This is a SUPER easy guide on Fluorine element.
In fact, the table mentioned below is the perfect information box (Which gives you every single detail about the Fluorine element in Periodic table.)
So if you want to know anything about the Fluorine element, then this guide is for you.
Let’s dive right into it!
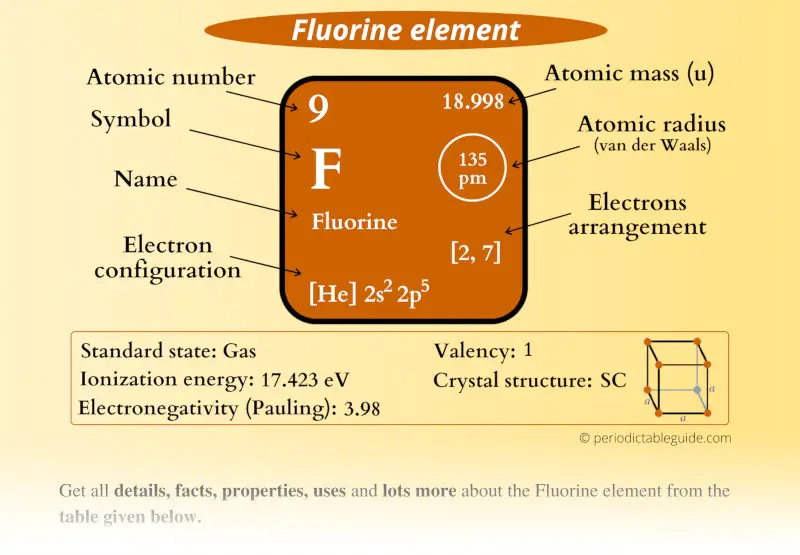
Fluorine Element (F) Information
| Appearance |  Gaseous state: Pale yellow Liquid state: Bright yellow Alpha fluorine: Opaque Beta fluorine: Transparent |
| State (at STP) | Gas |
| Position in Periodic table | 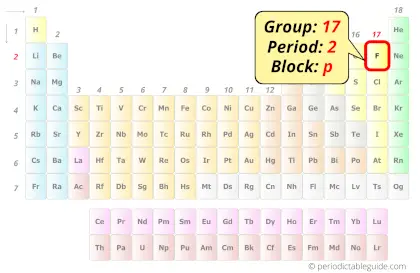 Group: 17, Period: 2, Block: p |
| Category | 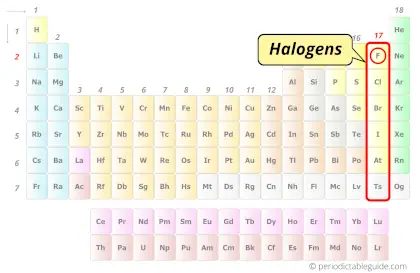 Nonmetals (Halogens) |
| Atomic number or Protons | 9 |
| Neutrons | 10 |
| Electrons | 9 |
| Symbol | F |
| Atomic mass | 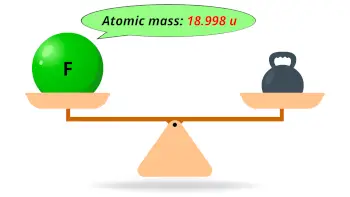 18.998 u |
| Electrons arrangement or Bohr model | 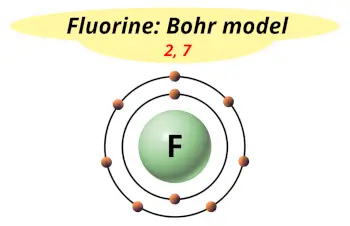 2, 7 |
| Electronic configuration | [He] 2s2 2p5 |
| Atomic radius | 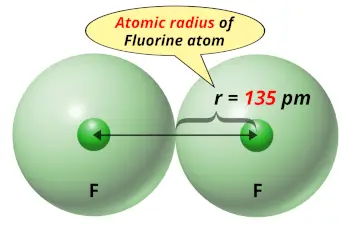 135 picometers (van der Waals radius) |
| Valence electrons | 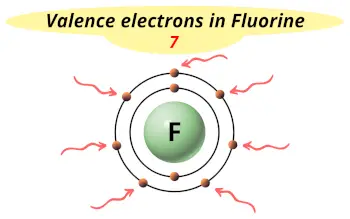 7 |
| 1st Ionization energy | 17.423 eV |
| Electronegativity | 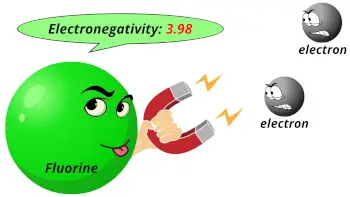 3.98 (Pauling scale) |
| Crystal structure | 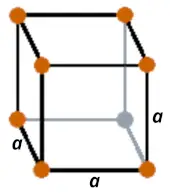 SC (Simple cubic) |
| Melting point of Fluorine (F2) | 53.48 K or -219.67 °C or -363.41 °F |
| Boiling point of Fluorine (F2) | 85.03 K or -188.11 °C or -306.6 °F |
| Density | 1.696 g/L |
| Main isotope | 19F |
| Who discovered Fluorine and when? |  Andre-Marie Ampere in 1810 |
| CAS number | 7782-41-4 |
Fluorine in Periodic table
Fluorine element is in group 17 and period 2 of the Periodic table. Fluorine is the p-block element and it belongs to halogens group.
