This is a SUPER easy guide on Carbon element.
In fact, the table mentioned below is the perfect information box (Which gives you every single detail about the Carbon element in Periodic table.)
So if you want to know anything about Carbon element, then this guide is for you.
Let’s finish this very quickly.
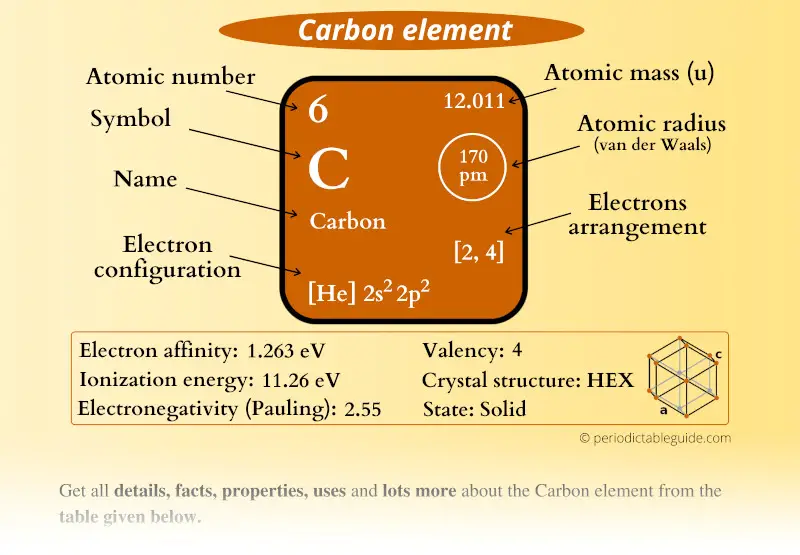
Carbon Element (C) Information
| Appearance |  Appearance of graphite: Shiny black Appearance of diamond: Clear |
| State (at STP) | Solid |
| Position in Periodic table | 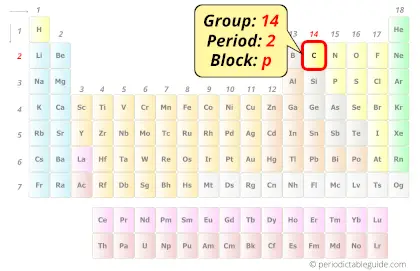 Group: 14, Period: 2, Block: p |
| Category | 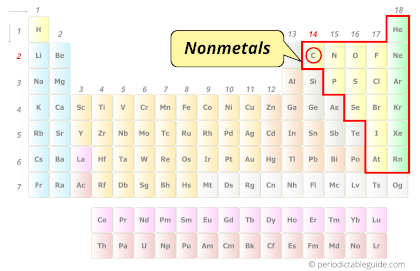 Nonmetals |
| Atomic number or Protons | 6 |
| Neutrons | 6 |
| Electrons | 6 |
| Symbol | C |
| Atomic mass |  12.011 u |
| Electrons arrangement or Bohr model | 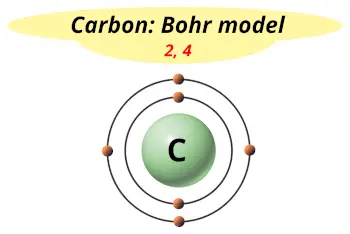 2, 4 |
| Electronic configuration | [He] 2s2 2p2 |
| Atomic radius | 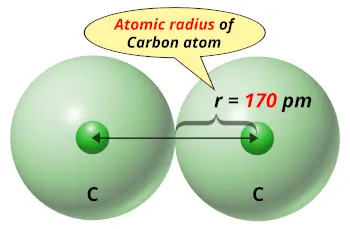 170 picometers (van der Waals radius) |
| Valence electrons | 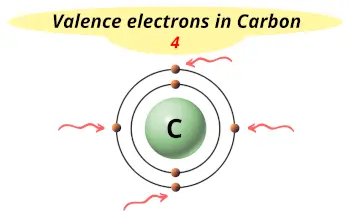 4 |
| 1st Ionization energy | 11.26 eV |
| Electronegativity | 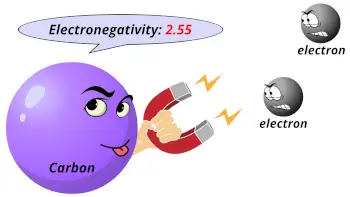 2.55 (Pauling scale) |
| Crystal structure | 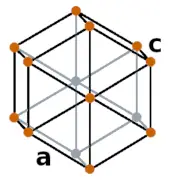 HEX (Hexagonal) |
| Density | Graphite: 2.267 g/cm3 Diamond: 3.515 g/cm3 |
| Main isotope | 12C, 13C, 14C |
| CAS number | Graphite: 7482-42-5 Diamond: 7482-40-3 |
Carbon in Periodic table
Carbon element is in group 14 and period 2 of the Periodic table. Carbon is the p-block element and it is classified as a nonmetal.
