This is a SUPER easy guide on Indium element.
In fact, the table mentioned below is the perfect information box (Which gives you every single detail about the Indium element in Periodic table.)
So if you want to know anything about Indium element, then this guide is for you.
Let’s finish this very quickly.
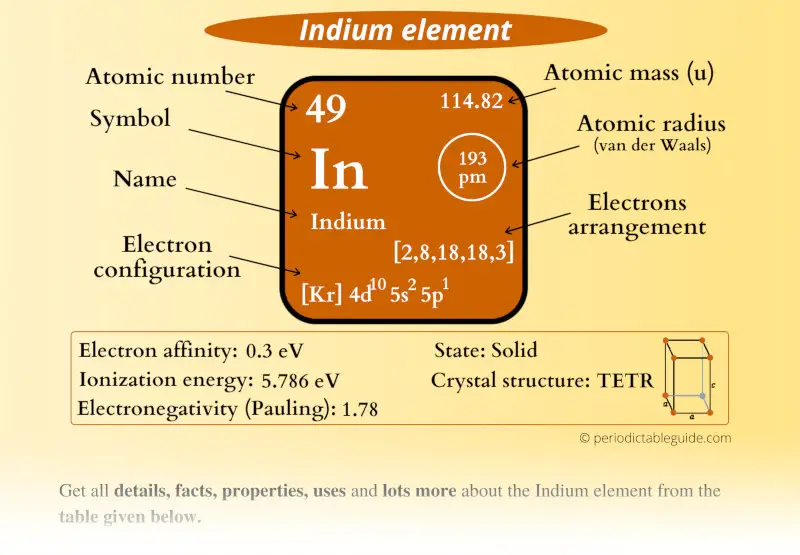
Indium Element (In) Information
| Appearance |  Silvery lustrous gray colored |
| State (at STP) | Solid |
| Position in Periodic table | 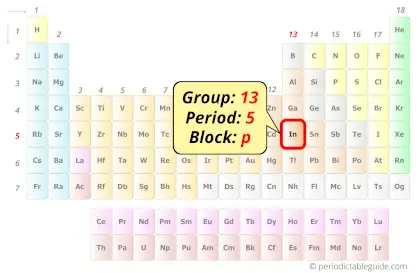 Group: 13, Period: 5, Block: p |
| Category | 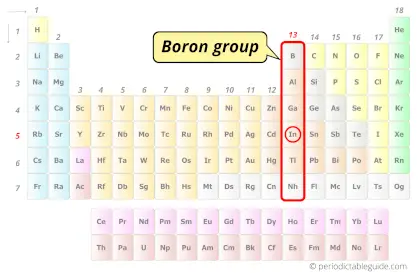 Boron group |
| Atomic number or Protons | 49 |
| Neutrons | 66 |
| Electrons | 49 |
| Symbol | In |
| Atomic mass | 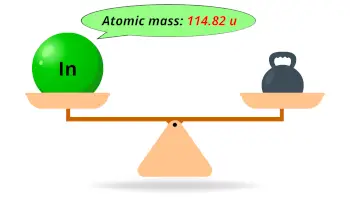 114.82 u |
| Electrons arrangement or Bohr model | 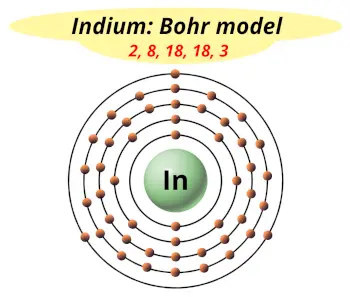 2, 8, 18, 18, 3 |
| Electronic configuration | [Kr] 4d10 5s2 5p1 |
| Atomic radius | 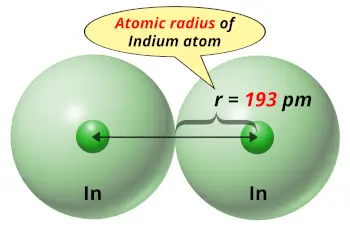 193 picometers (van der Waals radius) |
| Valence electrons | 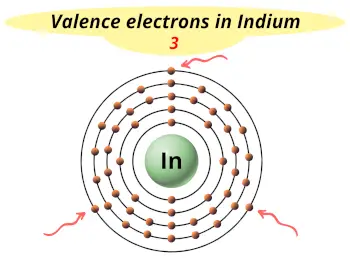 3 |
| 1st Ionization energy | 5.786 eV |
| Electronegativity | 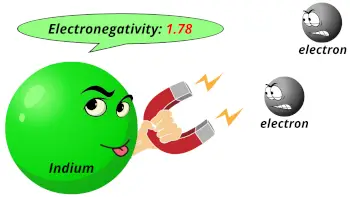 1.78 (Pauling scale) |
| Crystal structure | 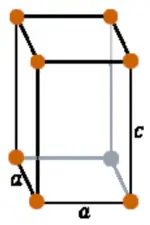 TETR (Tetragonal) |
| Melting point | 429.7 K or 156.5 °C or 313.8 °F |
| Boiling point | 2345 K or 2072 °C or 3762 °F |
| Density | 7.31 g/cm3 |
| Main isotope | 115In |
| Who discovered Indium and when? |  Hieronymous Theodor Richter and Ferdinand Reich (in 1863) |
| CAS number | 7440-74-6 |
Indium in Periodic table
Indium element is in group 13 and period 5 of the Periodic table. Indium is the p-block element and it belongs to boron group.
