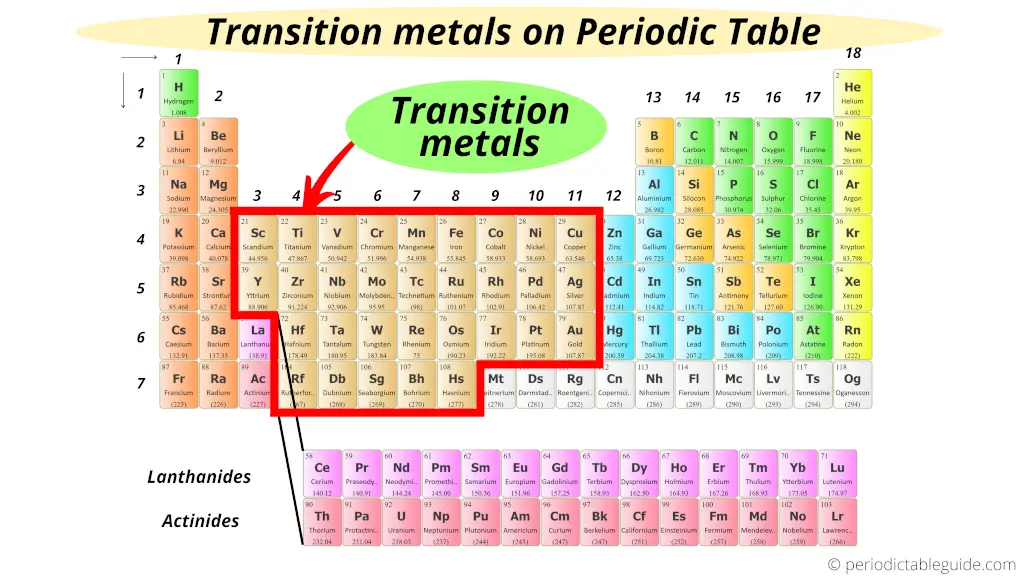
The transition metals are located in the middle of the Periodic table from group 3 to group 11.
From the above image, you can easily see where are Transition Metals located on the Periodic Table.
According to some chemists, the d-block elements are known as transition elements.
But wait… this is not completely true.
I’ll tell you the reason why all d-block elements are not transition metals.
Also, there is a lot more confusion for many students and teachers like,
Whether group 12 elements (Zn, Cd, Hg) are transition elements or not?
Whether Lanthanum and Actinium are included in transition elements or not?
Here I am going to explain you all these important things related to transition metals.
Here, I have covered;
- Why transition elements are called so?
- How many transition metals are there in the periodic table?
- Transition elements list
- Electronic configuration of transition metals
- Transition Metals facts
- Transition Metals uses
Let’s finish this quickly.
Why transition elements are called so?
The reason why transition metals are called so is very simple.
Here is a reason:
Transition elements are called so because their properties show the transition from electropositive s-block elements to the electronegative p-block elements.