| H | He | ||||||||||||||||
| Li | Be | B | C | N | O | F | Ne | ||||||||||
| Na | Mg | Al | Si | P | S | Cl | Ar | ||||||||||
| K | Ca | Sc | Ti | V | Cr | Mn | Fe | Co | Ni | Cu | Zn | Ga | Ge | As | Se | Br | Kr |
| Rb | Sr | Y | Zr | Nb | Mo | Tc | Ru | Rh | Pd | Ag | Cd | In | Sn | Sb | Te | I | Xe |
| Cs | Ba | La* | Hf | Ta | W | Re | Os | Ir | Pt | Au | Hg | Tl | Pb | Bi | Po | At | Rn |
| Fr | Ra | Ac** | Rf | Db | Sg | Bh | Hs | Mt | Ds | Rg | Cn | Nh | Fl | Mc | Lv | Ts | Og |
| *Ce | Pr | Nd | Pm | Sm | Eu | Gd | Tb | Dy | Ho | Er | Tm | Yb | Lu | ||||
| **Th | Pa | U | Np | Pu | Am | Cm | Bk | Cf | Es | Fm | Md | No | Lr |
←Move to: Boron (B) element – Periodic Table
→Move to: Nitrogen (N) element – Periodic Table
Why is Carbon in Group 14 and Period 2 of the Periodic table?
Carbon is in group 14 because it has 4 valence electrons.
Carbon is in period 2 because it has 2 shells or orbits.
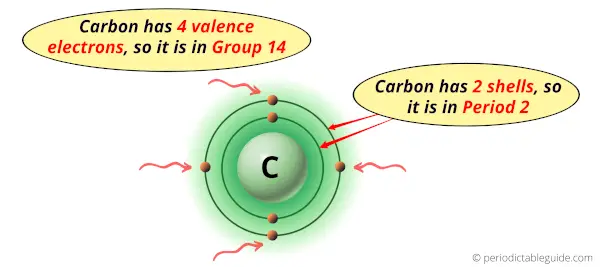
Now I’ll explain to you the perfect detailed reason why carbon is in group 14, why it is in period 2 and also why it is in p-block?
Let’s see the reasons one by one.
Why is Carbon in Group 14?
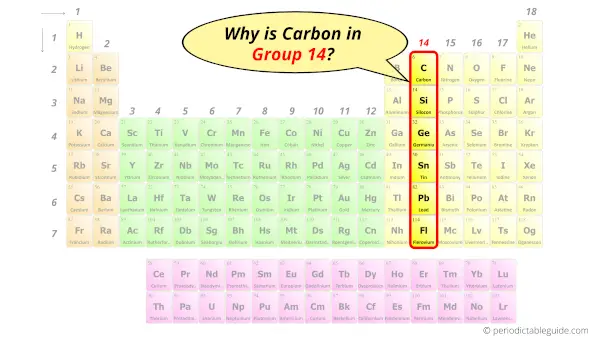
Do you know, how many electrons can be accommodated in the first shell, second shell, third shell, fourth shell, etc…?
Here is the table showing the capacity of orbits to hold electrons.
