This is a SUPER easy guide on Aluminum element.
In fact, the table mentioned below is the perfect information box (Which gives you every single detail about the Aluminum element in Periodic table.)
So if you want to know anything about Aluminum element, then this guide is for you.
Let’s finish this very quickly.
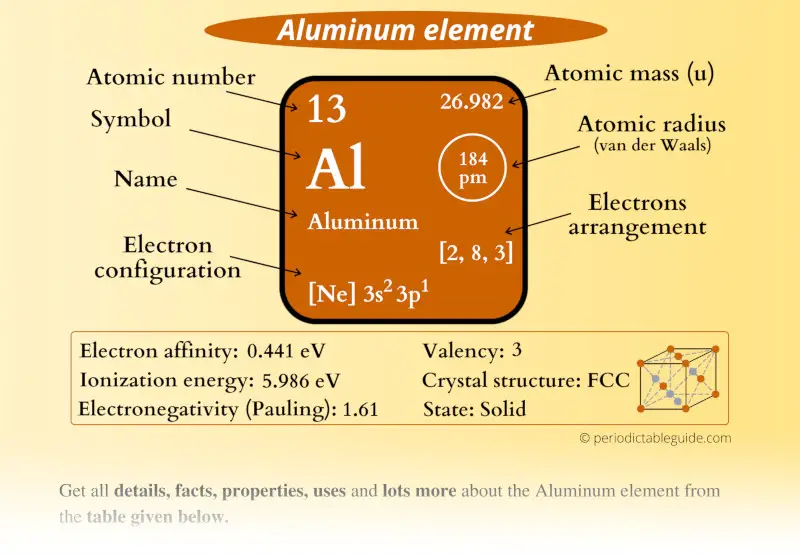
Aluminum Element (Al) Information
| Appearance |  Silvery grey |
| State (at STP) | Solid |
| Position in Periodic table | 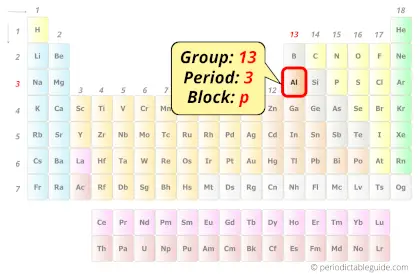 Group: 13, Period: 3, Block: p |
| Category | 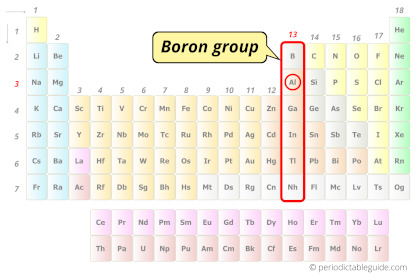 Boron group |
| Atomic number or Protons | 13 |
| Neutrons | 14 |
| Electrons | 13 |
| Symbol | Al |
| Atomic mass | 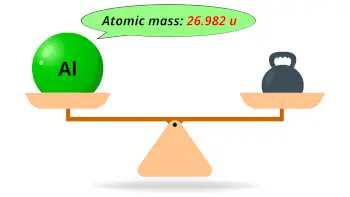 26.982 u |
| Electrons arrangement or Bohr model | 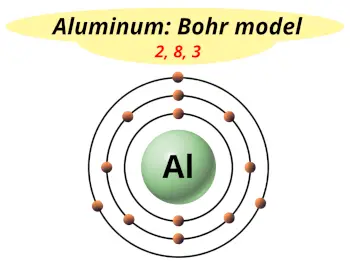 2, 8, 3 |
| Electronic configuration | [Ne] 3s2 3p1 |
| Atomic radius | 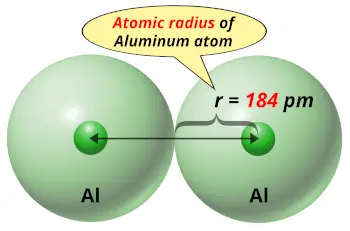 184 picometers (van der Waals radius) |
| Valence electrons | 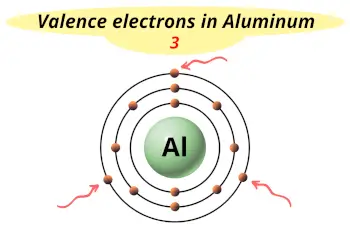 3 |
| 1st Ionization energy | 5.986 eV |
| Electronegativity | 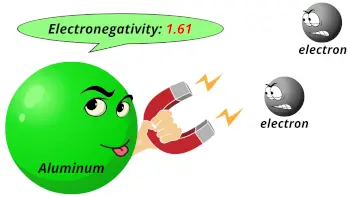 1.61 (Pauling scale) |
| Crystal structure | 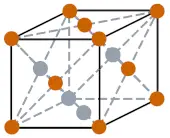 FCC (Face centered cubic) |
| Melting point | 933.47 K or 660.3 °C or 1220.5 °F |
| Boiling point | 2743 K or 2470 °C or 4478 °F |
| Density | 2.7 g/cm3 |
| Main isotope | 27Al |
| Who discovered Aluminum and when? |  Hans Christian in 1824 |
| CAS number | 7429-90-5 |
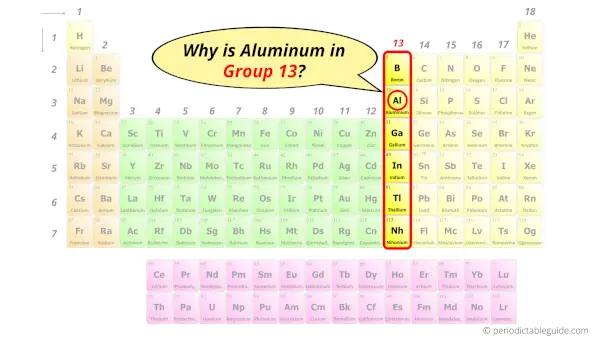
Aluminum in Periodic table
Aluminum element is in group 13 and period 3 of the Periodic table. Aluminum is the p-block element and it belongs to boron group.