| H | He | ||||||||||||||||
| Li | Be | B | C | N | O | F | Ne | ||||||||||
| Na | Mg | Al | Si | P | S | Cl | Ar | ||||||||||
| K | Ca | Sc | Ti | V | Cr | Mn | Fe | Co | Ni | Cu | Zn | Ga | Ge | As | Se | Br | Kr |
| Rb | Sr | Y | Zr | Nb | Mo | Tc | Ru | Rh | Pd | Ag | Cd | In | Sn | Sb | Te | I | Xe |
| Cs | Ba | La* | Hf | Ta | W | Re | Os | Ir | Pt | Au | Hg | Tl | Pb | Bi | Po | At | Rn |
| Fr | Ra | Ac** | Rf | Db | Sg | Bh | Hs | Mt | Ds | Rg | Cn | Nh | Fl | Mc | Lv | Ts | Og |
| *Ce | Pr | Nd | Pm | Sm | Eu | Gd | Tb | Dy | Ho | Er | Tm | Yb | Lu | ||||
| **Th | Pa | U | Np | Pu | Am | Cm | Bk | Cf | Es | Fm | Md | No | Lr |
←Move to: Oxygen (O) element – Periodic Table
→Move to: Neon (Ne) element – Periodic Table
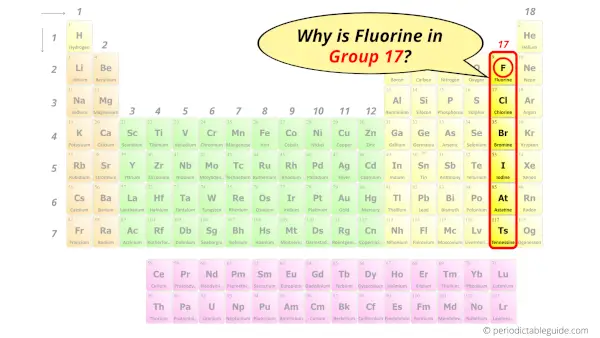
Why is Fluorine in Group 17?
Do you know, how many electrons can be accommodated in the first shell, second shell, third shell, fourth shell, etc…?
Here is the table showing the capacity of orbits to hold electrons.
Number of electrons in shells.
| Orbit / Shell (n) | Maximum no. of electrons this orbit can hold |
| K shell, n = 1 | 2 × 1² = 2 |
| L shell, n = 2 | 2 × 2² = 8 |
| M shell, n = 3 | 2 × 3² = 18 |
| N shell, n = 4 | 2 × 4² = 32 |
Thus,
- 1st shell can hold 2 electrons.
- 2nd shell can hold 8 electrons.
- 3rd shell can hold 18 electrons.
- 4th shell can hold 32 electrons.
Now the atomic number of fluorine (F) is 9.
Hence the fluorine element has electrons arrangement 2, 7.
This electron arrangement indicates that the outermost orbit of fluorine element (F) has 7 electrons.
Hence, it lies in group 17.
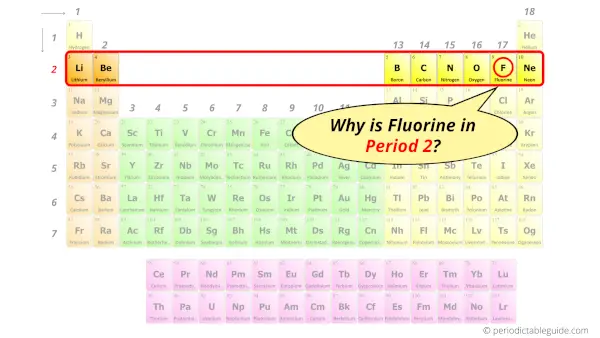
Why is Fluorine in Period 2?
Let me ask you a question.
How many shells does fluorine have?
It’s 2. Right?
You have already seen the bohr model of fluorine element in the above table.
From the Bohr model, it can be found that the number of orbits or shells in fluorine is 2. Hence, as fluorine has 2 orbits, it lies in period 2 of the Periodic table.