Number of electrons in shells.
| Orbit / Shell (n) | Maximum no. of electrons this orbit can hold |
| K shell, n = 1 | 2 × 1² = 2 |
| L shell, n = 2 | 2 × 2² = 8 |
| M shell, n = 3 | 2 × 3² = 18 |
| N shell, n = 4 | 2 × 4² = 32 |
Thus,
- 1st shell can hold 2 electrons.
- 2nd shell can hold 8 electrons.
- 3rd shell can hold 18 electrons.
- 4th shell can hold 32 electrons.
Now the atomic number of Carbon (C) is 6.
Hence, carbon element has the electrons arrangement 2, 4.
This electron arrangement indicates that the outermost orbit of Carbon (C) has 4 electrons.
Hence, it lies in group 14.
Why is Carbon in Period 2?
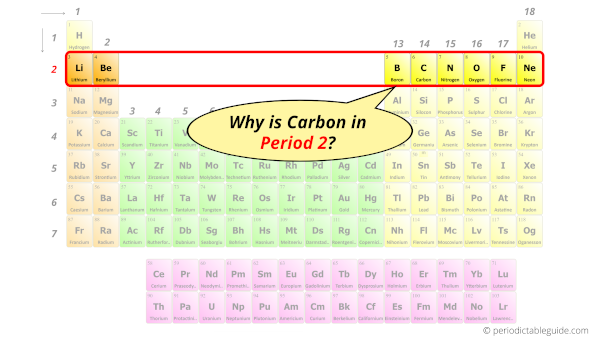
Let me ask you a question.
How many shells does carbon have?
It’s 2. Right?
You have already seen the bohr model of carbon atom in the above table.
From the Bohr model, it can be found that the number of orbits or shells in carbon is 2.
Hence, as carbon has 2 orbits, it lies in period 2 of the Periodic table.
Why is Carbon in p-block?
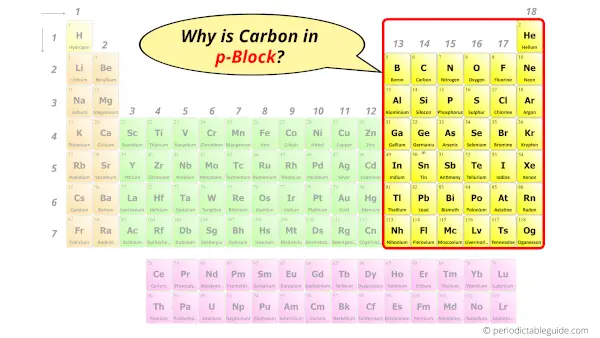
Before knowing this reason, first of all a simple question to you.
How can you determine the blocks wise position of elements?
The simple answer: The elements will lie in the s, p, d or f block will completely depend upon the subshell in which the last electron will enter.
For example; the electron configuration of carbon is [He] 2s2 2p2.
So the last electron of carbon enters the p-subshell or p-orbital.
Hence, carbon is the p-block element.
Why is Carbon Important?
Carbon is important for life because of many reasons, mentioned below.
#1 Carbon is present in all living organisms
Life does not exist without carbon.
Carbon is present in all the living organisms including humans, animals as well as plants.
#2 Carbon is also present on other planets and stars

Carbon is not only present on the earth, but it is also present on other planets in the form of carbon dioxide gas.
Carbon also exists on the sun and other stars.
#3 Carbon present in CO2 helps in maintaining earth’s temperature
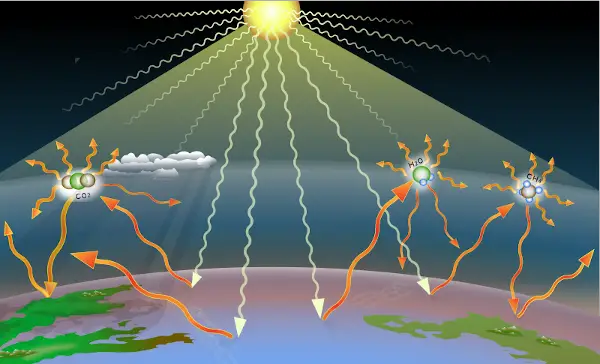
Carbon is also very important for the existence of life on the earth.
