This is a SUPER easy guide on Phosphorus element.
In fact, the table mentioned below is the perfect information box (Which gives you every single detail about the Phosphorus element in Periodic table.)
So if you want to know anything about the Phosphorus element, then this guide is for you.
Let’s dive right into it!
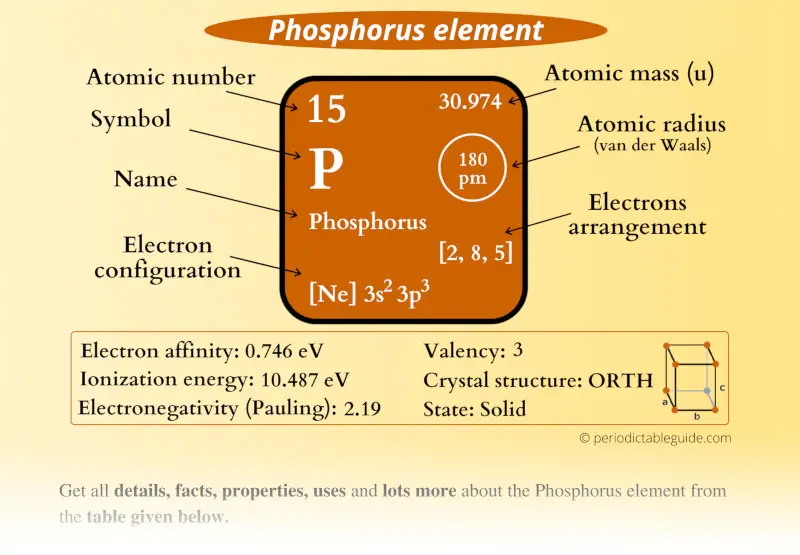
Phosphorus Element (P) Information
| Appearance |  Waxy white or yellow, Red, Violet, Metallic color |
| State (at STP) | Solid |
| Position in Periodic table | 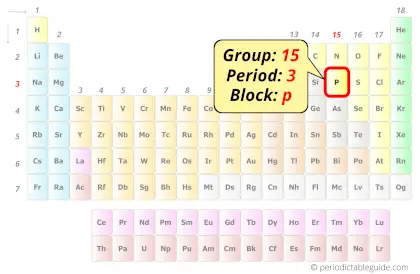 Group: 15, Period: 3, Block: p |
| Category | 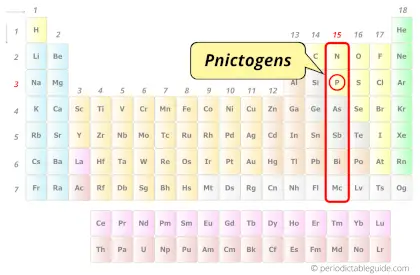 Pnictogens |
| Atomic number or Protons | 15 |
| Neutrons | 16 |
| Electrons | 15 |
| Symbol | P |
| Atomic mass | 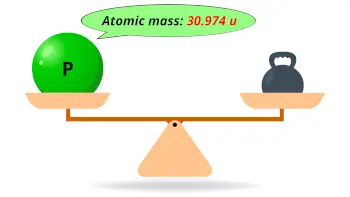 30.974 u |
| Electrons arrangement or Bohr model | 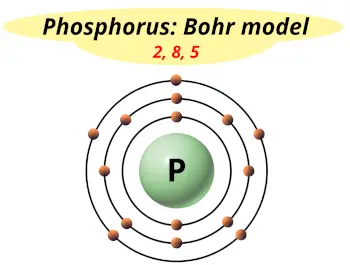 2, 8, 5 |
| Electronic configuration | [Ne] 3s2 3p3 |
| Atomic radius | 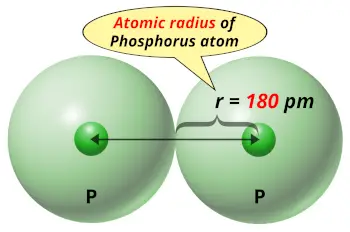 180 picometers (van der Waals radius) |
| Valence electrons | 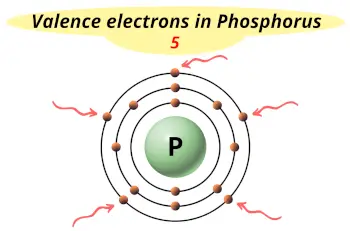 5 |
| 1st Ionization energy | 10.487 eV |
| Electronegativity | 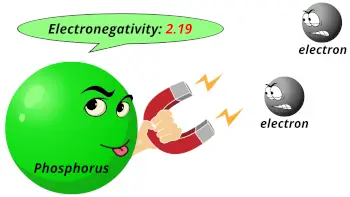 2.19 (Pauling scale) |
| Crystal structure | 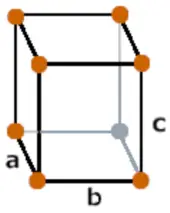 Orthorhombic |
| Melting point of Phosphorus (white) | 317.3 K or 44.15 °C or 111.5 °F |
| Boiling point of Phosphorus (white) | 553.7 K or 280.5 °C or 536.9 °F |
| Density | 1.823 g/cm3 |
| Main isotope | 31P |
| Who discovered Phosphorus and when? |  Hennig Brand in 1669 |
| CAS number | 12185-10-3 (white phosphorus) 7723-14-0 (red phosphorus) |
Phosphorus in Periodic table
Phosphorus element is in group 15 and period 3 of the Periodic table. Phosphorus is the p-block element and it belongs to Pnictogens group.
