This is a SUPER easy guide on Neon element.
In fact, the table mentioned below is the perfect information box (Which gives you every single detail about the Neon element in Periodic table.)
So if you want to know anything about Neon element, then this guide is for you.
Let’s finish this very quickly.
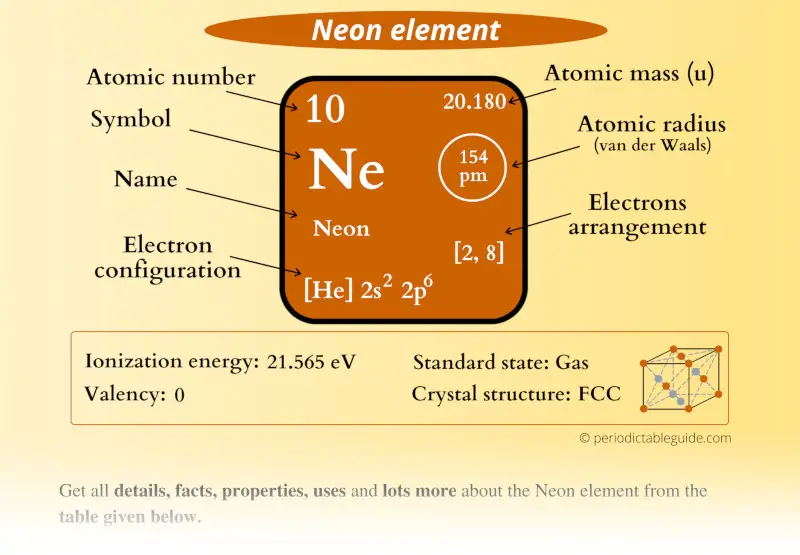
Neon Element (Ne) Information
| Appearance | Colorless gas |
| State (at STP) | Gas |
| Position in Periodic table | 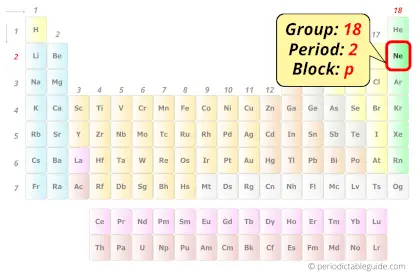 Group: 18, Period: 2, Block: p |
| Category |  Noble gases |
| Atomic number or Protons | 10 |
| Neutrons | 10 |
| Electrons | 10 |
| Symbol | Ne |
| Atomic mass | 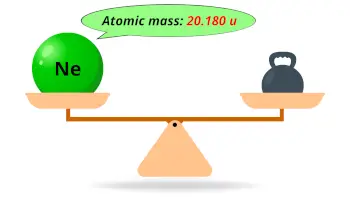 20.180 u |
| Electrons arrangement or Bohr model | 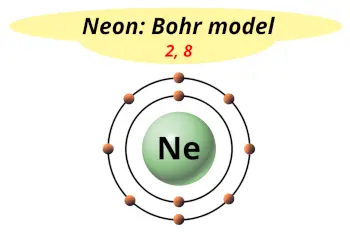 2, 8 |
| Electronic configuration | [He] 2s2 2p6 |
| Atomic radius | 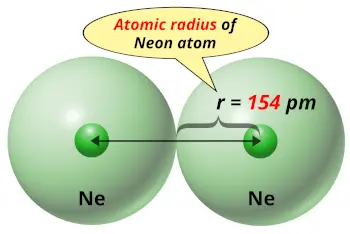 154 picometers (van der Waals radius) |
| Valence electrons | 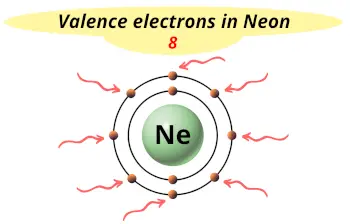 8 |
| 1st Ionization energy | 21.565 eV |
| Crystal structure | 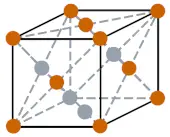 FCC (Face-centered cubic) |
| Melting point | 24.56 K or -248.59 °C or -415.46 °F |
| Boiling point | 27.104 K or -246.04 °C or -410.88 °F |
| Density | 0.9 g/L |
| Main isotope | 20Ne |
| Who discovered Neon and when? |  William Ramsey and Morris Travers (in 1898) |
| CAS number | 7440-01-9 |
Neon in Periodic table
Neon element is in group 18 and period 2 of the Periodic table. Neon is the p-block element and it belongs to Noble gases group.