The carbon element is present in Carbon dioxide which is a green-house gas.
Carbon dioxide gas holds the heat of the solar radiation and does not allow the heat to escape from the earth’s atmosphere.
It reflects few of the solar radiations back to the earth and keeps the earth’s atmosphere warm.
If carbon dioxide were not present on the earth’s surface, then earth would remain frozen all time.
#4 Fuels used in daily life, also contains carbon

Carbon is very important as it is present in fuels like methane, coal, natural gas, petroleum, crude oil, etc. which are used by us in our day to day life.
#5 Animals exhale carbon in the form of CO2 which is taken by plants during photosynthesis
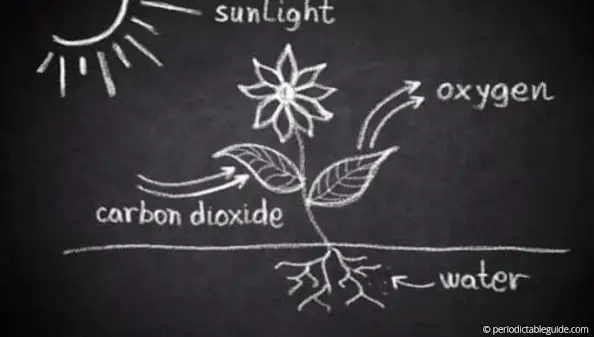
We inhale Oxygen gas and when this oxygen gas combines with the carbon in our body, it produces carbon dioxide.
This carbon dioxide is taken by the plants during the photosynthesis process and they give out pure oxygen.
What happens when Carbon is burnt?
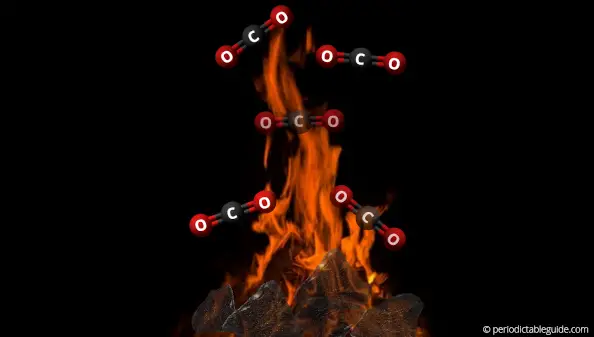
When carbon (C) is burnt in air, it reacts with oxygen (O2) and produces carbon dioxide (CO2).
Here is the chemical equation for the above reaction.
C + O2 ———> CO2
When the oxygen supply is reduced, the incomplete combustion takes place and carbon monoxide (CO) is obtained.
Here is the equation for the formation of carbon monoxide (CO).
2C + O2 ———> 2CO
Also see:
1). Why does boron burn green?
2). Why does Lithium emit red light on heating?
Why is Carbon black in color?
First of all, I want to clarify that the pure form of carbon is diamond and it is not black but it is colorless.

While graphite (the allotrope of carbon), is shiny black in color.

And the “soot” or “carbon black” is completely black in color.

Now the question is;
What decides the color of any substance?
The color of any substance depends upon the light absorption by the object.
If the object absorbs all the light, then it will appear completely black.
And if the object does not absorb any light (or it reflects all the light), then it will appear completely white.
Now, for graphite and diamond, the entire concept is based on how the electrons are bonded with each other.
You might be knowing that graphite is a good conductor of electricity. That means graphite has delocalized electrons which are responsible for electric current.
Also, these delocalized electrons absorb most of the light.
And as the light is absorbed, it appears shiny black in color.
While in diamond, the adjacent atoms are covalently bonded with each other. And so, these bonded electrons do not absorb any radiation. Also the structure of diamond is such that most of the light passes through it.
Hence, diamond appears to be colorless.
Note: Not all the diamonds are colorless.