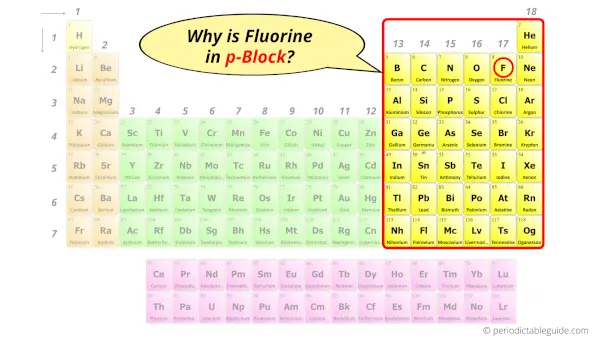
Why is Fluorine in p-block?
I will explain the reason behind this, but first of all I want to ask you a simple question.
How can you determine the blocks-wise position of elements?
The simple answer: The elements will lie in the s, p, d or f block will completely depend upon the subshell in which the last electron will enter.
For example; the electron configuration of fluorine is [He] 2s2 2p5.
So the last electron of fluorine enters the p-subshell or p-orbital.
Hence, fluorine is the p-block element.
8 Interesting facts about fluorine
Interesting facts about fluorine elements are mentioned below.
- Fluorine is the most electronegative element on the periodic table. That means fluorine atoms can attract electrons very rapidly as compared to other elements.
- The average amount of fluorine present in the human body is around 3 mg.
- Out of all the halogens present on the periodic table, fluorine is the lightest one having atomic mass 18.998 u.
- Fluorine is the 13th most abundant element found in the earth’s crust. It is not found naturally, but it always exists as a compound form with other elements as it is highly reactive.
- Although fluorine is the 13th abundant element in the earth’s crust, it is very rarely found in the universe.
- Amount of fluorine present in the universe is around 400 parts per billion.
- Fluorine element has only one stable isotope (i.e 19F), and it is highly sensitive to magnetic fields.
- Fluorine is obtained from its minerals fluorite (or fluorspar), which glows in the dark when they are exposed to the light.
Properties of fluorine
Physical and chemical properties of fluorine element are given below.
Physical properties of fluorine
The physical properties of fluorine element are listed below.
- At STP, fluorine element exist as a light pale-yellow color gas.
- In gaseous state, fluorine is a light pale-yellow color gas, while in a liquid state it is bright yellow colored.
- Atomic mass of fluorine is 18.998 u, which makes it the lightest halogen on the periodic table.
- Fluorine gas has a pungent smell.
- Liquid fluorine is soluble in liquid oxygen and ozone.
Chemical properties of fluorine
The chemical properties of fluorine element are listed below.
- Fluorine is a highly toxic and corrosive gas. And hence it was also called chemist killer.
- Fluorine is a highly reactive element and hence it is always found with other elements in a compound form.
- Fluorine is such a highly reactive element that it can also attack diamond.
- Fluorine does not react with oxygen gas and other inert gases like helium, neon and krypton.
- Fluorine is highly flammable and it also explosively reacts with water.
Uses of fluorine
Uses of fluorine element are listed below.
- Sodium fluoride (NaF) is added to the toothpaste which helps in preventing dental cavities and tooth decay.
- In manufacturing industries, Fluorine is used in the manufacturing of teflon.
- Fluorine element is also present in the refrigerants (chlorofluorocarbon (CFC)) which are used in refrigerators, air conditioners, etc.
- In the medical field, some drugs also contain fluorine in some proportion.
- Compounds made of fluorine are used to process nuclear fuels.
Explore our New Interactive Periodic Table (with Rotating Bohr Models and More)

Details about this Periodic table:
- Access detailed info on all elements: atomic mass, electron configurations, charges, and more.
- View rotating Bohr models for all 118 elements.
- Get a free HD image of the Periodic Table.
Note: For future use, bookmark this Periodic table or visit “PeriodicTableGuide.com”
External resources:
- Is Fluorine an Essential Element? | Fluorides |The National Academies Press. (n.d.). Is Fluorine an Essential Element? | Fluorides |the National Academies Press. https://doi.org/10.17226/20482
- Chemistry of Fluorine (Z=9). (2013, October 2). Chemistry LibreTexts. https://chem.libretexts.org/Bookshelves/Inorganic_Chemistry/Supplemental_Modules_and_Websites_(Inorganic_Chemistry)/Descriptive_Chemistry/Elements_Organized_by_Block/2_p-Block_Elements/Group_17%3A_The_Halogens/Z009_Chemistry_of_Fluorine_(Z9)
- Periodic Table of Elements: Los Alamos National Laboratory. (n.d.). Periodic Table of Elements: Los Alamos National Laboratory. https://periodic.lanl.gov/9.shtml
- Dehnen, S., Schafer, L. L., Lectka, T., & Togni, A. (2021, November 22). Fluorine: A Very Special Element and Its Very Special Impacts on Chemistry. Organic Letters, 23(23), 9013–9019. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.orglett.1c03799
- P. (n.d.). Fluorine | F (Element) – PubChem. Fluorine | F (Element) – PubChem. https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/element/Fluorine
