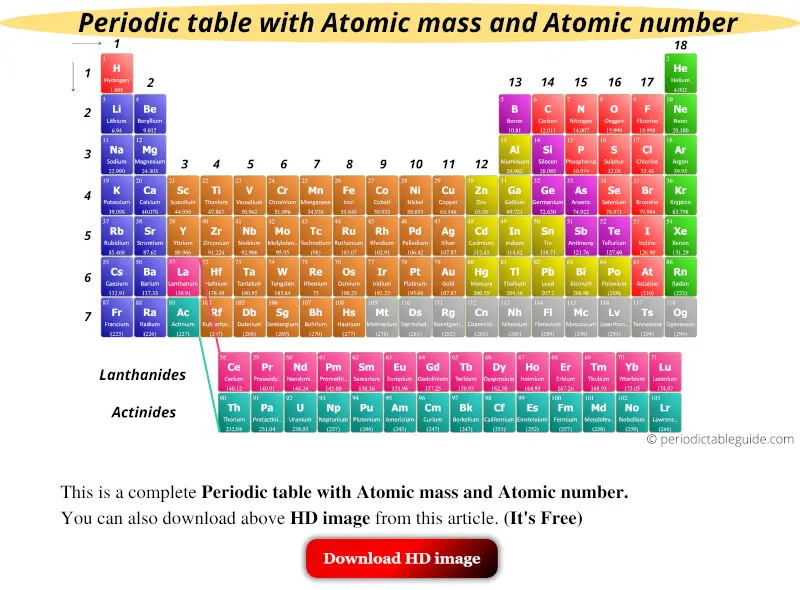
Modern periodic table with Atomic mass and Atomic number is shown in the above image.
But wait…
A few questions for you.
- Do you know, why are some atomic masses written in brackets ( ) in the above Periodic table?
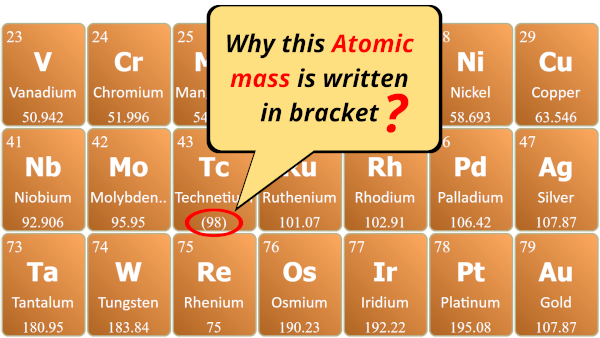
- What do they indicate?
- What type of elements are they?
I’ll clear all your doubts within a few seconds
+
You can also download the HD image of this modern Periodic table with atomic mass from this article. (It’s Free)
But, first things first. Let’s see what exactly is the atomic mass?
What exactly is the Atomic Mass in Periodic table?
In simple words, Atomic mass is the total mass of the single atom.

But the question is…
What are the atoms made up of ?
Atoms are made up of 3 subatomic particles.
- Protons
- Neutrons and
- Electrons
Hence, the Atomic mass is a sum total of masses of protons, neutrons and electrons.
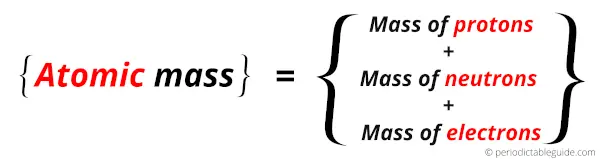
The atomic mass of an atom is measured in atomic mass unit (u).
But, do you know how much is 1 atomic mass unit?
1 atomic mass unit is 1/12th the mass of the single carbon-12 atom.
I’ll explain,
Just imagine that this cake is a whole carbon atom.

Now let’s divide this cake (carbon atom) in 12 equal parts.

Now, the one piece of these 12 pieces is known as 1/12th part. Got it?

So, one atomic mass unit is nothing but the mass of 1/12th part of the carbon-12 atom.

How much is 1 amu in grams?
1 amu is the one twelfth the mass of the carbon-12 atom.
We know that the mass of carbon-12 atom is 1.99 × 10-23 grams.
So dividing this mass with 12, we will get the value of 1 amu in grams.

Hence, 1 amu is equal to 1.66 × 10-24 grams.
Why are some atomic masses written in brackets ( ) on Periodic table?

All the elements whose atomic masses are written in brackets are the synthetic elements.
In other words, synthetic elements are those elements which are artificially prepared in the laboratory.
These synthetic elements have a very short half life.
In other words, these synthetic elements decays very fast and becomes half of their quantity.
These elements are generally prepared in laboratory for experimental and research work.
They are very unstable that it is very difficult to conduct any experiments or even it is difficult to measure their atomic masses.
Thus for the study of these elements, the atomic mass of their most stable isotopes are taken into consideration.
Hence, in the Periodic table, all the atomic masses written in brackets are the atomic masses of their most stable isotopes.
I hope you have clearly understood every single thing in the Modern periodic table with Atomic mass and Atomic number.
If you have any questions, feel free to ask me in the comments below.
Also let me know, has this article helped you or not?
Explore our New Interactive Periodic Table (with Rotating Bohr Models and More)

Details about this Periodic table:
- Access detailed info on all elements: atomic mass, electron configurations, charges, and more.
- View rotating Bohr models for all 118 elements.
- Get a free HD image of the Periodic Table.
Note: For future use, bookmark this Periodic table or visit “PeriodicTableGuide.com”
Suggested Important topics for you:
- Periodic table of elements (Detailed guide + HD image)
- Metals on the periodic table
- Nonmetals on the periodic table
- Metalloids on periodic table
- Halogens on periodic table
- Alkali metals on periodic table
- Alkaline earth metals on periodic table
- Transition metals on Periodic table
- Inner transition metals on periodic table
- Trends in periodic table