| H | He | ||||||||||||||||
| Li | Be | B | C | N | O | F | Ne | ||||||||||
| Na | Mg | Al | Si | P | S | Cl | Ar | ||||||||||
| K | Ca | Sc | Ti | V | Cr | Mn | Fe | Co | Ni | Cu | Zn | Ga | Ge | As | Se | Br | Kr |
| Rb | Sr | Y | Zr | Nb | Mo | Tc | Ru | Rh | Pd | Ag | Cd | In | Sn | Sb | Te | I | Xe |
| Cs | Ba | La* | Hf | Ta | W | Re | Os | Ir | Pt | Au | Hg | Tl | Pb | Bi | Po | At | Rn |
| Fr | Ra | Ac** | Rf | Db | Sg | Bh | Hs | Mt | Ds | Rg | Cn | Nh | Fl | Mc | Lv | Ts | Og |
| *Ce | Pr | Nd | Pm | Sm | Eu | Gd | Tb | Dy | Ho | Er | Tm | Yb | Lu | ||||
| **Th | Pa | U | Np | Pu | Am | Cm | Bk | Cf | Es | Fm | Md | No | Lr |
←Move to: Silicon (Si) element – Periodic Table
→Move to: Sulfur (S) element – Periodic Table
Why is Phosphorus in Group 15?
Do you know, how many electrons can be accommodated in the first shell, second shell, third shell, fourth shell, etc…?
Here is the table showing the capacity of orbits to hold electrons.
Number of electrons in shells.
| Orbit / Shell (n) | Maximum no. of electrons this orbit can hold |
| K shell, n = 1 | 2 × 1² = 2 |
| L shell, n = 2 | 2 × 2² = 8 |
| M shell, n = 3 | 2 × 3² = 18 |
| N shell, n = 4 | 2 × 4² = 32 |
Thus,
- 1st shell can hold 2 electrons.
- 2nd shell can hold 8 electrons.
- 3rd shell can hold 18 electrons.
- 4th shell can hold 32 electrons.
Now the atomic number of phosphorus (P) is 15.
Hence the phosphorus element has electrons arrangement 2, 8, 5.
This electron arrangement indicates that the outermost orbit of phosphorus element (P) has 5 electrons.
Hence, it lies in group 15.
Why is Phosphorus in Period 3?
Let me ask you a question.
How many shells does phosphorus have?
It’s 3. Right?