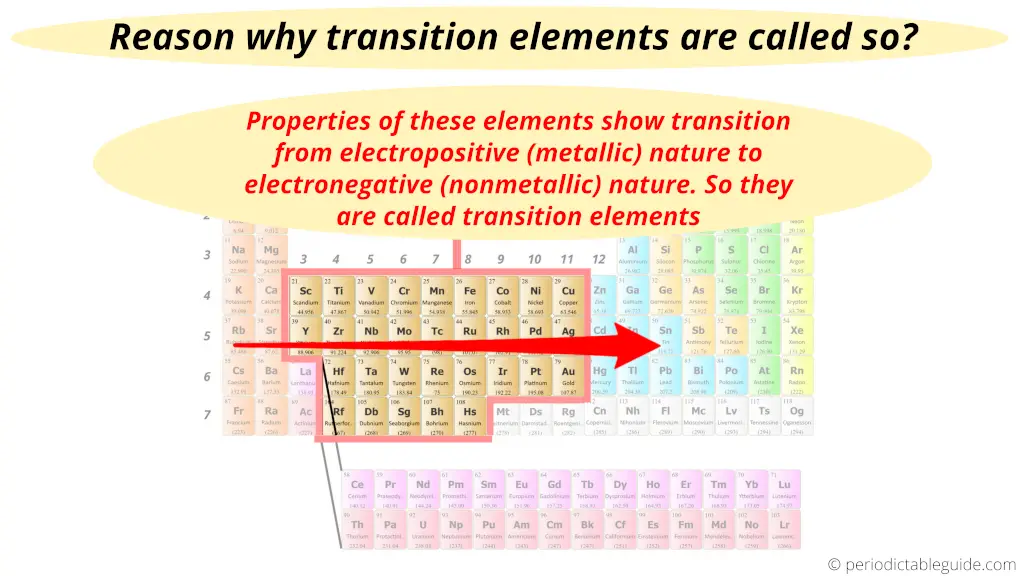
These elements form a bridge between the best metals and the best nonmetals. (Metals are on the left side of periodic table and nonmetals are on the right side of periodic table. And transition metals form a bridge between them).
In other words, the transition of metallic nature to nonmetallic nature appears in these elements.
As the properties of these elements show transition from electropositive nature to electronegative nature, they are called transition metals.
Definition by IUPAC
Transition elements (or transition metals) are those elements which have partially filled d-orbitals, either in their elemental form or most common oxidation states.
Relax!!! I know that you haven’t understood anything from this definition.
If you know about the elemental form (M) and oxidation state (M+, M2+, M3+, etc) then simply remember this sentence for transition metals.
Transition metals are those elements which possess incomplete d-orbitals, either they are like this (M) or like this (M+, M2+, M3+, etc).
Let’s proceed further.
How many transition metals are there in the periodic table?
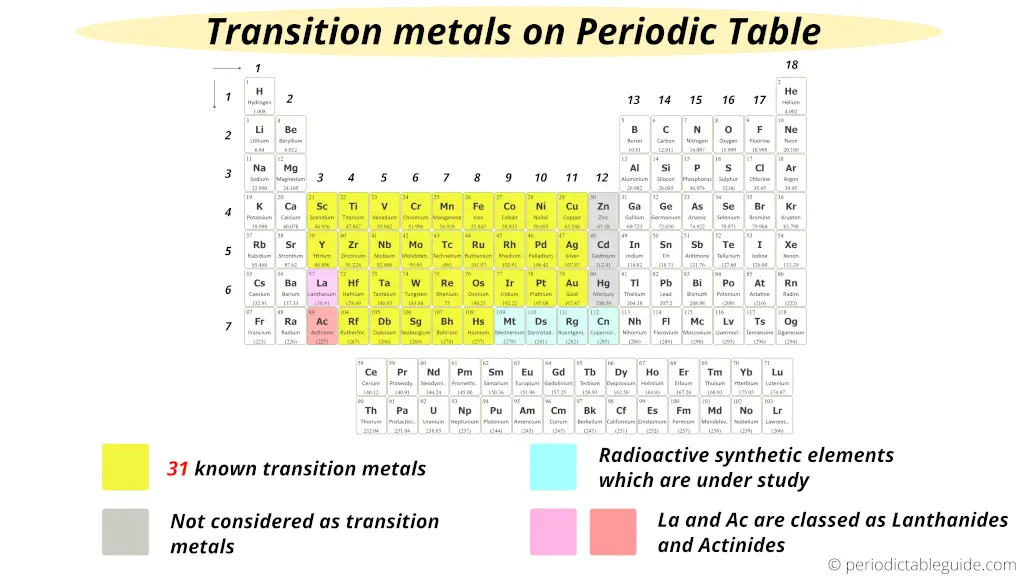
There are 31 commonly known transition metals on the periodic table as shown in the above image by yellow color. (According to the definition given by IUPAC)
But wait… This number is not true.