There may occur some impurities in the diamond and due to these impurities, they appear to be of different color.
This color of diamond depends upon the type of impurities present in it.
Is Carbon present in human body? How much?
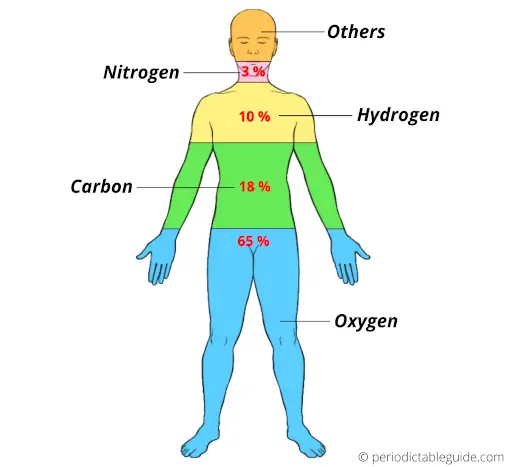
Yes carbon is present everywhere, in all living organisms.
In the human body, around 18.5 % of mass is because of carbon.
In other words, carbon consists of around 18.5 % of mass in the human body.
Carbon is the basic building block of our body. It is present in our body cells in the form of sugars like glucose.
Carbon enters our body from the food we intake.
Carbon is present in high quantities in foods which are rich in carbohydrates.
The molecules of proteins, lipids, carbohydrates, nucleic acids, contain carbon in it.
When we breathe in oxygen gas (O2), it combines with the carbon (C) of the body and finally carbon dioxide (CO2) is formed which comes out of the body when we exhale.
In this way carbon is a very important element of the human body.
Why Graphite is a good conductor of electricity and Diamond is not?
The simple answer: Graphite has free electrons which conducts electricity. While the diamond does not have free electrons, so it does not conduct electricity.
Explanation:
Graphite and diamond are the two different allotropes of carbon.
That means both of them are made up of carbon only, but they have a different crystal structure.
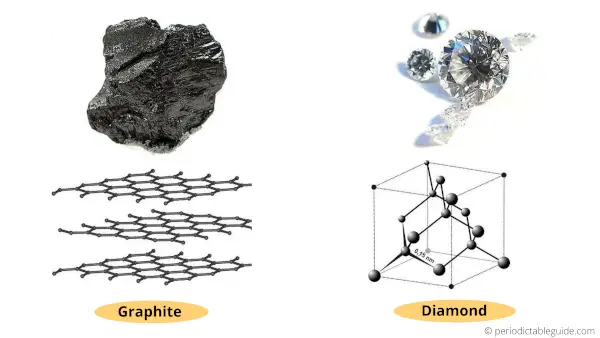
Carbon has a valency of 4. Hence it has a tendency to form 4 bonds.
Graphite has a crystal structure in which there are only 3 covalent bonds formed by the carbon atoms.
One electron remains delocalized and it is free to flow between the layers of graphite.
So when the electric current is allowed to pass through the graphite, it passes very easily because of the free electrons present in it.
Hence graphite is a good conductor of electricity.
Now diamond is also made up of carbon atoms. But in diamond, all the four valence electrons of carbon are covalently bonded with other adjacent atoms.
Thus, there are no free electrons to conduct electricity.
Hence, diamond is a bad conductor of electricity.
Why is Carbon more electronegative than silicon?
First of all, what is electronegativity?
Electronegativity: Electronegativity is a tendency to attract the shared pair of electrons.
For example, when two atoms are bonded with each other by sharing of electrons, the shared pair of electrons remains attracted towards one of the atoms.
The atom which has more electronegativity attracts the electron pair towards itself.