| H | He | ||||||||||||||||
| Li | Be | B | C | N | O | F | Ne | ||||||||||
| Na | Mg | Al | Si | P | S | Cl | Ar | ||||||||||
| K | Ca | Sc | Ti | V | Cr | Mn | Fe | Co | Ni | Cu | Zn | Ga | Ge | As | Se | Br | Kr |
| Rb | Sr | Y | Zr | Nb | Mo | Tc | Ru | Rh | Pd | Ag | Cd | In | Sn | Sb | Te | I | Xe |
| Cs | Ba | La* | Hf | Ta | W | Re | Os | Ir | Pt | Au | Hg | Tl | Pb | Bi | Po | At | Rn |
| Fr | Ra | Ac** | Rf | Db | Sg | Bh | Hs | Mt | Ds | Rg | Cn | Nh | Fl | Mc | Lv | Ts | Og |
| *Ce | Pr | Nd | Pm | Sm | Eu | Gd | Tb | Dy | Ho | Er | Tm | Yb | Lu | ||||
| **Th | Pa | U | Np | Pu | Am | Cm | Bk | Cf | Es | Fm | Md | No | Lr |
←Move to: Magnesium (Mg) element – Periodic Table
→Move to: Silicon (Si) element – Periodic Table
Why is Aluminum in Group 13?
Do you know, how many electrons can be accommodated in the first shell, second shell, third shell, fourth shell, etc…?
Here is the table showing the capacity of orbits to hold electrons.
Number of electrons in shells.
| Orbit / Shell (n) | Maximum no. of electrons this orbit can hold |
| K shell, n = 1 | 2 × 1² = 2 |
| L shell, n = 2 | 2 × 2² = 8 |
| M shell, n = 3 | 2 × 3² = 18 |
| N shell, n = 4 | 2 × 4² = 32 |
Thus,
- 1st shell can hold 2 electrons.
- 2nd shell can hold 8 electrons.
- 3rd shell can hold 18 electrons.
- 4th shell can hold 32 electrons.
Now the atomic number of aluminum (Al) is 13.
Hence the aluminum element has electrons arrangement 2, 8, 3.
This electron arrangement indicates that the outermost orbit of Aluminum element (Al) has 3 electrons.
Hence, it lies in group 13.
Why is Aluminum in Period 3?
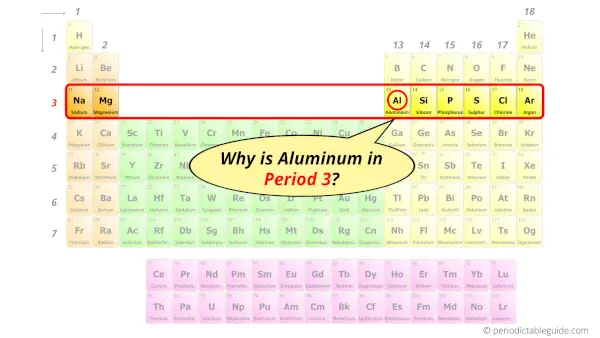
Let me ask you a question.
How many shells does aluminum have?
It’s 3. Right?
You have already seen the bohr model of aluminum element in the above table.
From the Bohr model, it can be found that the number of orbits or shells in aluminum is 3. Hence, as aluminum has 3 orbits, it lies in period 3 of the Periodic table.
Why is Aluminum in p-block?