There are various definitions of transition elements according to different authors.
- According to the definition given by IUPAC, the group 12 elements (Zn, Cd and Hg) are not considered as transition metals because they do not have incomplete d-orbitals either in their elemental state (Zn, Cd, Hg) or oxidation state (Zn2+, Cd2+, Hg2+). Read: The exact reason why group 12 elements are not included as transition elements? (Explained with examples)
- Some authors have defined transition elements on the basis of electron configuration, while some gave definition based on chemical properties, while the definition of transition metals is also somewhat different in inorganic chemistry textbooks.
- Also on the basis of electronic configuration, some researchers have included Lanthanum (La) and Actinium (Ac) as a transition metals, but according to Aufbau principle and inorganic chemistry, La and Ac are not considered as transition elements.
So to avoid this confusion, just remember these 3 points.
Summary of your confusion
- Finally as a summary, simply remember that the elements lying from group 3 to 11 are the transition metals on the periodic table.
- If La and Ac are included, then there are total 33 transition metals on the Periodic table.
- And if La and Ac are excluded, then there are total 31 transition metals on Periodic table.
Transition elements list
The list of transition metals (transition elements) with name and symbol is mentioned below.
| Group 3 | Group 4 | Group 5 | Group 6 | Group 7 | Group 8 | Group 9 | Group 10 | Group 11 | |
| Period 4 | Scandium (Sc) | Titanium (Ti) | Vanadium (V) | Chromium (Cr) | Manganese (Mn) | Iron (Fe) | Cobalt (Co) | Nickel (Ni) | Copper (Cu) |
| Period 5 | Yttrium(Y) | Zirconium (Zr) | Niobium (Nb) | Molybdenum (Mo) | Technetium (Tc) | Ruthenium (Ru) | Rhodium (Rh) | Palladium (Pd) | Silver (Ag) |
| Period 6 | Lanthanum (La) (if added) | Hafnium (Hf) | Tantalum (Ta) | Tungsten (W) | Rhenium (Re) | Osmium (Os) | Iridium (Ir) | Platinum (Pt) | Gold (Au) |
| Period 7 | Actinium (Ac) (if added) | Rutherfordium (Rf) | Dubnium (Db) | Seaborghium (Sg) | Bohrium (Bh) | Hassium (Hs) | Meitnerium (Mt) | Darmstadtium (Ds) | Roentgenium (Rg) |
Electronic configuration of transition metals
Electron configuration of transition metals are given below:
| Atomic number | Symbol | Name of element | Electronic configuration |
| 21 | Sc | Scandium | [Ar] 3d1 4s2 |
| 22 | Ti | Titanium | [Ar] 3d2 4s2 |
| 23 | V | Vanadium | [Ar] 3d3 4s2 |
| 24 | Cr | Chromium | [Ar] 3d5 4s1 |
| 25 | Mn | Manganese | [Ar] 3d5 4s2 |
| 26 | Fe | Iron | [Ar] 3d6 4s2 |
| 27 | Co | Cobalt | [Ar] 3d7 4s2 |
| 28 | Ni | Nickel | [Ar] 3d8 4s2 |
| 29 | Cu | Copper | [Ar] 3d10 4s1 |
| 39 | Y | Yttrium | [Kr] 4d1 5s2 |
| 40 | Zr | Zirconium | [Kr] 4d2 5s2 |
| 41 | Nb | Niobium | [Kr] 4d4 5s1 |
| 42 | Mo | Molybdenum | [Kr] 4d5 5s1 |
| 43 | Tc | Technetium | [Kr] 4d5 5s2 |
| 44 | Ru | Ruthenium | [Kr] 4d7 5s1 |
| 45 | Rh | Rhodium | [Kr] 4d8 5s1 |
| 46 | Pd | Palladium | [Kr] 4d4 |
| 47 | Ag | Silver | [Kr] 4d10 5s1 |
| 57 | La (if included) | Lanthanum | [Xe] 5d1 6s2 |
| 72 | Hf | Hafnium | [Xe] 4f14 5d2 6s2 |
| 73 | Ta | Tantalum | [Xe] 4f14 5d3 6s2 |
| 74 | W | Tungsten | [Xe] 4f14 5d4 6s2 |
| 75 | Re | Rhenium | [Xe] 4f14 5d5 6s2 |
| 76 | Os | Osmium | [Xe] 4f14 5d6 6s2 |