| H | He | ||||||||||||||||
| Li | Be | B | C | N | O | F | Ne | ||||||||||
| Na | Mg | Al | Si | P | S | Cl | Ar | ||||||||||
| K | Ca | Sc | Ti | V | Cr | Mn | Fe | Co | Ni | Cu | Zn | Ga | Ge | As | Se | Br | Kr |
| Rb | Sr | Y | Zr | Nb | Mo | Tc | Ru | Rh | Pd | Ag | Cd | In | Sn | Sb | Te | I | Xe |
| Cs | Ba | La* | Hf | Ta | W | Re | Os | Ir | Pt | Au | Hg | Tl | Pb | Bi | Po | At | Rn |
| Fr | Ra | Ac** | Rf | Db | Sg | Bh | Hs | Mt | Ds | Rg | Cn | Nh | Fl | Mc | Lv | Ts | Og |
| *Ce | Pr | Nd | Pm | Sm | Eu | Gd | Tb | Dy | Ho | Er | Tm | Yb | Lu | ||||
| **Th | Pa | U | Np | Pu | Am | Cm | Bk | Cf | Es | Fm | Md | No | Lr |
←Move to: Fluorine (F) element – Periodic Table
→Move to: Sodium (Na) element – Periodic Table
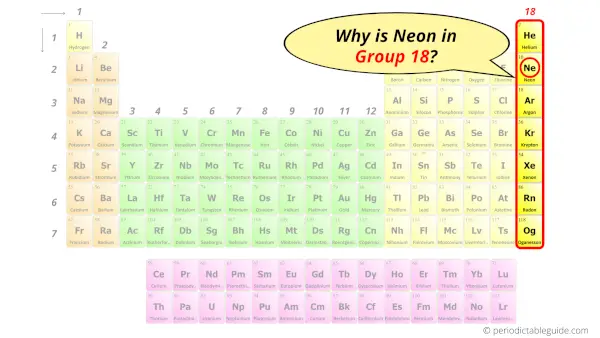
Why is Neon in Group 18?
Do you know, how many electrons can be accommodated in the 1st shell, 2nd shell, 3rd shell, 4th shell, etc…?
Here is the table showing the capacity of orbits to hold electrons.
Number of electrons in shells.
| Orbit / Shell (n) | Maximum no. of electrons this orbit can hold |
| K shell, n = 1 | 2 × 1² = 2 |
| L shell, n = 2 | 2 × 2² = 8 |
| M shell, n = 3 | 2 × 3² = 18 |
| N shell, n = 4 | 2 × 4² = 32 |
Thus,
- 1st shell can hold 2 electrons.
- 2nd shell can hold 8 electrons.
- 3rd shell can hold 18 electrons.
- 4th shell can hold 32 electrons.
Now the atomic number of neon (Ne) is 10.
Hence the neon element has electrons arrangement 2, 8.
This electron arrangement indicates that the outermost orbit of Neon element (Ne) has 8 electrons.
Hence, it lies in group 18.
Why is Neon in Period 2?
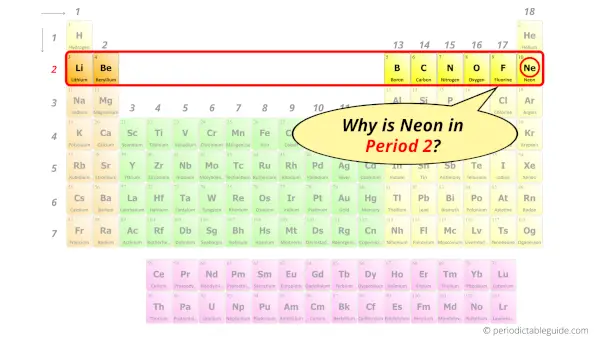
Do you know how many shells a neon atom has?
It’s 2. Right?
You have already seen the bohr model of neon atom in the above information table.