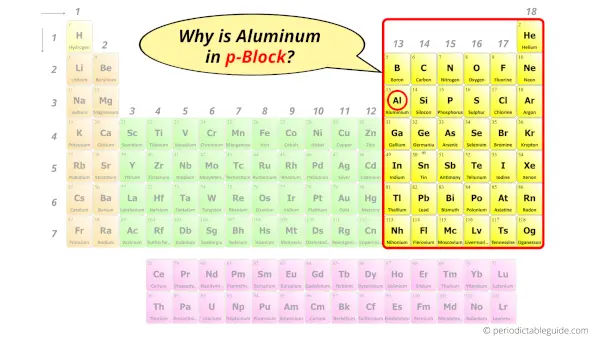
Before knowing this reason, first of all I want to ask you a simple question.
How can you determine the blocks-wise position of elements?
The simple answer: The elements will lie in the s, p, d or f block will completely depend upon the subshell in which the last electron will enter.
For example; the electron configuration of aluminum is [Ne] 3s2 3p1.
So the last electron of aluminum enters the p-subshell or p-orbital.
Hence, aluminum is the p-block element.
7 Interesting facts about Aluminum
Interesting facts about aluminum element are mentioned below.
- Earth’s crust contains large amounts of aluminium which makes aluminum the 3rd most abundant element found in the earth’s crust. (The first and second abundant elements are oxygen and silicon respectively).
- If we consider only metals, then aluminum is the most abundant metal found from the earth’s crust.
- Aluminum metal can reflect heat as well as light.
- Aluminum is recyclable, that means the aluminum products can be smelted and they can be reused.
- Around 75% of the total available aluminum is still in use today because it is easily recyclable.
- Aluminum is toxic for gilled animals (i.e fish), but is non-toxic for humans.
- Aluminum’s weight is around ⅓rd that of steel.
Properties of Aluminum
The physical and chemical properties of aluminum element are mentioned below.
Physical properties of Aluminum
Physical properties of aluminum are mentioned below.
- Aluminum is a silvery grey colored lightweight metal.
- Fresh film of aluminum is a silvery white in color, but the color may appear dull gray due to surface roughness.
- Aluminium is a ductile metal and hence it can be formed into different shapes.
- Aluminum is a lightweight metal having density of only 2.7 g/cm3 which is far less than the density of iron (i.e. 7.875 g/cm3).
- The 27Al isotope of aluminum is only the stable isotope.
- Pure aluminum possesses less strength, hence it is alloyed with other metals to increase its strength.
Chemical properties of Aluminum
Chemical properties of aluminum are mentioned below.
- In air, the aluminum reacts with oxygen and forms a thin oxide layer which protects it from corrosion.
- Aluminum metal gets corroded by salts like sodium chloride (NaCl). Because of this, the household pipes are not made up of aluminum.
- Aluminum reacts with nonmetals at higher temperature and forms aluminum nitrides, aluminum sulphides as well as aluminum halides.
Uses of Aluminum
Uses of aluminum are mentioned below.
- Aluminum is used to manufacture many different types of packaging.
- Aluminum is also used in medicines which helps in reducing stomach acidity.
- Aluminum foils are used for packaging of medicines as aluminum has a property to block bacteria, microorganisms, light, oxygen as well as other gases.
- Aluminum foil reflects heat, and hence it is used to pack warm food items.
- Aluminum being a lightweight metal, it is used in aerospace industries.
- Aluminum has good thermal conductivity, hence it is also used in some heat transfer applications.
- Aluminum metal also finds its applications in various other fields like construction, electrical engineering and electronics, machinery and equipment, consumer goods, etc.
Explore our New Interactive Periodic Table (with Rotating Bohr Models and More)

Details about this Periodic table:
- Access detailed info on all elements: atomic mass, electron configurations, charges, and more.
- View rotating Bohr models for all 118 elements.
- Get a free HD image of the Periodic Table.
Note: For future use, bookmark this Periodic table or visit “PeriodicTableGuide.com”
External resources:
- Periodic Table of Elements: Los Alamos National Laboratory. (n.d.). Periodic Table of Elements: Los Alamos National Laboratory. https://periodic.lanl.gov/13.shtml
- C&EN: IT’S ELEMENTAL: THE PERIODIC TABLE – ALUMINUM. (n.d.). C&EN: IT’S ELEMENTAL: THE PERIODIC TABLE – ALUMINUM. https://pubsapp.acs.org/cen/80th/print/aluminum.html
- Aluminium – Element information, properties and uses | Periodic Table. (n.d.). Aluminium – Element Information, Properties and Uses | Periodic Table. https://www.rsc.org/periodic-table/element/13/aluminium
- P. (n.d.). Aluminum | Al (Element) – PubChem. Aluminum | Al (Element) – PubChem. https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/element/Aluminum
- Aluminium – Wikipedia. (2017, March 31). Aluminium – Wikipedia. https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Aluminium