You have already seen the bohr model of phosphorus element in the above table.
From the Bohr model, it can be found that the number of orbits or shells in phosphorus is 3. Hence, as phosphorus has 3 orbits, it lies in period 3 of the Periodic table.
Why is Phosphorus in p-block?
Before knowing this reason, first of all I want to ask you a simple question.
How can you determine the blocks-wise position of elements?
The simple answer: The elements will lie in the s, p, d or f block will completely depend upon the subshell in which the last electron will enter.
For example; the electron configuration of phosphorus is [Ne] 3s2 3p3.
So the last electron of phosphorus enters the p-subshell or p-orbital.
Hence, phosphorus is the p-block element.
7 Interesting facts about Phosphorus
Interesting facts about phosphorus element are mentioned below.
- According to the study in 2013, meteorites may have brought phosphorus on the earth.
- Average human body contains around 750 grams of phosphorus. [1]. In the human body, phosphorus is present in bones as well as DNA and RNA.
- Pure phosphorus is harmful for the human body.
- White phosphorus when comes in contact with the body, it causes chemical burns.
- The amount of phosphorus is abundant in the earth’s crust and it is about 1050 ppm by weight.
- Phosphorus is the 11th most abundant element in the earth crust.
- The first striking matchstick was made of white phosphorus combined with other elements, but nowadays matchsticks are made of phosphorus sesquisulfide (whose chemical formula is P4 S3).
Properties of Phosphorus
The physical and chemical properties of phosphorus element are mentioned below.
Physical properties of Phosphorus
Physical properties of phosphorus are mentioned below.
- Phosphorus is a waxy white in color. Apart from this the phosphorus is also found in yellow, red, and metallic colors.
- White phosphorus slightly glows in the air.
- Phosphorus is a nonmetal and it is a bad conductor of heat and electricity.
- The melting point of white phosphorus is 44.15 °C and its boiling point is 280.5 °C.
- The metallic colored phosphorus has an ability to conduct electricity.
Chemical properties of Phosphorus
Chemical properties of phosphorus are mentioned below.
- Phosphorus is a chemically reactive element and it is not found in a free state, but is always found as a compound with other elements.
- Phosphorus has many isotopes, but out of them only one is stable (i.e 31P) and has an abundance of 100%.
- When phosphorus is heated with metals it forms phosphides.
- Phosphorus element can easily combine with halogens.
- White phosphorus is very reactive to oxygen and so it is kept inside water in labs.

Uses of Phosphorus
Uses of phosphorus are mentioned below.
- Red phosphorus is used on the side of a matchstick box for igniting the matchstick.
- Phosphorus is mainly used in preparation of fertilizers for plants.
- Phosphorus is also used in making of flares, LEDs, matchsticks as well as it is used in production of steel.
- Phosphorus containing compound, Sodium triphosphate is used in making detergents and food preservatives.
- Dicalcium phosphate is used in toothpaste which acts as a polishing agent.
Explore our New Interactive Periodic Table (with Rotating Bohr Models and More)

Details about this Periodic table:
- Access detailed info on all elements: atomic mass, electron configurations, charges, and more.
- View rotating Bohr models for all 118 elements.
- Get a free HD image of the Periodic Table.
Note: For future use, bookmark this Periodic table or visit “PeriodicTableGuide.com”
External resources:
- Phosphorus – American Chemical Society. (n.d.). American Chemical Society. https:///greenchemistry/research-innovation/endangered-elements/phosphorus.html
- Krafft, F. (1969, September). Phosphorus. From Elemental Light to Chemical Element. Angewandte Chemie International Edition in English, 8(9), 660–671. https://doi.org/10.1002/anie.196906601
- Phosphorus – Element information, properties and uses | Periodic Table. (n.d.). Phosphorus – Element Information, Properties and Uses | Periodic Table. https://www.rsc.org/periodic-table/element/15/phosphorus
- Phosphorus – Wikipedia. (2011, November 19). Phosphorus – Wikipedia. https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Phosphorus
