitals.
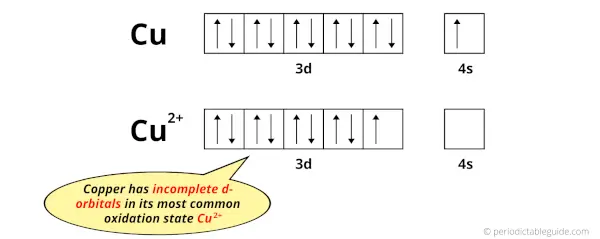
You can see that all the d-orbitals are completely filled (all the 10 electrons are present) in the elemental state (Cu) but they are incomplete (only 9 electrons are present) in their oxidation state (Cu2+).
In short, copper element have incomplete d-orbitals in its oxidation state (Cu2+).
Hence, according to the definition mentioned above, copper is a transition metal.
8 Interesting facts about Copper
Interesting facts about copper element are mentioned below.
- The word copper was derived from the latin word “cuprum”.
- Approximately 2/3rd of the Copper is found mostly from the igneous rocks on the earth.
- In the earth’s crust, copper is found in abundance (around 50 ppm).
- After iron and aluminum, copper is the 3rd most used metal in the industries.
- Most of the copper produced nowadays is used in manufacturing electrical wires and other electrical transmissions.
- Most of the metals on the periodic table are silvery grey in color, but copper is the only metal in reddish orange color.
- Copper metal is the 2nd best thermal conductor as well as electrical conductor after silver.
- Around 80% of copper present today can be recycled and it can be used again and again.
Properties of Copper
The physical and chemical properties of copper element are mentioned below.
Physical properties of Copper
Physical properties of copper are mentioned below.
- Copper is a transition metal that has a reddish orange metallic luster.
- The atomic mass of copper is 63.546 u and its density is 8.96 g/cm3.
- Copper is a ductile metal that can be drawn into thin wires.
- The melting point of copper is 1084.6 °C and its boiling point is 2562 °C.
- Copper has naturally occurring isotopes as well as it has synthetic isotopes too. Out of the naturally occurring isotopes, 63Cu is the most abundant (around 69%).
- Copper is a very good conductor of heat and electricity.
Chemical properties of Copper
Chemical properties of copper are mentioned below.
- Copper atom contain incomplete d-orbitals in its most common oxidation state (Cu2+), hence copper is classified as a transition metal on the periodic table.
- Copper slowly reacts with water and air and it turns dull-greenish in color. This is because the oxidation reaction of copper takes place.
- The copper element present in a sample gives a greenish color in a flame test.
Uses of Copper
Uses of copper are mentioned below.
- Copper is also an essential element found in the human body for the formation of red blood cells.
- Copper is also used as an alloying metal with other metals which gives different properties. Most common copper alloys are bronze and brass.
- Copper metal is used in manufacturing plumbing pipes, coins as well as cookwares.
- Copper is a natural antibacterial agent. Hence the brass (which is an alloy of copper) is used in door handles of public buildings, which prevents disease transmission.
- Brass is also used in making ship hulls which prevents the growth of algae and other microorganisms.
- As copper is an excellent conductor of electricity, it is also used in buildings as an earthing to protect against lightning.
- Copper is present in most of the electrical devices including TV, radio, laptops, smart phones, etc.
Explore our New Interactive Periodic Table (with Rotating Bohr Models and More)

Details about this Periodic table:
- Access detailed info on all elements: atomic mass, electron configurations, charges, and more.
- View rotating Bohr models for all 118 elements.
- Get a free HD image of the Periodic Table.
Note: For future use, bookmark this Periodic table or visit “PeriodicTableGuide.com”
External resources:
- Copper – Wikipedia. (2018, August 22). Copper – Wikipedia. https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Copper
- Copper – Element information, properties and uses | Periodic Table. (n.d.). Copper – Element Information, Properties and Uses | Periodic Table. https://www.rsc.org/periodic-table/element/29/copper
- P. (n.d.). Copper | Cu (Element) – PubChem. Copper | Cu (Element) – PubChem. https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/element/Copper
- It’s Elemental – The Element Copper. (n.d.). It’s Elemental – the Element Copper. https://education.jlab.org/itselemental/ele029.html
- Copper. (n.d.). Copper. https://webbook.nist.gov/cgi/cbook.cgi?ID=7440-50-8