From the Bohr model, it can be found that the number of orbits or shells in neon is 2. Hence, as neon has 2 orbits, it lies in period 2 of the Periodic table.
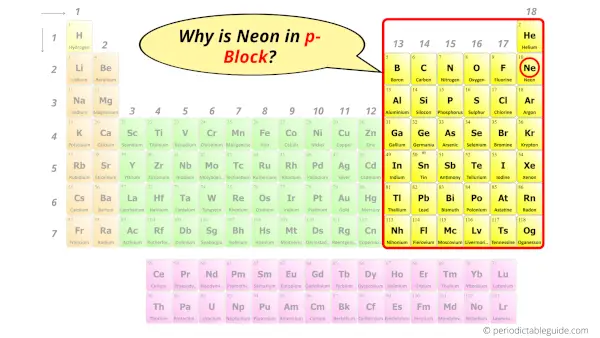
Why is Neon in p-block?
Before knowing this reason, first of all I want to ask you a simple question.
How can you determine the blocks-wise position of elements?
The simple answer: The elements will lie in the s, p, d or f block will completely depend upon the subshell in which the last electron will enter.
For example; the electron configuration of neon is [He] 2s2 2p6.
So the last electron of neon enters the p-subshell or p-orbital.
Hence, neon is the p-block element.
9 Interesting facts about Neon
Interesting facts about neon element are mentioned below.
- Neon element is the 4th most abundant element found in the entire universe. [1]
- The name “neon” came from the Greek word “novum”, which means new.
- Neon gas is lighter than air and its density is ⅔rd the density of the air.
- Neon is the second lightest noble gas in the noble gas family. (Helium is the lightest of all the noble gases.)
- Neon gas is lighter than air so it always goes up in the earth’s atmosphere.
- Neon is very rarely available on the earth and it is approximately 55 times more expensive than helium gas.
- Neon is an inert gas and it does not have any mineral ores. Neon is majorly obtained by liquefying the air. [2]
- A balloon filled with neon will rise in the air but it will rise at a much slower rate as compared to the balloon filled with helium gas.
- Neon gas is present in stars.
Properties of Neon
The physical and chemical properties of neon element are mentioned below.
Physical properties of Neon
Physical properties of neon are mentioned below.
- Neon gas is a colorless and odourless gas.
- Neon exists in a gaseous state at room temperature. Neon becomes liquid between the narrow temperature range of -245.9 °C and -248.6 °C.
- Density of neon is 0.9 g/L which is less than the density of air (i.e 1.29 g/L).
Chemical properties of Neon
Chemical properties of neon are mentioned below.
- Neon is chemically inert. So it does not form stable compounds with any other elements.
- Unlike helium gas, neon is slightly soluble in water.
- The crystal structure of neon is FCC (Face-centered cubic)
Uses of Neon
Uses of neon are mentioned below.
- Neon gas is used in neon sign boards which produce reddish-orange light.
- Liquified neon gas is also used as a cryogenic refrigerant. Refrigerating capacity of liquid neon is around 40 times more than that of the liquid helium gas.
- Helium-neon lasers are made by combining neon gas with helium gas.
- The light emitted from ionized neon can pass through the water fog. Hence the neon lights are used in cold regions as well as on airports.
- Neon lights are used in botanical gardens as well as greenhouses which helps in increasing the chlorophyll content in the plants.
Explore our New Interactive Periodic Table (with Rotating Bohr Models and More)

Details about this Periodic table:
- Access detailed info on all elements: atomic mass, electron configurations, charges, and more.
- View rotating Bohr models for all 118 elements.
- Get a free HD image of the Periodic Table.
Note: For future use, bookmark this Periodic table or visit “PeriodicTableGuide.com”
External resources:
- Neon – Element information, properties and uses | Periodic Table. (n.d.). Neon – Element Information, Properties and Uses | Periodic Table. https://www.rsc.org/periodic-table/element/10/neon
- Neon – Wikipedia. (2007, February 27). Neon – Wikipedia. https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Neon
- It’s Elemental – The Element Neon. (n.d.). It’s Elemental – the Element Neon. https://education.jlab.org/itselemental/ele010.html
- P. (n.d.). Neon | Ne (Element) – PubChem. Neon | Ne (Element) – PubChem. https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/element/Neon