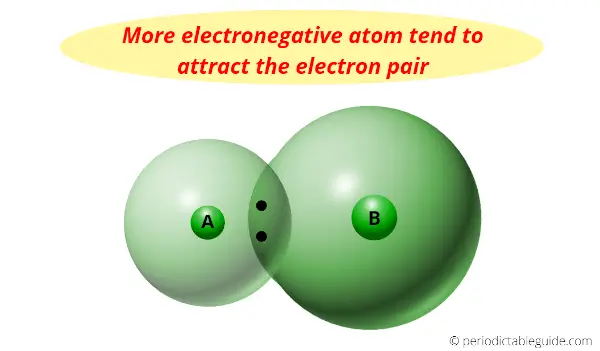
Now the question is, why is Carbon more electronegative than silicon?
Answer:
Carbon atom is smaller in size as compared to Silicon.
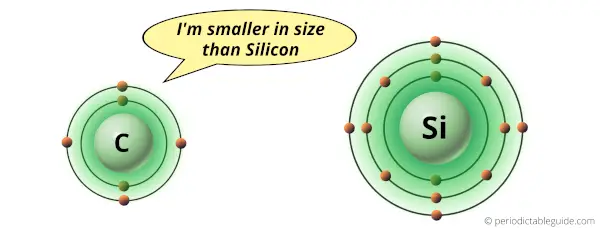
Due to small size of carbon atom, it attracts the shared electron pair with a greater force.
While silicon atom is bigger in size, so it attracts the electron pair with lesser force.
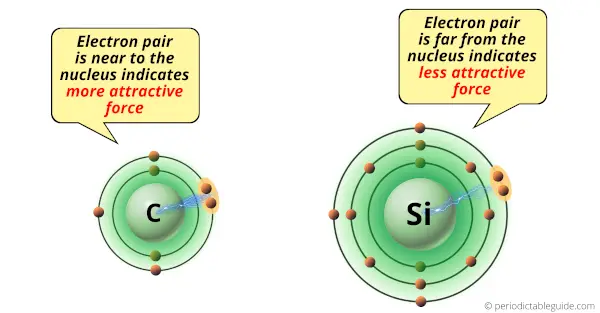
Hence, as the carbon atom is smaller than silicon atom, it is more electronegative than silicon.
Interesting facts about Carbon
Interesting facts about Carbon element are mentioned below.
- Carbon is also called a “King of elements” as it forms more compounds than any other elements.
- Around 18.5 % of our body mass is due to carbon element. The molecules of proteins, lipids, carbohydrates, nucleic acids, contain carbon in it.
- Graphite (the allotrope of carbon) is the only nonmetal which is a good conductor of electricity.
- Diamond (the allotrope of carbon) is the hardest substance known in the world.
- Carbon is the 4th most abundant element in the universe, while it is the 15th most abundant element found from the earth’s crust. And carbon has been known to humans since prehistoric time.
- Our body removes carbon in the form of carbon dioxide gas (CO2), when we exhale.
- Carbon present in CO2 helps in maintaining earth’s temperature. Carbon dioxide gas holds the heat of the solar radiation and does not allow the heat to escape from the earth’s atmosphere. It reflects few of the solar radiation back to the earth and keeps the earth warm.
Explore our New Interactive Periodic Table (with Rotating Bohr Models and More)

Details about this Periodic table:
- Access detailed info on all elements: atomic mass, electron configurations, charges, and more.
- View rotating Bohr models for all 118 elements.
- Get a free HD image of the Periodic Table.
Note: For future use, bookmark this Periodic table or visit “PeriodicTableGuide.com”
External resources:
- Carbon – Wikipedia. (2007, December 6). Carbon – Wikipedia. https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Carbon
- Carbon – Element information, properties and uses | Periodic Table. (n.d.). Carbon – Element Information, Properties and Uses | Periodic Table. https://www.rsc.org/periodic-table/element/6/carbon
- P. (n.d.). Carbon | C (Element) – PubChem. Carbon | C (Element) – PubChem. https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/element/Carbon
- It’s Elemental – The Element Carbon. (n.d.). It’s Elemental – the Element Carbon. https://education.jlab.org/itselemental/ele006.html
- Hazen, R. M. (n.d.). Why Carbon? Scientific American Blog Network. https://blogs.scientificamerican.com/observations/why-carbon/