| 77 | Ir | Iridium | [Xe] 4f14 5d7 6s2 |
| 78 | Pt | Platinum | [Xe] 4f14 5d9 6s1 |
| 79 | Au | Gold | [Xe] 4f14 5d10 6s1 |
| 89 | Ac (if included) | Actinium | [Rn] 6d1 7s2 |
| 104 | Rf | Rutherfordium | [Rn] 5f14 6d2 7s2 |
| 105 | Db | Dubnium | [Rn] 5f14 6d3 7s2 |
| 106 | Sb | Seaborgium | [Rn] 5f14 6d4 7s2 |
| 107 | Bh | Bohrium | [Rn] 5f14 6d5 7s2 |
| 108 | Hs | Hassium | [Rn] 5f14 6d6 7s2 |
Also Read:
1). Where are and how many inner transition metals are on periodic table?
2). Where are Halogens on periodic table?
3). Where are Alkali metals on periodic table?
4). Where are Alkaline earth metals on periodic table?
5). Where are Noble gases on periodic table?
Transition Metals facts
The facts of transition elements are mentioned below.
- Transition elements can have valence electrons in the shell other than the outer shell.
- Transition metals like iron (Fe), zinc (Zn) and copper (Cu) provide necessary nutrients for human health.
- Iron (Fe), Cobalt (Co) and nickel (Ni) are those transition metals which produce magnetic field.
- Some transition elements act as a catalyst in a chemical reaction, which increases the rate of reaction.
- Gold (Au), Silver (Ag), Platinum (Pt) are the transition elements which do not corrode. They are obtained in the pure form in nature.
Transition Metals uses
The uses of transition elements are mentioned below.
- Copper (Cu) is a transition metal which is used in electrical equipment for making conducting wires.
- Nickel (Ni) is used for preparing stainless steel.
- Transition metals like Gold (Au) and Silver (Ag) are used in jewelry as they are highly resistive to air and water at room temperature.
- Tungsten (W) element is mainly used as a filament in the light bulb, as it has a high melting point.
- Nickel (Ni) is generally used as a component in rechargeable batteries.
Explore our New Interactive Periodic Table (with Rotating Bohr Models and More)

Details about this Periodic table:
- Access detailed info on all elements: atomic mass, electron configurations, charges, and more.
- View rotating Bohr models for all 118 elements.
- Get a free HD image of the Periodic Table.
Note: For future use, bookmark this Periodic table or visit “PeriodicTableGuide.com”
Summary
In the very beginning of the article, I gave you a single image which shows you where are transition metals located on the periodic table.
Well, transition metals are located in the middle of the Periodic table from group 3 to group 11.
Then we saw the reason why they are called transition metals?
Later on, I showed you a list of transition elements with names, symbols and electronic configuration.
And lastly we discussed some facts about transition elements as well as uses of transition elements.
I hope you have enjoyed this article.
Feel free to ask me in the comments if you have any doubts.
Also let me know in the comments, has this article helped you or not?
Suggested Important articles for you:
- Periodic table of elements (Detailed guide + HD image)
- Metals on the periodic table
- Nonmetals on the periodic table
- Metalloids on periodic table
- Halogens on periodic table
- Alkali metals on periodic table
- Alkaline earth metals on periodic table
- Noble gases on periodic table
- Inner transition metals on periodic table
- Periodic trends in periodic table