| H | He | ||||||||||||||||
| Li | Be | B | C | N | O | F | Ne | ||||||||||
| Na | Mg | Al | Si | P | S | Cl | Ar | ||||||||||
| K | Ca | Sc | Ti | V | Cr | Mn | Fe | Co | Ni | Cu | Zn | Ga | Ge | As | Se | Br | Kr |
| Rb | Sr | Y | Zr | Nb | Mo | Tc | Ru | Rh | Pd | Ag | Cd | In | Sn | Sb | Te | I | Xe |
| Cs | Ba | La* | Hf | Ta | W | Re | Os | Ir | Pt | Au | Hg | Tl | Pb | Bi | Po | At | Rn |
| Fr | Ra | Ac** | Rf | Db | Sg | Bh | Hs | Mt | Ds | Rg | Cn | Nh | Fl | Mc | Lv | Ts | Og |
| *Ce | Pr | Nd | Pm | Sm | Eu | Gd | Tb | Dy | Ho | Er | Tm | Yb | Lu | ||||
| **Th | Pa | U | Np | Pu | Am | Cm | Bk | Cf | Es | Fm | Md | No | Lr |
←Move to: Cadmium (Cd) element – Periodic Table
→Move to: Tin (Sn) element – Periodic Table
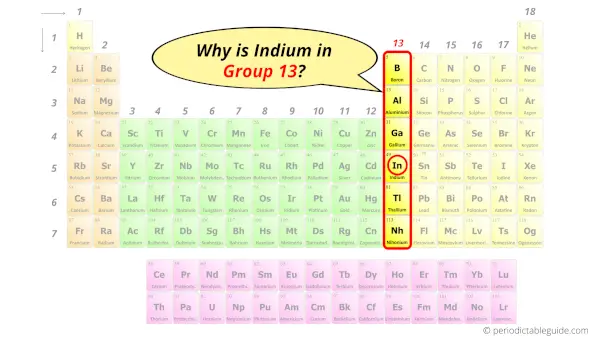
Why is Indium in Group 13?
Do you know, how many electrons can be accommodated in the first shell, second shell, third shell, fourth shell, etc…?
Here is the table showing the capacity of orbits to hold electrons.
Number of electrons in shells.
| Orbit / Shell (n) | Maximum no. of electrons this orbit can hold (2 × n2) |
| K shell, n = 1 | 2 × 1² = 2 |
| L shell, n = 2 | 2 × 2² = 8 |
| M shell, n = 3 | 2 × 3² = 18 |
| N shell, n = 4 | 2 × 4² = 32 |
| . . . | . . . |
Thus,
- 1st shell can hold 2 electrons.
- 2nd shell can hold 8 electrons.
- 3rd shell can hold 18 electrons.
- 4th shell can hold 32 electrons, and so on.
Now the atomic number of indium (In) is 49.
Hence the electron arrangement in indium is 2, 8, 18, 18, 3. And the electron configuration of indium is 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6 3d10 4s2 4p6 4d10 5s2 5p1.
This electron arrangement and electron configuration indicates that the outermost orbit (i.e orbit number 5) of indium atom has 3 electrons.
Hence, it lies in group 13.
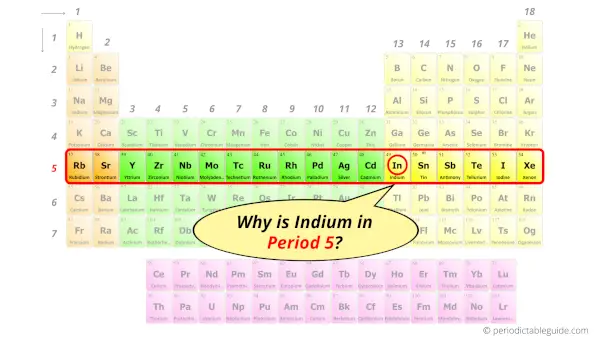
Why is Indium in Period 5?
Let me ask you a question.
How many shells does indium have?
It’s 5. Right?
You have already seen the bohr model of indium atom in the above table.
From the Bohr model, it can be found that the number of orbits or shells in indium is 5. Hence, as indium has 5 orbits, it lies in period 5 of the Periodic table.
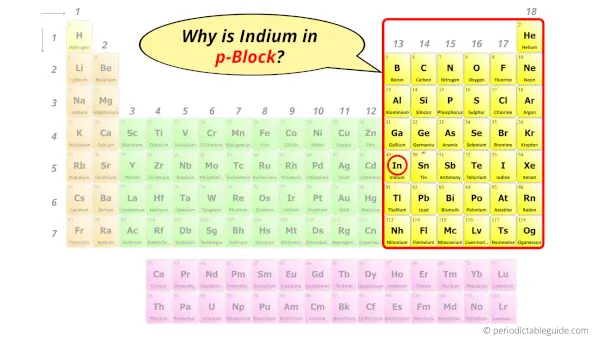
Why is Indium in p-block?
Before knowing this reason, first of all I want to ask you a simple question.
How can you determine the blocks-wise position of elements?
The simple answer: The elements will lie in the s, p, d or f block will completely depend upon the subshell in which the last electron will enter.
For example; the electron configuration of indium is [Kr] 4d10 5s2 5p1.
So the last electron of indium enters the p-subshell or p-orbital.
Hence, indium is the p-block element.
7 Interesting facts about Indium
Interesting facts about indium element are mentioned below.
- The name indium was derived from the latin word “indicum”, which means violet.
- Indium is the 61st most abundant element found from the earth’s crust.
- The proportion of indium in earth’s crust is estimated to be 0.1 ppm (parts per million).
- If we talk about the abundance of indium by weight, then its proportion is 250 parts per billion in the earth’s crust.
- Canada is the leading producer of indium and it produces around 75 tons of indium annually.
- Indium element was discovered by Hieronymous Theodor Richter and Ferdinand Reich in 1863.
- Indium is generally obtained during the processing of zinc ore.
Properties of Indium
The physical and chemical properties of indium element are mentioned below.
Physical properties of Indium
Physical properties of indium are mentioned below.
- Indium is a solid metal that has a silvery lustrous gray color.
- Indium is a soft metal and when it is bent, it produces screaming or cracking sound.
- The melting point of indium is 156.5 °C and its boiling point is 2072 °C.
- The atomic mass of indium is 114.82 u and its density is 7.31 g/cm3.
- Indium has a tetragonal crystal structure.
- Indium has various isotopes, but out of those isotopes, the 115In is the most abundant (around 95%).
Chemical properties of Indium
Chemical properties of indium are mentioned below.
- Indium has 3 valence electrons, and it loses these 3 electrons during a chemical reaction to become stable.
- Indium metal does not show any reaction with water.
- Indium can react with halides (which are strong oxidizing agents).
- The first ionization energy of indium is 5.786 eV.
- Electronegativity of indium is 1.78 on the Pauling scale.
Uses of Indium
Uses of indium are mentioned below.
- Indium tin oxide (ITO) is a compound which contains indium is widely used in LCD’s.
- Indium is also used as an alloying element with other metals, to improve their properties.
- Indium is alloyed with gold in small proportions which gives hardness to gold.
- As indium has low melting point, it is used in manufacturing of fusible plugs.
- Indium is also used as a coating material on high speed bearings as well as other metal surfaces.
- Apart from this, indium is also used in electrical devices like thermistors, rectifiers, etc.
Explore our New Interactive Periodic Table (with Rotating Bohr Models and More)

Details about this Periodic table:
- Access detailed info on all elements: atomic mass, electron configurations, charges, and more.
- View rotating Bohr models for all 118 elements.
- Get a free HD image of the Periodic Table.
Note: For future use, bookmark this Periodic table or visit “PeriodicTableGuide.com”
External resources:
- Indium – American Chemical Society. (n.d.). American Chemical Society. https:///greenchemistry/research-innovation/endangered-elements/indium.html
- Indium | Chemistry. (2012, April 9). Chemistry. https://uwaterloo.ca/chemistry/international-year-chemistry/periodic-table-project/indium
- US GOV, N. O. (n.d.). INDIUM | CAMEO Chemicals | NOAA. INDIUM | CAMEO Chemicals | NOAA. https://cameochemicals.noaa.gov/chemical/25034
- It’s Elemental – The Element Indium. (n.d.). It’s Elemental – the Element Indium. https://education.jlab.org/itselemental/ele049.html
